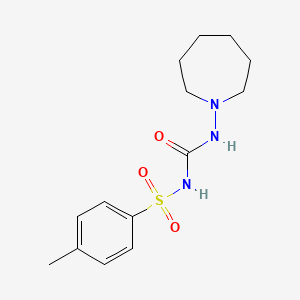

1. Tolinase
1. 1156-19-0
2. Tolinase
3. Norglycin
4. Tolanase
5. Diabewas
6. Tolazolamide
7. Tolazamida
8. Tolazamidum
9. 1-(hexahydro-1-azepinyl)-3-p-tolylsulfonylurea
10. U-17835
11. N-(p-toluenesulfonyl)-n'-hexamethyleniminourea
12. Nsc-70762
13. 1-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
14. 4-(p-tolylsulfonyl)-1,1-hexamethylenesemicarbazide
15. Nci-c03327
16. 1-(azepan-1-yl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
17. U 17835
18. Ccris 591
19. Urea, 1-(hexahydroazepin-1-yl)-3-p-tolylsulfonyl-
20. Einecs 214-588-3
21. Urea, 1-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)-
22. Brn 1323565
23. Benzenesulfonamide, N-[[(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-
24. N-(azepan-1-ylcarbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
25. 9lt1bro48q
26. Benzenesulfonamide, N-(((hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)amino)carbonyl)-4-methyl-
27. Mls000028534
28. 1-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-toluenesulfonyl)urea
29. Chebi:9613
30. N-[(azepan-1-ylamino)carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
31. N-(((hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-amino)carbonyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
32. Nsc70762
33. Ncgc00016009-10
34. Smr000058290
35. Cas-1156-19-0
36. Dsstox_cid_1358
37. Dsstox_rid_76105
38. Dsstox_gsid_21358
39. Tolazamidum [inn-latin]
40. Tolazamida [inn-spanish]
41. 1-(((((4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)amino)carbonyl)amino)azepane
42. Tolinase (tn)
43. Hsdb 3192
44. Sr-01000003105
45. Nsc 70762
46. Unii-9lt1bro48q
47. 1-[(azepan-1-ylamino)carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
48. 1-[({[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]amino}carbonyl)amino]azepane
49. Ronase
50. Ai3-50826
51. N-{[(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-amino]carbonyl}-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
52. Prestwick_865
53. Tolazamide [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
54. Spectrum_001269
55. Tolazamide [mi]
56. Tolazamide [inn]
57. Tolazamide [jan]
58. Opera_id_1740
59. Prestwick0_000554
60. Prestwick1_000554
61. Prestwick2_000554
62. Prestwick3_000554
63. Spectrum2_001449
64. Spectrum3_001473
65. Spectrum4_000240
66. Spectrum5_001204
67. Lopac-t-2408
68. Tolazamide [hsdb]
69. Tolazamide [usan]
70. Tolazamide [vandf]
71. Chembl817
72. Benzenesulfonamide, N-(((hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-amino)carbonyl)-4-methyl-
73. T 2408
74. Tolazamide [mart.]
75. 3-azepan-1-yl-1-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl-urea
76. Nciopen2_008361
77. Tolazamide [usp-rs]
78. Tolazamide [who-dd]
79. Cbiol_001918
80. Lopac0_001195
81. Oprea1_061180
82. Schembl34417
83. Bspbio_000627
84. Bspbio_001505
85. Bspbio_003025
86. Kbiogr_000225
87. Kbiogr_000939
88. Kbioss_000225
89. Kbioss_001749
90. Tolazamide (jan/usp/inn)
91. 1-(azepan-1-yl)-3-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)urea
92. 5-20-04-00062 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
93. Mls001076161
94. Divk1c_000212
95. Spectrum1501201
96. Spbio_001317
97. Spbio_002548
98. Bpbio1_000691
99. Gtpl6847
100. Wln: T7ntj Amvmswr D1
101. Dtxsid3021358
102. Tolazamide [orange Book]
103. Bcbcmap01_000061
104. Hms500k14
105. Kbio1_000212
106. Kbio2_000225
107. Kbio2_001749
108. Kbio2_002793
109. Kbio2_004317
110. Kbio2_005361
111. Kbio2_006885
112. Kbio3_000449
113. Kbio3_000450
114. Kbio3_002525
115. Zinc57512
116. Ninds_000212
117. Bio1_000204
118. Bio1_000693
119. Bio1_001182
120. Bio2_000225
121. Bio2_000705
122. Hms1361l07
123. Hms1569p09
124. Hms1791l07
125. Hms1921p19
126. Hms1989l07
127. Hms2089l10
128. Hms2092l09
129. Hms2096p09
130. Hms2232l21
131. Hms3259o18
132. Hms3263p11
133. Hms3369l04
134. Hms3402l07
135. Hms3713p09
136. Pharmakon1600-01501201
137. Tolazamide [usp Monograph]
138. Bcp23550
139. Hy-b0920
140. Tox21_110281
141. Tox21_201507
142. Tox21_300416
143. Tox21_501195
144. Ccg-39178
145. Nsc758149
146. Akos015913823
147. N-[[(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
148. Tox21_110281_1
149. Db00839
150. Ks-1438
151. Lp01195
152. Nc00590
153. Nsc-758149
154. Sdccgsbi-0051162.p004
155. Benzenesulfonamide, {n-[[(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-}
156. Idi1_000212
157. Idi1_033975
158. Ncgc00016009-01
159. Ncgc00016009-02
160. Ncgc00016009-03
161. Ncgc00016009-04
162. Ncgc00016009-05
163. Ncgc00016009-06
164. Ncgc00016009-07
165. Ncgc00016009-08
166. Ncgc00016009-09
167. Ncgc00016009-11
168. Ncgc00016009-12
169. Ncgc00016009-13
170. Ncgc00016009-14
171. Ncgc00016009-15
172. Ncgc00016009-16
173. Ncgc00016009-17
174. Ncgc00016009-19
175. Ncgc00016009-24
176. Ncgc00023701-03
177. Ncgc00023701-04
178. Ncgc00023701-05
179. Ncgc00023701-06
180. Ncgc00023701-07
181. Ncgc00023701-08
182. Ncgc00023701-09
183. Ncgc00023701-10
184. Ncgc00254501-01
185. Ncgc00259058-01
186. Ncgc00261880-01
187. 1-(azepan-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
188. Sbi-0051162.p003
189. Ab00052247
190. Eu-0101195
191. Ft-0675268
192. Sw196991-3
193. Tolbutamide Impurity C [ep Impurity]
194. C71499
195. D00379
196. Ab00052247-15
197. Ab00052247_16
198. Ab00052247_17
199. A921617
200. 1-(azepan-1-yl)-3-[(4-methylbenzene)sulfonyl]urea
201. 3-(azepan-1-yl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl-urea
202. Q7814101
203. Sr-01000003105-2
204. Sr-01000003105-4
205. Sr-01000003105-5
206. Sr-01000003105-8
207. W-109110
208. Brd-k32164935-001-06-8
209. Brd-k32164935-001-17-5
210. Brd-k32164935-001-28-2
211. F2173-1137
212. 1-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-3-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)urea
213. 1-[(([(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]amino)carbonyl)amino]azepane #
214. Tolazamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
215. Benzenesulfonamide, N-[[(hexahydro-1-azepinyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-
| Molecular Weight | 311.40 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O3S |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 311.13036271 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 311.13036271 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 431 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tolazamide |
| PubMed Health | Tolazamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Tolazamide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolazamide is a white or creamy-white powder very slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.The chemical name is 1-(Hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfo... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolazamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tolazamide |
| PubMed Health | Tolazamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Tolazamide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolazamide is a white or creamy-white powder very slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.The chemical name is 1-(Hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfo... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolazamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
Hypoglycemic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...THIS POTENT AGENT LACKS ANTIDIURETIC ACTION & MAY BE ESPECIALLY USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF PT WHO HAVE TENDENCY TO RETAIN WATER.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 596
SULFONYLUREAS SHOULD BE USED ONLY IN SUBJECTS WITH DIABETES OF MATURITY-ONSET TYPE WHO CANNOT BE TREATED WITH DIET ALONE OR WHO ARE UNWILLING OR UNABLE TO TAKE INSULIN IF WT REDN & DIETARY CONTROL FAIL. /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1522
ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC
The Merck Index. 9th ed. Rahway, New Jersey: Merck & Co., Inc., 1976., p. 1223
Sulfonylureas are indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet and exercise in the treatment and control of certain patients with NIDDM (Type II diabetes; previously known as adult onset diabetes, maturity onset diabetes, ketosis resistant diabetes, or stable diabetes), which occurs in individuals who produce or secrete insufficient quantities of endogenous insulin or who have developed resistance to endogenous insulin. An attempt to control diabetes through changes; in diet and level of physical activity is usually first line management before beginning pharmacologic treatment. Those patients not responding adequately to diet alone or those patients requiring diet plus insulin, especially if they require 40 USP Units or less of insulin a day, may be candidates for therapy with a sulfonylurea as monotherapy or combination therapy. /Included in US product labeling; Sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents/
USP. Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 19th ed. Volume I.Micromedex, Inc. Englewood, CO., 1999. Content Prepared by the U.S. Pharmacopieal Convention, Inc., p. 284
HEMATOLOGICAL (LEUKOPENIA, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, THROMBOCYTOPENIA, PANCYTOPENIA, & HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA), CUTANEOUS (RASHES, PHOTOSENSITIVITY), GI (NAUSEA, VOMITING, RARELY HEMORRHAGE), & HEPATIC (INCR SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE, CHOLESTATIC JAUNDICE) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
...CONTRAINDICATED IN DIABETES COMPLICATED BY ACIDOSIS, KETOSIS, SEVERE INFECTIONS, COMA, SEVERE TRAUMA, OR MAJOR SURGERY.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 905
MOST REACTIONS ARE OBSERVED IN PT OVER 50 YR OF AGE, & THEY ARE MORE LIKELY TO OCCUR IN PT WITH IMPAIRED HEPATIC OR RENAL FUNCTION. OVERDOSAGE OR INADEQUATE OR IRREGULAR FOOD INTAKE MAY INITIATE HYPOGLYCEMIA.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
SULFONYLUREAS SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PT WITH HEPATIC OR RENAL INSUFFICIENCY BECAUSE OF IMPORTANT ROLE OF LIVER IN THEIR METABOLISM & OF KIDNEY IN EXCRETION OF DRUGS & THEIR METABOLITES. /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1522
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TOLAZAMIDE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For use as an adjunct to diet to lower the blood glucose in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (Type II) whose hyperglycemia cannot be satisfactorily controlled by diet alone.
Tolazamide is an oral blood glucose lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolazamide appears to lower the blood glucose acutely by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, an effect dependent upon functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets. The mechanism by which tolazamide lowers blood glucose during long-term administration has not been clearly established. With chronic administration in Type II diabetic patients, the blood glucose lowering effect persists despite a gradual decline in the insulin secretory response to the drug. Extrapancreatic effects may be involved in the mechanism of action of oral sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs. Some patients who are initially responsive to oral hypoglycemic drugs, including tolazamide, may become unresponsive or poorly responsive over time. Alternatively, tolazamide may be effective in some patients who have become unresponsive to one or more other sulfonylurea drugs. In addition to its blood glucose lowering actions, tolazamide produces a mild diuresis by enhancement of renal free water clearance.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB05 - Tolazamide
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Route of Elimination
Tolazamide is metabolized to five major metabolites ranging in hypoglycemic activity from 0% to 70%. They are excreted principally in the urine.
AFTER ORAL ADMIN PEAK PLASMA LEVELS REACH PEAK IN 4-8 HR.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 905
TOLAZAMIDE IS SLOWLY ABSORBED; ONSET OF HYPOGLYCEMIC ACTION OCCURS @ 4-6 HR & PERSISTS @ SIGNIFICANT LEVEL UP TO 15 HR AFTER SINGLE DOSE. TOLAZAMIDE IS METABOLIZED TO NUMBER OF HYPOGLYCEMIC SUBSTANCES THAT ARE LARGELY EXCRETED BY KIDNEY.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
Some metabolites with moderate activity excreted via kidney. /from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 48-37
Excreted (percentage)...85-95 /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for TOLAZAMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Tolazamide is metabolized to five major metabolites ranging in hypoglycemic activity from 0 to 70%.
TOLAZAMIDE IS METABOLIZED TO A NUMBER OF HYPOGLYCEMIC SUBSTANCES...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
Sulfonylureas are rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, transported in the blood in highly protein-bound complexes, and subjected to extensive hepatic metabolism (except for chlorpropamide). Wide variation exists among the sulfonylureas in hepatic metabolism and remnal clearance, factors that tend to alter the steady-state serum levels. Metabolites may be active, so there may be a variation between the plasma half-life of the parent drug and the degree of hypoglycemia encountered. /Sulfonylurea/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Active metabolites may accumulate in renal failure. /from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 48-37
Although the exact metabolic fate of tolazamide has not been clearly established, the drug is metabolized, probably in the liver, to two hydroxymetabolites, p-toluenesulfonamide, p-carboxytolazamide, and an unidentified metabolite; several of these metabolites are pharmacologically active. Tolazamide is excreted in urine principally as metabolites; small amounts are excreted in urine unchanged.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 1999. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1999 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2747
The average biological half-life of the drug is 7 hours.
PLASMA T/2 IS ABOUT 7 HR...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 905
AVG BIOLOGICAL HALF LIFE...IS 7 HR.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 1999. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1999 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2749
Half-life...7 /hours/ /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Sulfonylureas likely bind to ATP-sensitive potassium-channel receptors on the pancreatic cell surface, reducing potassium conductance and causing depolarization of the membrane. Depolarization stimulates calcium ion influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, raising intracellular concentrations of calcium ions, which induces the secretion, or exocytosis, of insulin.
Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 723
Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood glucose and controls the storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Therefore, sulfonylureas are effective only in patients whose pancreata are capable of producing insulin. /Sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents/
USP. Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 19th ed. Volume I.Micromedex, Inc. Englewood, CO., 1999. Content Prepared by the U.S. Pharmacopieal Convention, Inc., p. 284