
1. Apo-tolbutamide
2. Artosin
3. Diabetol
4. Diaval
5. Dolipol
6. Orabet
7. Orinase
8. Rastinon
9. Tolbutamid R.a.n.
1. 64-77-7
2. Orinase
3. Arkozal
4. Willbutamide
5. Butamide
6. Diabetamid
7. Ipoglicone
8. Artosin
9. Tolbutamid
10. Aglicid
11. Diabetol
12. Dolipol
13. Glyconon
14. Rastinon
15. Tolumid
16. Diaben
17. Orabet
18. 1-butyl-3-tosylurea
19. 1-butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
20. Tolylsulfonylbutylurea
21. Diabuton
22. Diasulfon
23. Dirastan
24. Pramidex
25. Tolbusal
26. Artozin
27. Butamid
28. Drabet
29. Mobenol
30. Oralin
31. Orezan
32. Orinaz
33. Oterben
34. Toluina
35. Toluvan
36. Tolbutamidum
37. Sk-tolbutamide
38. N-(butylcarbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
39. N-n-butyl-n'-tosylurea
40. Tolbutamida
41. 1-butyl-3-(p-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea
42. 1-p-toluenesulfonyl-3-butylurea
43. N-butyl-n'-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
44. N-butyl-n'-p-toluenesulfonylurea
45. 3-(p-tolyl-4-sulfonyl)-1-butylurea
46. N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-n'-butylurea
47. N-butyl-n'-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea
48. N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)-n'-butylurea
49. Hls 831
50. Orinase (tn)
51. 1-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
52. N-(sulfonyl-p-methylbenzene)-n'-n-butylurea
53. N-(p-tolylsulfonyl)-n'-butylcarbamide
54. Benzenesulfonamide, N-[(butylamino)carbonyl]-4-methyl-
55. Nci-c01763
56. N-4-methylbenzolsulfonyl-n-butylurea
57. N-[(butylamino)carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
58. D 860
59. Urea, 1-butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)-
60. 1-butyl-3-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea
61. N-butyl-n'-toluene-p-sulfonylurea
62. 3-butyl-1-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)urea
63. N-(p-methylbenzenesulfonyl)-n'-butylurea
64. 3-butyl-1-[(4-methylbenzene)sulfonyl]urea
65. Benzenesulfonamide, N-((butylamino)carbonyl)-4-methyl-
66. Nsc-23813
67. 1-butyl-3-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)urea
68. Chembl782
69. 982xcm1foi
70. Mls000028399
71. Arcosal
72. Beglucin
73. Butamidum
74. Diabesan
75. Tarasina
76. Tolbutone
77. Chebi:27999
78. Tolbet
79. N-((butylamino)carbonyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
80. Nsc-87833
81. Cas-64-77-7
82. Ncgc00015999-10
83. Smr000058363
84. Tolbutamide Form I^l^
85. Dsstox_cid_1359
86. Dsstox_rid_76106
87. Dsstox_gsid_21359
88. Tolbutamidum [inn-latin]
89. Tolbutamida [inn-spanish]
90. Tolumide
91. Ccris 592
92. N-4-(methylbenzolsulfonyl)-n-butylurea
93. Hsdb 3393
94. Sr-01000003059
95. Einecs 200-594-3
96. Mfcd00027169
97. Nsc 23813
98. U 2043
99. Unii-982xcm1foi
100. Brn 1984428
101. N-(sulfonyl-p-methylbenzene)-n'-butylurea
102. Tolbutamide Il
103. Tolbutamide Iii
104. Tolbutamide [usp:inn:ban:jan]
105. Prestwick_471
106. Spectrum_000447
107. Tolbutamide Form I^h^
108. Opera_id_112
109. Tolbutamide [mi]
110. Prestwick0_000190
111. Prestwick1_000190
112. Prestwick2_000190
113. Prestwick3_000190
114. Spectrum2_001210
115. Spectrum3_000599
116. Spectrum4_000358
117. Spectrum5_001272
118. Lopac-t-0891
119. Tolbutamide [inn]
120. Tolbutamide [jan]
121. N-n-butyl-n''-tosylurea
122. Tolbutamide [hsdb]
123. Wln: 4mvmswr D1
124. T 0891
125. Tolbutamide [vandf]
126. Nciopen2_009592
127. Tolbutamide [mart.]
128. Bidd:pxr0179
129. Cbiol_001920
130. Lopac0_001154
131. Schembl15918
132. Bspbio_000119
133. Bspbio_001507
134. Bspbio_002078
135. Kbiogr_000227
136. Kbiogr_000795
137. Kbiogr_002275
138. Kbioss_000227
139. Kbioss_000927
140. Kbioss_002276
141. Tolbutamide [usp-rs]
142. Tolbutamide [who-dd]
143. Tolbutamide [who-ip]
144. 4-11-00-00396 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
145. Mls001148399
146. Mls002152944
147. Divk1c_000341
148. Spectrum1500581
149. Spbio_001000
150. Spbio_002040
151. Bpbio1_000131
152. Gtpl6848
153. Tolbutamide (jp17/usp/inn)
154. Tolbutamide, Analytical Standard
155. Dtxsid8021359
156. Hms501b03
157. Kbio1_000341
158. Kbio2_000227
159. Kbio2_000927
160. Kbio2_002275
161. Kbio2_002795
162. Kbio2_003495
163. Kbio2_004843
164. Kbio2_005363
165. Kbio2_006063
166. Kbio2_007411
167. Kbio3_000453
168. Kbio3_000454
169. Kbio3_001578
170. Kbio3_002755
171. Tolbutamide [orange Book]
172. Cmap_000008
173. Ninds_000341
174. Bio1_000206
175. Bio1_000695
176. Bio1_001184
177. Bio2_000227
178. Bio2_000707
179. Hms1361l09
180. Hms1568f21
181. Hms1791l09
182. Hms1989l09
183. Hms2089c17
184. Hms2092m21
185. Hms2095f21
186. Hms2232h16
187. Hms3259a08
188. Hms3263h09
189. Hms3402l09
190. Hms3651n03
191. Hms3712f21
192. Pharmakon1600-01500581
193. Tolbutamide [ep Monograph]
194. Tolbutamide [usp Monograph]
195. Bcp09192
196. Hy-b0401
197. Nsc23813
198. Tolbutamidum [who-ip Latin]
199. Zinc1530703
200. N-butyl-n''-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
201. Tox21_110279
202. Tox21_201612
203. Tox21_302795
204. Tox21_501154
205. Bdbm50027886
206. Ccg-39141
207. Nsc757354
208. Nsc813220
209. S2443
210. 1-butyl-3-(para-tolylsulfonyl)-urea
211. Akos015894999
212. Tox21_110279_1
213. Db01124
214. Lp01154
215. Nc00543
216. Nsc-757354
217. Nsc-813220
218. Sdccgsbi-0051121.p004
219. Tolbutamide 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
220. Idi1_000341
221. Idi1_033977
222. N-(n-butyl)-n'-p-toluene-sulfonylurea
223. Ncgc00015999-01
224. Ncgc00015999-02
225. Ncgc00015999-03
226. Ncgc00015999-04
227. Ncgc00015999-05
228. Ncgc00015999-06
229. Ncgc00015999-07
230. Ncgc00015999-08
231. Ncgc00015999-09
232. Ncgc00015999-11
233. Ncgc00015999-12
234. Ncgc00015999-13
235. Ncgc00015999-14
236. Ncgc00015999-15
237. Ncgc00015999-16
238. Ncgc00015999-17
239. Ncgc00015999-19
240. Ncgc00015999-20
241. Ncgc00015999-29
242. Ncgc00022721-03
243. Ncgc00022721-04
244. Ncgc00022721-05
245. Ncgc00022721-06
246. Ncgc00022721-07
247. Ncgc00022721-08
248. Ncgc00022721-09
249. Ncgc00022721-10
250. Ncgc00256548-01
251. Ncgc00259161-01
252. Ncgc00261839-01
253. Ac-12490
254. As-14136
255. N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-n''-butylurea
256. N-butyl-n''-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea
257. Sbi-0051121.p003
258. Tolbutamide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
259. Db-054728
260. Ab00052110
261. Eu-0101154
262. Ft-0603265
263. Sw196681-3
264. T3690
265. Bim-0051121.0001
266. C07148
267. D00380
268. D87667
269. U-2043
270. Ab00052110-16
271. Ab00052110_17
272. Ab00052110_18
273. Tolbutamide, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
274. A834879
275. Q414275
276. Sr-01000003059-2
277. Sr-01000003059-4
278. Sr-01000003059-7
279. W-104820
280. Brd-k85119730-001-06-5
281. Brd-k85119730-001-17-2
282. N'-butyl-n-(p-tolylsulfonyl)carbamimidate;tolbutamide
283. Z44591715
284. Tolbutamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
285. 1-(([(butylamino)carbonyl]amino)sulfonyl)-4-methylbenzene #
286. Tolbutamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 270.35 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H18N2O3S |
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 270.10381361 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 270.10381361 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 354 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tolbutamide |
| PubMed Health | Tolbutamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
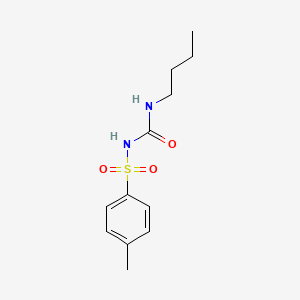
| Drug Label | Tolbutamide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolbutamide is a pure, white, crystalline compound which is practically insoluble in water. The chemical name is benzenesulfonamide, N-[(butylamino)-carbonyl]-4-methyl-. It... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolbutamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tolbutamide |
| PubMed Health | Tolbutamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Tolbutamide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolbutamide is a pure, white, crystalline compound which is practically insoluble in water. The chemical name is benzenesulfonamide, N-[(butylamino)-carbonyl]-4-methyl-. It... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolbutamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
Hypoglycemic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IT IS USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF SELECTED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS, NAMELY MILD UNCOMPLICATED, STABLE DIABETES OF ADULT ONSET & WHICH CANNOT BE CONTROLLED BY DIET ALONE. ... IN DIABETIC PT PEAK EFFECT IS REACHED IN 5 TO 8 HR. DURATION OF ACTION IS USUALLY LESS THAN 24 HR...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 905
THERE IS NO FIXED DOSAGE OF SULFONYLUREA TO BE USED IN DIABETES MELLITUS. TREATMENT IS GUIDED BY INDIVIDUAL PATIENT'S RESPONSE... /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1523
...REPORTS HAVE APPEARED OF SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF REACTIVE HYPOGLYCEMIAS DUE TO A VARIETY OF CAUSES WITH SULFONYLUREAS. /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1523
VET: OCCASIONAL, AS AN ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENT FOR DOGS.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 608
TOXIC EFFECTS OF TOLBUTAMIDE INCL GI UPSET, WEAKNESS, HEADACHE, TINNITUS, PARESTHESIAS, ALLERGIC REACTIONS (PRURITUS, ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME, MACULOPAPULAR RASH, ALL USUALLY TRANSIENT)...CHOLESTATIC JAUNDICE MAY OCCUR (RARELY)... RARE LEUKOPENIA, THROMBOCYTOPENIA, PANCYTOPENIA & AGRANULOCYTOSIS OCCUR.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 905
Despite this relative lack of teratogenicity, tolbutamide should be avoided in pregnancy since the drug will not provide good control in patients who cannot be controlled by diet alone.
Briggs, G.G, R.K. Freeman, S.J. Yaffe. A Reference Guide to Fetal and Neonatal Risk. Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation. 4th ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins 1994., p. 832
SULFONYLUREAS SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PT WITH HEPATIC OR RENAL INSUFFICIENCY BECAUSE OF IMPORTANT ROLE OF LIVER IN THEIR METAB & OF KIDNEY IN EXCRETION OF DRUG & THEIR METABOLITES. ... THESE AGENTS ARE ALSO NOT RECOMMENDED FOR USE IN PREGNANCY... /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1522
Maternal Medication Usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Tolbutamide: Possible jaundice. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 142 (1994)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TOLBUTAMIDE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For treatment of NIDDM (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Tolbutamide, a first-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent, is used with diet to lower blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus type II. Tolbutamide is twice as potent as the related second-generation agent glipizide. Tolbutamide lowers blood sugar by stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin and helping the body use insulin efficiently. The pancreas must be able to produce insulin for this drug to work.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB03 - Tolbutamide
V - Various
V04 - Diagnostic agents
V04C - Other diagnostic agents
V04CA - Tests for diabetes
V04CA01 - Tolbutamide
Absorption
Readily absorbed following oral administration. Tolbutamide is detectable in plasma 30-60 minutes following oral administration of a single dose with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 3-5 hours. Absorption is unaltered if taken with food but is increased with high pH.
Route of Elimination
Unchanged drug and metabolites are eliminated in the urine and feces. Approximately 75-85% of a single orally administered dose is excreted in the urine principally as the 1-butyl-3-p-carboxyphenylsulfonylurea within 24 hours.
AFTER ORAL ADMIN, SULFONYLUREAS ARE RAPIDLY ABSORBED. /SULFONYLUREAS/
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 689
TOLBUTAMIDE CAN BE DETECTED IN BLOOD WITHIN 30 MIN AFTER ORAL ADMIN; PEAK CONCN ARE REACHED WITHIN 3 TO 5 HR. .../IT/ IS BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEINS. ... HALF-LIFE OF TOLBUTAMIDE IS ABOUT 5 HR.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
IN CONTRAST TO STUDIES REPORTED IN ANIMALS, METABOLIC CLEARANCE OF...TOLBUTAMIDE IN MAN HAS BEEN SHOWN TO BE UNALTERED BY FASTING.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 4: A Review of the Literature Published during 1974 and 1975. London: The Chemical Society, 1977., p. 350
Excreted (percentage)...100 /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Metabolized in the liver principally via oxidation of the p-methyl group producing the carboxyl metabolite, 1-butyl-3-p-carboxyphenylsulfonylurea. May also be metabolized to hydroxytolbutamide. Tolbutamide does not undergo acetylation like antibacterial sulfonamides as it does not have a p-amino group.
...MAJOR TOLBUTAMIDE METAB IN MAN HAS BEEN IDENTIFIED AS 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA... 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA IS ALSO FORMED IN SMALL AMT.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 218
IN RAT, MAJOR URINARY METAB, 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA COMPRISED 75% OF DOSE, BUT SMALL AMT OF 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA & P-TOLYLSULFONYLUREA, COMPRISING 5% OF DOSE, WERE ALSO PRESENT.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 219
ALTHOUGH 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA HAS BEEN REPORTED AS PRINCIPAL METAB IN CAT.../IT IS CLAIMED/ THAT CAT METABOLIZES TOLBUTAMIDE IN SAME WAY AS DOG. .../IT HAS BEEN SHOWN/ THAT TOLBUTAMIDE IS TRANSFORMED INTO 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA IN GUINEA PIGS & RABBITS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 219
IN CONTRAST TO RATS, RABBITS & MAN, DOGS METABOLIZE TOLBUTAMIDE...INTO P-TOLYLSULFONYLUREA & P-TOLYLSULFONAMIDE BY MECHANISM INVOLVING HYDROLYSIS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 417
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for TOLBUTAMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Tolbutamide has known human metabolites that include 4-Hydroxytolbutamide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Approximately 7 hours with interindividual variations ranging from 4-25 hours. Tolbutamide has the shortest duration of action, 6-12 hours, of the antidiabetic sulfonylureas.
Half-life...3-25 /hours/ /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in patients with NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor (receptor 1) on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP-potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin-containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose.
SULFONYLUREAS STIMULATE ISLET TISSUE TO SECRETE INSULIN. ... SULFONYLUREAS CAUSE DEGRANULATION OF BETA CELLS, A PHENOMENON ASSOC WITH INCR RATE OF SECRETION OF INSULIN. /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1520
ALTHOUGH MOLECULAR MECHANISM...NOT UNDERSTOOD, SEVERAL PERTINENT OBSERVATIONS HAVE BEEN MADE. ...TOLBUTAMIDE IS RESTRICTED IN ITS ACTION TO EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & DOES NOT NEED TO ENTER BETA CELL. INVOKED RELEASE OF INSULIN IS IMMEDIATE & INTIMATELY RELATED TO ACTION OF GLUCOSE...MAY SENSITIZE CELL TO NORMAL SECRETAGOGUE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1520
Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 723