
1. Bifenac
2. Clotam
3. Gea 6414
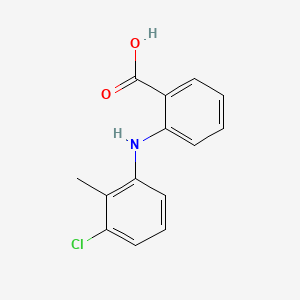
4. N-(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)anthranilic Acid
5. N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)anthranilic Acid
6. Rociclyn
1. 13710-19-5
2. Clotam
3. 2-[(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]benzoic Acid
4. Tolfedine
5. N-(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)anthranilic Acid
6. Gea 6414
7. Acido Tolfenamico
8. 2-((3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)benzoic Acid
9. Acide Tolfenamique
10. Acidum Tolfenamicum
11. 2-(3-chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic Acid
12. Benzoic Acid, 2-[(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]-
13. N-(2-methyl-3-chlorophenyl)anthranilic Acid
14. N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)-anthranilic Acid
15. Nsc-757873
16. Anthranilic Acid, N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)-
17. Chebi:32243
18. N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)anthranilic
19. 3g943u18km
20. Mfcd00133865
21. Ncgc00016705-05
22. Bifenac
23. N-(3-chloro-ortho-tolyl) Anthranilic Acid
24. Cas-13710-19-5
25. Dsstox_cid_25409
26. Dsstox_rid_80860
27. Dsstox_gsid_45409
28. Benzoic Acid, 2-((3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)-
29. Tolfine
30. 2-([3-chloro-2-methylphenyl]amino)benzoic Acid
31. Sr-01000000102
32. N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)anthranilic Acid
33. Tolfenamic
34. Tolfenamic-acid
35. Unii-3g943u18km
36. Acide Tolfenamique [inn-french]
37. Acido Tolfenamico [inn-spanish]
38. Acidum Tolfenamicum [inn-latin]
39. Tolfenamic Acid [inn:ban:jan]
40. Prestwick_579
41. Einecs 237-264-3
42. Clotam (tn)
43. Tolfenamicacid
44. Brn 0657821
45. Spectrum_001263
46. Tolfenamic Acid, Nsaid
47. Prestwick0_000205
48. Prestwick1_000205
49. Prestwick2_000205
50. Prestwick3_000205
51. Spectrum2_001446
52. Spectrum3_001762
53. Spectrum4_000238
54. Spectrum5_001143
55. Oprea1_692996
56. Schembl25190
57. Tolfenamic Acid (jan/inn)
58. Bspbio_000189
59. Bspbio_003223
60. Kbiogr_000935
61. Kbioss_001743
62. Tolfenamic Acid [mi]
63. Flufenamic Acid Analogue, 32
64. Mls000028531
65. Bidd:gt0343
66. Spectrum1501198
67. Tolfenamic Acid [inn]
68. Tolfenamic Acid [jan]
69. Spbio_001311
70. Spbio_002110
71. Bpbio1_000209
72. Chembl121626
73. Cid_610479
74. Gtpl8769
75. Zinc2188
76. Dtxsid1045409
77. Tolfenamic Acid [mart.]
78. Bdbm35905
79. Kbio2_001743
80. Kbio2_004311
81. Kbio2_006879
82. Kbio3_002723
83. Yeznlouzaiomlt-uhfffaoysa-
84. Tolfenamic Acid [who-dd]
85. Hms1568j11
86. Hms1921p13
87. Hms2090d04
88. Hms2095j11
89. Hms2230j13
90. Hms3370a02
91. Hms3651e06
92. Hms3712j11
93. Hms3884m16
94. Pharmakon1600-01501198
95. Hy-b0335
96. Tox21_110570
97. Ccg-39189
98. Nsc757873
99. S1959
100. Tolfenamic Acid [ep Impurity]
101. Akos012836098
102. Tolfenamic Acid [ep Monograph]
103. Tox21_110570_1
104. 2-(3-chloro-o-toluidino)benzoic Acid
105. Db09216
106. Nsc 757873
107. 2(3-chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic Acid
108. Ncgc00016705-01
109. Ncgc00016705-02
110. Ncgc00016705-03
111. Ncgc00016705-04
112. Ncgc00016705-06
113. Ncgc00016705-07
114. Ncgc00016705-10
115. Ncgc00022587-03
116. Ncgc00022587-04
117. Ncgc00022587-05
118. As-13748
119. Da-11289
120. N-(3-chloro-ortho-tolyl)anthranilic Acid
121. Smr000058289
122. Sy052546
123. Sbi-0051687.p002
124. 2-(3-chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic Acid #
125. Ab00052244
126. Ft-0652603
127. Sw196753-3
128. Unm000001237003
129. 2-(3-chloro-2-methylphenylamino)benzoic Acid
130. 2-((3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)benzoicacid
131. D01183
132. D78227
133. Q59412
134. Tolfenamic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
135. Ab00052244-15
136. Ab00052244_16
137. Ab00052244_17
138. Tolfenamic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
139. A807198
140. Benzoic Acid, 2-(3-chloro-2-methylphenylamino)-
141. 2-[(3-chloranyl-2-methyl-phenyl)amino]benzoic Acid
142. J-006962
143. Sr-01000000102-2
144. Sr-01000000102-3
145. Tolfenamic Acid, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
146. Brd-k50133271-001-05-4
147. Brd-k50133271-001-10-4
148. Tolfenamic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
149. Tolfenamic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 261.70 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H12ClNO2 |
| XLogP3 | 5.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 261.0556563 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 261.0556563 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 298 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
In the information for tolfenamic acid, it is stated that this drug, being an NSAID, is effective in treating the pain associated with the acute attack of migraines in adults.
Studies have shown that tolfenamic acid presents a non-dose dependent partial inhibition of irritant-induced temperature rise as well as a dose-dependent inhibition of skin edema. By studying its NSAID properties more closely, it was noted a dose-related inhibition of serum thromboxane which indicated the inhibition of COX-1. In the same line, there was noted a inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis which marks a related COX-2 inhibition. The maximal inhibition of thromboxane was greater than 80% as well as is proven to be a potent prostaglandin E inhibitor.
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Serotonin Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate serotonin receptors, thereby blocking the actions of serotonin or SEROTONIN RECEPTOR AGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin Antagonists.)
Prostaglandin Antagonists
Compounds that inhibit the action of prostaglandins. (See all compounds classified as Prostaglandin Antagonists.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AG - Fenamates
M01AG02 - Tolfenamic acid
Absorption
Tolfenamic acid pharmacokinetic is marked by a short tmax of 0.94-2.04 h. It also presented a linear pharmacokinetic profile with an AUC from 13-50 mcg/ml.h if administered in a dose of 2-8 mg/kg respectively. The oral absorption is delayed and it gives a mean lag-time to absorption of 32 min. The peak plasma concentration of 11.1 mcg/ml. The bioavailability of tolfenamic acid is around 75%.
Route of Elimination
Tolfenamic acid is cleared relatively fast and it undergoes by hepatic metabolism where the produced metabolites are renally cleared as glucuronic acid conjugates. Most of the elimination occurs by extrarenal mechanisms in which the unchanged drug together with its glucuronide in urine accounts for only 8.8% of the administered dose.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution is of 1.79-3.2 L/kg. When tested intravenously, the reported steady-state volume of distribution was 0.33 L/kg.
Clearance
The estimated clearance rate of tolfenamic acid is 0.142-0.175 L.h/kg. When tested intravenously, the reported clearance rate was 72.4 ml.h/kg.
The first pass metabolism accounts for 20% of the administered dose of tolfenamic acid. Urine metabolite studies have demonstrated the identification of five metabolites from which three of them are monohydroxylated, one is monohydroxylated and hydroxylated and one last metabolite that presented and oxidized methyl group to form a carboxyl group. Two of these hydroxylated metabolites are N-(2-hydroxymethyl-3-chlorophenyl)-anthranilic acid and N-(2-hydroxymethyl-3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-anthranilic acid.
The estimated half-life of tolfenamic acid is 8.01-13.50 hours. When tested intravenously, the reported half-life was 6.1h.
Tolfenamic acid inhibits the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, and it also presents inhibitory actions on the prostaglandin receptors. As commonly thought, the mechanism of action of tolfenamic acid is based on the major mechanism of NSAIDs which consists of the inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 pathways to inhibit prostaglandin secretion and action and thus, to exert its anti-inflammatory and pain-blocking action. Nonetheless, some report currently indicates that tolfenamic acid inhibits leukotriene B4 chemotaxis of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes leading to an inhibition of even 25% of the chemotactic response. This activity is a not ligand specific additional anti-inflammatory mechanism of tolfenamic acid.