
1. Anhydrous Tolmetin Sodium
2. Anhydrous, Tolmetin Sodium
3. Dihydrate Tolmetin Sodium
4. Mcn 2559
5. Mcn-2559
6. Mcn2559
7. Sodium Anhydrous, Tolmetin
8. Sodium, Tolmetin
9. Tolectin
10. Tolmetin Sodium
11. Tolmetin Sodium Anhydrous
12. Tolmetin Sodium, Anhydrous
13. Tolmetin Sodium, Dihydrate
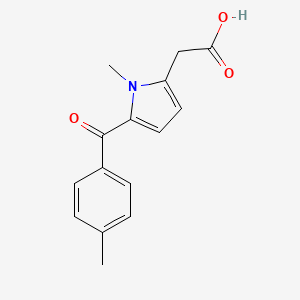
1. 26171-23-3
2. 1-methyl-5-p-toluoylpyrrole-2-acetic Acid
3. Tolectin
4. Tolmetine
5. Tolmetinum
6. Tolmetina [dcit]
7. Mcn-2559
8. Tolmetina
9. Tolmetino
10. Tolmetine [inn-french]
11. Tolmetinum [inn-latin]
12. Tolmetino [inn-spanish]
13. 1h-pyrrole-2-acetic Acid, 1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-
14. Mcn 2559
15. 2-(1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl)acetic Acid
16. 2-[1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)pyrrol-2-yl]acetic Acid
17. 1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-pyrrole-2-acetic Acid
18. 5-(p-toluoyl)-1-methylpyrrole-2-acetic Acid
19. Acido 1-metil-5-(p-tolnil)-pirrol-2-acetico
20. 2-[1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl]acetic Acid
21. Pyrrole-2-acetic Acid, 1-methyl-5-p-toluoyl-
22. Chembl1020
23. D8k2jpn18b
24. [1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl]acetic Acid
25. Chebi:71941
26. 1-methyl-5-p-toluoyl-pyrrole-2-acetic Acid
27. 2-{1-methyl-5-[(4-methylphenyl)carbonyl]-1h-pyrrol-2-yl}acetic Acid
28. Hsdb 3403
29. Tolmetin (usan/inn)
30. Mcn-2559-21-98
31. Einecs 247-497-2
32. Unii-d8k2jpn18b
33. Brn 0485305
34. Tolmetin [usan:inn:ban]
35. 1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1h-pyrrole-2-acetic Acid
36. Acido 1-metil-5-(p-tolnil)-pirrol-2-acetico [spanish]
37. Spectrum_000935
38. Tolmetin [hsdb]
39. Tolmetin [usan]
40. Tolmetin [inn]
41. Tolmetin [jan]
42. Tolmetin [mi]
43. Tolmetin [vandf]
44. Prestwick0_000856
45. Prestwick1_000856
46. Prestwick2_000856
47. Prestwick3_000856
48. Spectrum2_001205
49. Spectrum3_000603
50. Spectrum4_000359
51. Spectrum5_001194
52. Tolmetin [who-dd]
53. Schembl3150
54. Oprea1_869397
55. Bspbio_000871
56. Bspbio_002106
57. Kbiogr_000797
58. Kbioss_001415
59. 5-22-06-00392 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
60. Bidd:gt0468
61. Divk1c_000213
62. Spbio_000990
63. Spbio_002792
64. Bpbio1_000959
65. Gtpl7311
66. Zinc2191
67. Dtxsid2043951
68. Kbio1_000213
69. Kbio2_001415
70. Kbio2_003983
71. Kbio2_006551
72. Kbio3_001606
73. Ninds_000213
74. Hms2090d06
75. Hms3886i03
76. Bcp09085
77. Hy-b1799
78. Bdbm50295287
79. Mfcd00599595
80. S4832
81. Akos015850645
82. Ccg-267033
83. Cs-w008734
84. Db00500
85. Gs-6529
86. Sb63879
87. Idi1_000213
88. Tolmetin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
89. Ncgc00094796-03
90. 1-methyl-5-p-toluoylpyrrole-2-aceticacid
91. Sbi-0051537.p002
92. Ft-0649942
93. Ft-0675272
94. 1-methyl- 5-(p-toluoyl)pyrrole-2-acetic Acid
95. C07149
96. D02355
97. 171t233
98. A818238
99. 1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)pyrrole-2-acetic Acid
100. J-504975
101. Q3992411
102. Brd-k82562631-236-02-0
103. Brd-k82562631-325-03-9
104. F6782-4251
105. [1-methyl-5-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl]-acetic Acid
106. [1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl]acetic Acid #
107. [1-methyl-5-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-1h-pyrrol-2-yl]-acetic Acid(tolmetin)
108. Tlt
| Molecular Weight | 257.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H15NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 257.10519334 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 257.10519334 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 59.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 347 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal; Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IN SEVERAL CONTROLLED STUDIES IN PT WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS, TOLMETIN REDUCED SEVERITY OF SYMPTOMS (...JOINT SWELLING, PAIN, NUMBER OF INFLAMED JOINTS, DURATION OF MORNING STIFFNESS). ITS EFFECTIVENESS WAS MAINTAINED WITH LONG-TERM USE (TWO YEARS). /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 388
EFFICACY...IN A DAILY DOSE OF ABOUT 1.2 G WAS COMPARABLE TO...3.9 G OF ASPIRIN DAILY. /OTHER/...STUDIES IN PT WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS INDICATED...DAILY DOSE OF ABOUT 1.2 G OF TOLMETIN WAS EQUALLY EFFECTIVE TO ABOUT 150 MG INDOMETHACIN. ...SIMILAR EFFECTIVENESS /COMPARED TO/ IBUPROFEN & PHENYLBUTAZONE. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 388
...SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE IN TREATMENT OF JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS; HOWEVER, THE NUMBER OF PT STUDIED WAS SMALL & ADDNL STUDIES ARE NECESSARY TO ESTABLISH THE EFFECTIVE DOSE. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for TOLMETIN (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
IN CLINICAL STUDIES, PEPTIC ULCER OCCURRED IN APPROX 2% OF PT. IT IS... ADVISABLE TO USE TOLMETIN CAUTIOUSLY IN PT WITH A HISTORY OF PEPTIC ULCER. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389
TOLMETIN DECR PLATELET ADHESIVENESS & INCR BLEEDING TIME; THUS, IT SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PT WITH BLEEDING DISORDERS. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389
TOLMETIN...COMMONLY PRODUCES GASTROINTESTINAL REACTIONS (25% OF RECIPIENTS), & THEY RANGE FROM TRANSIENT MILD EFFECTS, SUCH AS NAUSEA, TO SERIOUS REACTIONS REQUIRING CESSATION OF THERAPY. ... URTICARIA, HEADACHE, WATER RETENTION, DIZZINESS, & HYPERTENSION HAVE ALSO BEEN REPORTED. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 494
TOLMETIN CAUSES PSEUDOPROTEINURIA IN TESTS INVOLVING ACID PPT; THUS, OTHER METHODS FOR DETECTING PROTEINURIA SHOULD BE USED FOR PT RECEIVING THIS DRUG. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TOLMETIN (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, including the treatment of acute flares long-term management. Also for treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
FDA Label
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent. Studies in animals have shown tolmetin to possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity. In the rat, tolmetin prevents the development of experimentally induced polyarthritis and also decreases established inflammation. In patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or osteaoarthritis, tolmetin is as effective as aspirin and indomethacin in controlling disease activity, but the frequency of the milder gastrointestinal adverse effects and tinnitus was less than in aspirin-treated patients, and the incidence of central nervous system adverse effects was less than in indomethacin-treated patients. In patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, tolmetin is as effective as aspirin in controlling disease activity, with a similar incidence of adverse reactions. tolmetin has produced additional therapeutic benefit when added to a regimen of gold salts and, to a lesser extent, with corticosteroids. Tolmetin should not be used in conjunction with salicylates since greater benefit from the combination is not likely, but the potential for adverse reactions is increased.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with cyclooxygenase (PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASES) and thereby prevent its substrate-enzyme combination with arachidonic acid and the formation of eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB03 - Tolmetin
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M02 - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02A - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02AA - Antiinflammatory preparations, non-steroids for topical use
M02AA21 - Tolmetin
Absorption
Rapidly and almost completely absorbed with peak plasma levels being reached within 30-60 minutes after an oral therapeutic dose.
THE DRUG IS RAPIDLY ABSORBED AFTER ORAL ADMIN, PEAK PLASMA LEVELS OCCUR IN 30 TO 60 MIN. IT IS EXCRETED LARGELY IN URINE, PRIMARILY AS CONJUGATES OR METABOLITES. ITS PLASMA HALF-LIFE IS APPROX 1 HR. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389
GI ABSORPTION IS ABOUT 90% OR GREATER...WITH PEAK LEVELS WITHIN 20-60 MIN FOR TOLMETIN... PROTEIN BINDING IS EXTENSIVE, BEING 90% OR GREATER... HEPATIC BIOTRANSFORMATION & RENAL EXCRETION WITH SOME FECAL EXCRETION OF METABOLITES ARE THE MEANS OF ELIMINATION. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 493
TOLMETIN IS RAPIDLY & COMPLETELY ABSORBED FOLLOWING ORAL ADMIN TO MAN, & CONCN ACHIEVED IN PLASMA ARE NOT REDUCED BY CONCOMITANT ADMIN OF GASTRIC ANTACIDS. PEAK CONCN ARE ACHIEVED 20-60 MIN AFTER ORAL ADMIN, & T/2 IN PLASMA IS BETWEEN 1 & 3 HR.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 709
AFTER ABSORPTION, TOLMETIN IS EXTENSIVELY (99%) BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEINS. VIRTUALLY ALL OF THE DRUG CAN BE RECOVERED IN URINE AFTER 24 HR; SOME IS UNCHANGED (17%), BUT MOST IS CONJUGATED (10%) OR OTHERWISE METABOLIZED. THE MAJOR METABOLITE TRANSFORMATION IS DECARBOXYLATION.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 709
TOLMETIN SODIUM WAS RAPIDLY & COMPLETELY ABSORBED (PEAK TIME, 20-60 MIN) & ELIMINATED RAPIDLY FROM PLASMA WITH BIPHASIC DECAY CURVE & ELIMINATION T/2 OF APPROX 2.1 HR.
GRINDEL JM ET AL; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 26(1) 122 (1979)
Essentially all of the administered dose is recovered in the urine in 24 hours either as an inactive oxidative metabolite or as conjugates of tolmetin.
URINE METABOLITES 1-METHYL-5-(4-CARBOXYBENZOYL)-1H-PYRROLE-2-ACETIC ACID & TOLMETIN GLUCURONIDE NOTED AFTER TOLMETIN SODIUM.
GRINDEL JM ET AL; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 26(1) 122 (1979)
Tolmetin has known human metabolites that include Tolmetin glucuronide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Biphasic elimination from the plasma consisting of a rapid phase with a half-life of one to 2 hours followed by a slower phase with a half-life of about 5 hours.
The mode of action of tolmetin is not known. However, studies in laboratory animals and man have demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory action of tolmetin is not due to pituitary-adrenal stimulation. Tolmetin inhibits prostaglandin synthetase in vitro and lowers the plasma level of prostaglandin E in man. This reduction in prostaglandin synthesis may be responsible for the anti-inflammatory action. Tolmetin does not appear to alter the course of the underlying disease in man.
ALTHOUGH IT DIFFERS CHEMICALLY FROM ASPIRIN & OTHER NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS, ITS PHARMACOLOGIC PROPERTIES ARE SIMILAR. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 388
...INHIBITS PROSTAGLANDIN SYNTHETASE IN VITRO. IT ALSO HAS BEEN SHOWN TO LOWER PLASMA LEVEL OF PROSTAGLANDIN E IN MAN. HOWEVER, SIGNIFICANCE OF THESE ACTIONS IN RELATION TO CLINICAL EFFECTS IS NOT KNOWN. /TOLMETIN SODIUM/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 389