

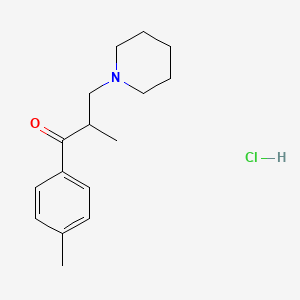

1. Hydrochloride, Tolperisone
2. Midocalm
3. Mydeton
4. Mydocalm
5. Tolperisone
1. 3644-61-9
2. Tolperisone Hcl
3. Midocalm
4. Muscalm
5. Tolperisone (hydrochloride)
6. 2,4'-dimethyl-3-piperidinopropiophenone Hydrochloride
7. 2-methyl-3-piperidino-1-p-tolylpropan-1-one Hydrochloride
8. Tolperisone Hydrochloride [jan]
9. 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-one Hydrochloride
10. N-553
11. 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(1-piperidinyl)-1-propanone Hydrochloride
12. 3644-61-9 (hcl)
13. 8z075k2tig
14. 1-piperidino-2-methyl-3-(p-tolyl)-3-propanone Hydrochloride
15. Ncgc00094929-01
16. Dsstox_cid_25868
17. Dsstox_rid_81187
18. Dsstox_gsid_45868
19. Arantoick
20. Atmosgen
21. Besnoline
22. Isocalm
23. Kineorl
24. Metosomin
25. Abbsa
26. 2-methyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)-1-p-tolylpropan-1-one Hydrochloride
27. 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-piperidin-1-ylpropan-1-one;hydrochloride
28. Cas-3644-61-9
29. Tolperisonehydrochloride
30. Einecs 222-876-5
31. Av 650
32. Unii-8z075k2tig
33. 1-propanone, 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(1-piperidinyl)-, Hydrochloride
34. Muscalm (tn)
35. Mfcd00058211
36. Biocalm
37. Minacalm
38. Naismeritin
39. Tolfree
40. Tolisartine
41. Tolpidol
42. Ncgc00182078-02
43. Mls004773941
44. Schembl872770
45. Spectrum1501194
46. 2,4'-dimethyl-3-piperidino-propiophenone Hydrochloride
47. Chembl1395150
48. Dtxsid2045868
49. Chebi:32244
50. Propiophenone, 2,4'-dimethyl-3-piperidino-, Hydrochloride
51. Tolperisone Hydrochloride (jp17)
52. Hms1921p09
53. Pharmakon1600-01501194
54. Hy-b1139
55. Tox21_111360
56. Tox21_113139
57. Ccg-40311
58. Nsc757872
59. S4200
60. Tolperisone Hydrochloride [mi]
61. 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(1-piperidyl)propan-1-one Hydrochloride
62. Akos005167032
63. Tox21_111360_1
64. Ac-4685
65. Cs-4744
66. Ncgc00094929-02
67. Ncgc00178060-03
68. Tolperisone Hydrochloride [mart.]
69. As-12472
70. Bp-10588
71. Smr003500666
72. Tolperisone Hydrochloride [who-dd]
73. Ft-0603642
74. Ft-0675274
75. Sw219278-1
76. T1319
77. A18694
78. D01507
79. H12066
80. 644t619
81. Sr-01000872774
82. Tolperisone Hydrochloride, >=98% (hplc), Solid
83. Sr-01000872774-1
84. W-106614
85. Q27271220
86. F9995-4198
87. 2-methyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)propan-1-one Hydrochloride
88. 1-propanone, 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(1-piperidinyl)-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 281.82 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H24ClNO |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 281.1546421 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 281.1546421 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 20.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 262 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Muscle Relaxants, Central
A heterogeneous group of drugs used to produce muscle relaxation, excepting the neuromuscular blocking agents. They have their primary clinical and therapeutic uses in the treatment of muscle spasm and immobility associated with strains, sprains, and injuries of the back and, to a lesser degree, injuries to the neck. They have been used also for the treatment of a variety of clinical conditions that have in common only the presence of skeletal muscle hyperactivity, for example, the muscle spasms that can occur in MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. (From Smith and Reynard, Textbook of Pharmacology, 1991, p358) (See all compounds classified as Muscle Relaxants, Central.)