

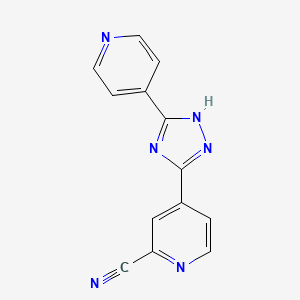

1. 4-(5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-(1,2,4) Triazol-3-yl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile
2. Fyx-051
1. 577778-58-6
2. Fyx 051
3. Fyx-051
4. 4-(5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile
5. Topiroxostat [inn]
6. 2-pyridinecarbonitrile, 4-[5-(4-pyridinyl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-
7. 5-(2-cyano-4-pyridyl)-3-(4-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole
8. Chembl1078685
9. 4-(5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)picolinonitrile
10. 4-(5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile
11. Mfcd17167057
12. 0j877412jv
13. 4-[5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]pyridine-2-carbonitrile
14. Topiloric
15. Uriadec
16. 4-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)picolinonitrile
17. Unii-0j877412jv
18. Uriadec (tn)
19. Topiroxostat (jan/inn)
20. Topiroxostat [mi]
21. Topiroxostat [jan]
22. Schembl860420
23. Topiroxostat [who-dd]
24. Schembl18056618
25. Gtpl10592
26. Dtxsid80206462
27. Bcp09957
28. Ex-a1197
29. 4-(5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-(1,2,4) Triazol-3-yl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile
30. 4-[5-(4-pyridyl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]pyridine-2-carbonitrile
31. Bdbm50267750
32. Bdbm50311275
33. S3719
34. Zinc13536586
35. 4-[5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-[1,2,4]triazol-3-yl]-pyridine-2-carbonitrile
36. Akos026750465
37. Akos026751485
38. (fyx-051)"
39. Ccg-266938
40. Cs-2033
41. Db01685
42. Ncgc00378610-01
43. Ncgc00378610-02
44. Ac-30740
45. As-56359
46. Hy-14874
47. Sy116097
48. Ft-0700966
49. A14144
50. D09786
51. Q15725832
| Molecular Weight | 248.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H8N6 |
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 248.08104428 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 248.08104428 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 91.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 344 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for the treatment of gout and hyperurcemia in Japan.
Topiroxostat reduces the synthesis of uric acid by competitively inhibiting xanthine oxidase in a selective and time-dependent manner. It serves to reduce the concentration of insoluble urates and uric acid in tissues, plasma and urine. Topiroxostat is not reported to cause QT prolongation.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Absorption
The time to reach peak plasma concentration of 229.9 ng/mL was 0.67 hour following a single oral dose of 20mg topiroxostat. The oral bioavailability in male rats was 69.6% after oral administration of a single dose of 1mg/kg.
Route of Elimination
Urinary excretion and fecal excretion of radiolabeled topiroxostat are 30.4% and 40.9% of total dose of 1mg/kg administered to rats, respectively. Within 24 h after a single oral administration of 120mg of topiroxostat, the main metabolites of topiroxostat, N-oxide, N1-gluculonide, and N2-gluculonide, are excreted into urine about 4.8, 43.3, and 16.1 % of the dose, respectively. Unchanged topiroxostat and the hydroxide metabolite was 0.1% or less.
Volume of Distribution
The distribution of 14C-topiroxostat (20, 200, and 2000 ng/mL) in human blood cells was 6.7% to 12.8%.
Clearance
The apparent total body clearance rate is 89.5 L/h and the renal clearance rate is 17.4 mL/h following a single oral dose of 20mg topiroxostat.
Topiroxostat is mainly inactivated by hepatic metabolism. 2-hydroxy topiroxostat is formed from primary hydroxylation of the drug by xanthine oxidase and still retains an inhibitory activity on the enzyme. Topiroxostat N-oxide is another major metabolite that can be detected in plasma and urine. It is determined that the N-oxide and hydroxide metabolites are pyridine N-oxide and pyridine 2 (or 6)-hydroxide, respectively. Topiroxostat is mainly inactivated by hepatic metabolism where it undergoes glucuronidation. The metabolism of topiroxostat to N1-and N2-glucuronide conjugates is mainly mediated by UGT1A1, 1A7, and 1A9, with UGT1A9 being the most predominant.
FYX-051 has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[3-(2-cyanopyridin-4-yl)-5-pyridin-4-yl-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid and 4-[2-[(3R,4S,5S,6S)-6-carboxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]-5-pyridin-4-yl-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]pyridine-2-carbonitrilium.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The mean half life of topiroxostat after a single oral dose of 20mg topiroxostat is 5 hours under fasting condition. The complex of molybdenum (IV)- topiroxostat has an approximate half life of 20.4 hours.
Uric acid synthesis depends on the action of xanthine oxidase activity in the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine, followed by the conversion of xanthine to uric acid. Xanthine oxidase consists of a molybdenum ion as cofactor in the active center that has different redox states upon substrate binding. When a substrate such as hypoxanthine or xanthine binds, xanthine oxidase hydroxylates it and molybdenum ion is reduced from hexavalent, Mo(VI), to tetravalent form, Mo(IV). Molybdenum ion is reoxidized into hexavalent state once the hydroxylated substrate, xanthine or uric acid, dissociates from the active site. Topiroxostat is shown to interact with multiple amino acid residues of the solvent channel and additionally forms a reaction intermediate by covalent binding with molybdenum (IV) ion via an oxygen atom. It also forms hydrogen bonds with molybdenum (VI) ion, suggesting that it has multiple inhibition modes to xanthine oxidase. Enhanced binding interactions to xanthine oxidase achieves delayed dissociation of topiroxostat from the enzyme. 2-hydroxy-topiroxostat, the metabolite formed by primary hydroxylation of topiroxostat by xanthine oxidase, also causes time and concentration-dependent inhibition of the enzyme. Topiroxostat is shown to inhibit ATP-binding cassette transporter G2 (ABCG2) in vitro, which is a membrane protein responsible for recovering uric acid in the kidneys and secreting uric acid from the intestines.
