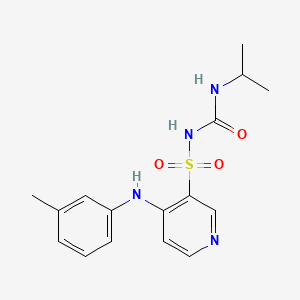

1. 1-isopropyl-3-((4-(3-methylphenylamino)pyridine)-3-sulfonyl)urea
2. 1-isopropyl-3-((4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl)sulfonyl)urea
3. Demadex
4. Torasemide
1. Torasemide
2. 56211-40-6
3. Demadex
4. Luprac
5. Torasemida
6. Torasemidum
7. Torasemidum [inn-latin]
8. Torasemida [inn-spanish]
9. Unat
10. Ac-4464
11. Torasemide Anhydrous
12. Jdl 464
13. Torem
14. Bm-02015
15. Ac4464
16. N-(isopropylcarbamoyl)-4-(m-tolylamino)pyridine-3-sulfonamide
17. Soaanz
18. Upcard
19. 1-isopropyl-3-((4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl)sulfonyl)urea
20. Ac 4464
21. Jdl-464
22. Bm 02015
23. 1-[4-(3-methylanilino)pyridin-3-yl]sulfonyl-3-propan-2-ylurea
24. Torasemide [inn]
25. Torsemide (demadex)
26. Torasemide, Anhydrous
27. Bm02.015
28. N-(((1-methylethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-((3-methylphenyl)amino)-3-pyridinesulfonamide
29. Bm-02.015
30. Mls001165687
31. Chebi:9637
32. W31x2h97fb
33. 3-pyridinesulfonamide, N-(((1-methylethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-((3-methylphenyl)amino)-
34. Torsemide [usan]
35. Ncgc00016879-01
36. Smr000466313
37. Toradiur
38. Cas-56211-40-6
39. 1-{4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonyl}-3-(propan-2-yl)urea
40. Dsstox_cid_3690
41. N-[(isopropylamino)carbonyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
42. 3-pyridinesulfonamide, N-[[(1-methylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]-
43. Dsstox_rid_77149
44. Dsstox_gsid_23690
45. Dilutol
46. Torocard
47. Sutril
48. Torrem
49. Torasemide N
50. 4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]-n-(propan-2-ylcarbamoyl)pyridine-3-sulfonamide
51. N-{[(1-methylethyl)amino]carbonyl}-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
52. Torsemide (usp)
53. Demadex (tn)
54. Luprac (tn)
55. Ccris 6736
56. Torasemide (jan/inn)
57. Torsemide [usan:usp]
58. Gj-1090
59. Brn 0498515
60. Unii-w31x2h97fb
61. Mfcd00866166
62. Ks-1123
63. Pw-2132
64. Spectrum_001776
65. Torsemide [mi]
66. Torasemide [jan]
67. Prestwick0_001030
68. Prestwick1_001030
69. Prestwick2_001030
70. Prestwick3_001030
71. Spectrum2_001142
72. Spectrum3_001832
73. Spectrum4_000290
74. Spectrum5_001699
75. Torsemide [vandf]
76. Torasemide [mart.]
77. Torsemide [usp-rs]
78. Chembl1148
79. Torasemide [who-dd]
80. Schembl41184
81. Bspbio_001219
82. Bspbio_003503
83. Kbiogr_000820
84. Kbioss_002257
85. Cid_41781
86. Mls000759418
87. Mls001195611
88. Mls001424121
89. Mls006010744
90. Bidd:gt0623
91. Spectrum1505211
92. Spbio_001063
93. Spbio_003080
94. Bpbio1_001341
95. Gtpl7312
96. Zinc5823
97. Torsemide [orange Book]
98. Dtxsid2023690
99. Torsemide [usp Impurity]
100. Bdbm64107
101. Kbio2_002256
102. Kbio2_004824
103. Kbio2_007392
104. Kbio3_003008
105. Torasemide For System Suitability
106. Torasemide [ep Monograph]
107. Torsemide [usp Monograph]
108. Hms1571m21
109. Hms1922n05
110. Hms2051l21
111. Hms2098m21
112. Hms2234n14
113. Hms3373g20
114. Hms3393l21
115. Hms3715m21
116. Hms3744g19
117. Albb-027267
118. Bcp07286
119. Hy-b0247
120. Tox21_110662
121. Ccg-40257
122. S1698
123. Stl388026
124. Torsemide, >=98% (hplc), Solid
125. Akos015894937
126. Tox21_110662_1
127. Bm02015
128. Db00214
129. Nc00238
130. Ncgc00016879-02
131. Ncgc00016879-03
132. Ncgc00016879-04
133. Ncgc00016879-06
134. Ncgc00016879-07
135. Ncgc00095141-01
136. Ncgc00095141-02
137. Ncgc00095141-03
138. Ac-18762
139. Ab00514011
140. Ft-0630689
141. Ft-0675300
142. T2538
143. D00382
144. T72621
145. Ab00514011-09
146. Ab00514011_10
147. Ab00514011_11
148. 211t406
149. A830961
150. Q419948
151. Sr-01000759362
152. Torasemide Anhydrous [ema Epar Veterinary]
153. Q-201846
154. Sr-01000759362-5
155. Brd-k30480208-001-05-2
156. Torsemide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
157. 1-isopropyl-3-((4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl)sulphonyl)urea
158. 4-(3-methylanilino)-n-(propan-2-ylcarbamoyl)pyridine-3-sulfonamide
159. Torasemide Anhydrous, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
160. 1-isopropyl-3-[[4-(3-methylanilino)-3-pyridyl]sulfonyl]urea;torsemide
161. N-(isopropylcarbamoyl)-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
162. N-[(propan-2-yl)carbamoyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
163. N-({4-[(3-methylphenyl)imino]-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-yl}sulfonyl)propane-2-carbamimidic Acid
164. Torasemide For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 348.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H20N4O3S |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 348.12561169 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 348.12561169 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 109 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 518 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Demadex |
| PubMed Health | Torsemide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DEMADEX (torsemide) is a diuretic of the pyridine-sulfonylurea class. Its chemical name is 1-isopropyl-3-[(4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl) sulfonyl] urea and its structural formula is:Its empirical formula is C16H20N4O3S, its pKa is 7.1, and its molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Torsemide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 100mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Torsemide |
| PubMed Health | Torsemide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DEMADEX (torsemide) is a diuretic of the pyridine-sulfonylurea class. Its chemical name is 1-isopropyl-3-[(4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl) sulfonyl] urea and its structural formula is:Its empirical formula is C16H20N4O3S, its pKa is 7.1, and its molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Torsemide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 50mg/5ml (10mg/ml); 5mg; 20mg/2ml (10mg/ml); 100mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Pliva Pharm Ind; Sun Pharm Inds; Aurobindo Pharma; Par Pharm; Roxane; Luitpold; Eurohlth Intl |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Demadex |
| PubMed Health | Torsemide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DEMADEX (torsemide) is a diuretic of the pyridine-sulfonylurea class. Its chemical name is 1-isopropyl-3-[(4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl) sulfonyl] urea and its structural formula is:Its empirical formula is C16H20N4O3S, its pKa is 7.1, and its molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Torsemide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 100mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Torsemide |
| PubMed Health | Torsemide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DEMADEX (torsemide) is a diuretic of the pyridine-sulfonylurea class. Its chemical name is 1-isopropyl-3-[(4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl) sulfonyl] urea and its structural formula is:Its empirical formula is C16H20N4O3S, its pKa is 7.1, and its molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Torsemide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 50mg/5ml (10mg/ml); 5mg; 20mg/2ml (10mg/ml); 100mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Pliva Pharm Ind; Sun Pharm Inds; Aurobindo Pharma; Par Pharm; Roxane; Luitpold; Eurohlth Intl |
Torasemide is indicated for the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, renal or hepatic diseases. From this condition, it has been observed that torasemide is very effective in cases of kidney failure. As well, torasemide is approved to be used as an antihypertensive agent either alone or in combination with other antihypertensives.
FDA Label
For treatment of clinical signs, including oedema and effusion, related to congestive heart failure in dogs.
It is widely known that administration of torasemide can attenuate renal injury and reduce the severity of acute renal failure. This effect is obtained by increasing urine output and hence, facilitating fluid, acid-base and potassium control. This effect is obtained by the increase in the excretion of urinary sodium and chloride. Several reports have indicated that torasemide presents a long-lasting diuresis and less potassium excretion which can be explained by the effect that torasemide has on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This effect is very similar to the effect observed with the administration of combination therapy with [furosemide] and [spironolactone] and it is characterized by a decrease in plasma brain natriuretic peptide and improved measurements of left ventricular function. Above the aforementioned effect, torasemide presents a dual effect .in which the inhibition of aldosterone which donates torasemide with a potassium-sparing action. Torasemide has been shown to reduce extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure in hypertensive patients suffering from chronic kidney disease. As well, some reports have indicated that torasemide can reduce myocardial fibrosis by reducing the collagen accumulation. This effect is suggested to be related to the decrease in aldosterone which in order has been shown to reduce the production of the enzyme procollagen type I carboxy-terminal proteinase which is known to be overexpressed in heart failure patients.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Sodium Potassium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM-POTASSIUM-CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS which are concentrated in the thick ascending limb at the junction of the LOOP OF HENLE and KIDNEY TUBULES, DISTAL. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA and HYPERGLYCEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Potassium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
QC03CA04
C03CA04
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03C - High-ceiling diuretics
C03CA - Sulfonamides, plain
C03CA04 - Torasemide
Absorption
Torasemide is the diuretic with the highest oral bioavailability even in advanced stages of chronic kidney disease. This bioavailability tends to be higher than 80% regardless of the patient condition. The maximal serum concentration is reported to be of 1 hour and the absorption parameters are not affected by its use concomitantly with food.
Route of Elimination
Torasemide is mainly hepatically processed and excreted in the feces from which about 70-80% of the administered dose is excreted by this pathway. On the other hand, about 20-30% of the administered dose is found in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of torasemide is 0.2 L/kg.
Clearance
The clearance rate of torasemide is considerably reduced by the presence of renal disorders.
Torasemide is extensively metabolized in the liver and only 20% of the dose remains unchanged and it is recovered in the urine. Metabolized via the hepatic CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 mainly by reactions of hydroxylation, oxidation and reduction to 5 metabolites. The major metabolite, M5, is pharmacologically inactive. There are 2 minor metabolites, M1, possessing one-tenth the activity of torasemide, and M3, equal in activity to torasemide. Overall, torasemide appears to account for 80% of the total diuretic activity, while metabolites M1 and M3 account for 9% and 11%, respectively.
Torasemide has known human metabolites that include N-[(4-{[3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]imino}-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl]propane-2-carbamimidic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The average half-life of torasemide is 3.5 hours.
As mentioned above, torasemide is part of the loop diuretics and thus, it acts by reducing the oxygen demand in the medullary thick ascending loop of Henle by inhibiting the Na+/K+/Cl- pump on the luminal cell membrane surface. This action is obtained by the binding of torasemide to a chloride ion-binding site of the transport molecule. Torasemide is known to have an effect in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by inhibiting the downstream cascade after the activation of angiotensin II. This inhibition will produce a secondary effect marked by the reduction of the expression of aldosterone synthase, TGF-B1 and thromboxane A2 and a reduction on the aldosterone receptor binding.