


1. 1 N-(3'-4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl) Anthranilic Acid (n-5'), N(3',4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl) Anthranilic Acid (n-5')
2. 2-((3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl)amino)benzoic Acid
3. Mk-341
4. Mk341
5. N (3', 4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl) Anthranilic Acid (n-5')
6. N-(3',4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl)anthranilic Acid
7. Rizaben
8. Tranilast Hydrate
9. Tranilast Sodium Salt
1. 53902-12-8
2. Trans-tranilast
3. Rizaben
4. 70806-55-2
5. Tranilastum
6. Mk 341
7. N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)anthranilic Acid
8. Tranilast Trans-
9. Mk-341
10. Sb-252218
11. (e)-2-(3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylamido)benzoic Acid
12. Tranilast (sb 252218)
13. Hvf50smy6e
14. Nsc-758970
15. 2-((3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl)amino)benzoic Acid
16. Mls000028468
17. Chebi:77572
18. Ncgc00018185-05
19. Smr000058373
20. 2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]amino]benzoic Acid
21. 2-{[(2e)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]amino}benzoic Acid
22. (e)-2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]amino]benzoic Acid
23. Benzoic Acid, 2-((3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl)amino)-
24. Tranilastum [inn-latin]
25. 2-(3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylamido)benzoic Acid
26. Tranilast [usan:inn:jan]
27. 2-[[(e)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]amino]benzoic Acid
28. 2-[(2e)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enamido]benzoic Acid
29. Tranpro
30. Mfcd00864787
31. 2-({(2e)-3-[3,4-bis(methyloxy)phenyl]prop-2-enoyl}amino)benzoic Acid
32. Rizaben (tn)
33. N-(3',4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl)anthranilic Acid
34. Sr-01000003092
35. N-(3',4'-dimethoxycinnamoyl) Anthranilic Acid
36. Unii-hvf50smy6e
37. Benzoic Acid, 2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]amino]-
38. Anthranilic Acid, N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)-
39. Tranilast- Bio-x
40. Nu-3450
41. Tranilast [inn]
42. Tranilast [jan]
43. Tranilast [mi]
44. Sb 252218
45. Tranilast [usan]
46. Opera_id_1657
47. Dsstox_cid_3693
48. Tranilast [mart.]
49. T 0318
50. Tranilast [who-dd]
51. Dsstox_rid_77152
52. Dsstox_gsid_23693
53. Lopac0_001193
54. Schembl29875
55. Bspbio_003561
56. Zinc797
57. 53902-17-3
58. Mls000759509
59. Mls001065902
60. Mls001077269
61. Mls001424045
62. Mls002207030
63. Mls006010043
64. Spectrum1505333
65. Chembl415324
66. Gtpl6326
67. Tranilast (jp17/usan/inn)
68. Bdbm21613
69. Chebi:92320
70. Hms2051f05
71. Hms2089l07
72. Hms2094i21
73. Hms2230f18
74. Hms3263p07
75. Hms3412g17
76. Hms3648a16
77. Hms3676g17
78. Hms3713j04
79. Pharmakon1600-01505333
80. (2-phenylthiazol-5-yl)methylamine
81. Amy14167
82. Bcp06359
83. Bcp15888
84. Hy-b0195
85. Tox21_110836
86. Tox21_501193
87. Ac-940
88. Ccg-39992
89. Hsci1_000076
90. Nsc758970
91. S5871
92. Akos002841076
93. Tranilast, >=98% (hplc), Powder
94. Db07615
95. Ks-1193
96. Lp01193
97. Nc00171
98. Nsc 758970
99. Sdccgsbi-0051160.p004
100. Ncgc00018185-04
101. Ncgc00018185-06
102. Ncgc00018185-08
103. Ncgc00018185-09
104. Ncgc00018185-10
105. Ncgc00018185-20
106. Ncgc00018185-23
107. Ncgc00018185-26
108. Ncgc00021458-04
109. Ncgc00021458-05
110. Ncgc00021458-07
111. Ncgc00261878-01
112. Ac-35254
113. Bd164491
114. N-5'
115. Sb252218
116. Sbi-0051160.p003
117. Cas-53902-12-8
118. Eu-0101193
119. S1439
120. Sw197551-3
121. N-(3 ,4 -dimethoxycinnamoyl)anthranilic Acid
122. D02027
123. Ab00382987-18
124. Ab00382987-19
125. Ab00382987_21
126. 902t173
127. A829819
128. A923780
129. 2-(3,4-dimethoxy-trans-cinnamoylamino)benzoic Acid
130. Q-201849
131. Q2325594
132. Sr-01000003092-2
133. Sr-01000003092-4
134. Sr-01000003092-9
135. Brd-k17849083-001-02-2
136. Brd-k17849083-001-03-0
137. Brd-k19533706-001-01-9
138. Q27164069
139. Sr-01000003092-16
140. 2-[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-acryloylamino]-benzoic Acid
141. 2-[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoylamino]benzoic Acid
142. 2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxoprop-2-enyl]amino]benzoic Acid
143. 2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl]amino]benzoic Acid
144. Tranilast; 2-[[3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]amino] Benzoic Acid
145. D27
| Molecular Weight | 327.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
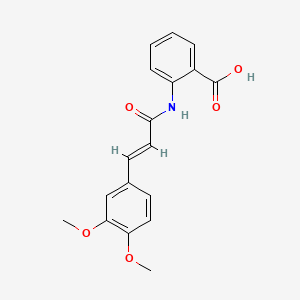
| Molecular Formula | C18H17NO5 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 327.11067264 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 327.11067264 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 84.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 464 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of bronchial asthma, keloid and hypertrophic scar, and allergic disorders such as asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
Anti-Allergic Agents
Agents that are used to treat allergic reactions. Most of these drugs act by preventing the release of inflammatory mediators or inhibiting the actions of released mediators on their target cells. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p475) (See all compounds classified as Anti-Allergic Agents.)
