


1. Jatrosom
2. Parnate
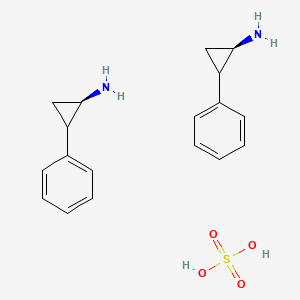
3. Sulfate, Tranylcypromine
4. Trans 2 Phenylcyclopropylamine
5. Trans-2-phenylcyclopropylamine
6. Transamine
7. Tranylcypromine
8. Tranylcypromine Sulfate
1. Tranylcypromine Sulfate
2. 13492-01-8
3. Tranylcypromine Sulfate (usp)
4. Chebi:9653
5. D00826
| Molecular Weight | 364.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H24N2O4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 364.14567842 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 364.14567842 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 197 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
A chemically heterogeneous group of drugs that have in common the ability to block oxidative deamination of naturally occurring monoamines. (From Gilman, et al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed, p414) (See all compounds classified as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors.)
