
1. Acid, All-trans-retinoic
2. Acid, Beta-all-trans-retinoic
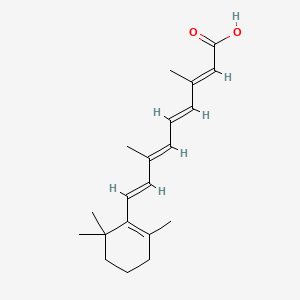
3. Acid, Retinoic
4. Acid, Trans-retinoic
5. Acid, Vitamin A
6. All Trans Retinoic Acid
7. All-trans-retinoic Acid
8. Beta All Trans Retinoic Acid
9. Beta-all-trans-retinoic Acid
10. Potassium Salt, Tretinoin
11. Retin A
12. Retin-a
13. Retinoic Acid
14. Salt, Tretinoin Potassium
15. Salt, Tretinoin Sodium
16. Salt, Tretinoin Zinc
17. Sodium Salt, Tretinoin
18. Trans Retinoic Acid
19. Trans-retinoic Acid
20. Tretinoin Potassium Salt
21. Tretinoin Sodium Salt
22. Tretinoin Zinc Salt
23. Vesanoid
24. Vitamin A Acid
25. Zinc Salt, Tretinoin
1. Retinoic Acid
2. 302-79-4
3. All-trans-retinoic Acid
4. Vitamin A Acid
5. Trans-retinoic Acid
6. Atra
7. Retin-a
8. Vesanoid
9. Aberel
10. Eudyna
11. Renova
12. Airol
13. All-trans Retinoic Acid
14. All-trans-vitamin A Acid
15. Dermairol
16. Aknoten
17. Aknefug
18. Cordes Vas
19. Epi-aberel
20. Tretinon
21. Tretin M
22. Retin A
23. Atralin
24. All-trans-vitamin A1 Acid
25. All-trans-tretinoin
26. Retionic Acid
27. All Trans Retinoic Acid
28. Vitamin A1 Acid, All-trans-
29. Retin-a Micro
30. Beta-retinoic Acid
31. All-(e)-retinoic Acid
32. Vitamin A Acid, All-trans-
33. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
34. Retinoate
35. Retinoic Acid, All-trans-
36. Alltrans-retinoic Acid
37. Nsc-122758
38. Retacnyl
39. Vesnaroid
40. Ro 1-5488
41. Tretinoin, All-trans-
42. All Trans-retinoic Acid
43. Stieva-a
44. Tretinoine
45. Solage
46. All-trans-beta-retinoic Acid
47. Effederm
48. .beta.-retinoic Acid
49. Kerlocal
50. Oristar Rna
51. Retinoic Acid, All Trans
52. Tretinoin/all-trans Retinoic Acid
53. Aberela [norway]
54. Avitoin [norway]
55. Effederm [france]
56. A-acido (argentina)
57. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
58. (all-e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
59. Mls000028588
60. B-retinoic Acid
61. Tretinoine [inn-french]
62. Tretinoinum [inn-latin]
63. At-ra
64. Tretinoina [inn-spanish]
65. Tretinoino [inn-spanish]
66. Chembl38
67. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
68. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all-e)-
69. Nsc122758
70. Atragen
71. Retinova
72. Smr000058245
73. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
74. Chebi:15367
75. 15-apo-beta-caroten-15-oic Acid
76. 5688utc01r
77. Tretinoin (tn)
78. Beta-ra
79. Acnavit [denmark]
80. Agn 100335
81. Rea
82. 9-cis-ra
83. Retin A (tn)
84. Ncgc00017280-10
85. Tretinoinum
86. Aberela
87. Acnavit
88. Avitoin
89. Betarretin
90. Tretinoina
91. Tretinoino
92. A-vitaminsyre
93. Mfcd00001551
94. All-trans-b-retinoic Acid
95. Dsstox_cid_1239
96. Cordes Vas [germany]
97. A-vitaminsyre [denmark]
98. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid (ecl)
99. Dsstox_rid_76031
100. Dsstox_gsid_21239
101. Trans-retinoate
102. Beta-retinoate
103. Tretinoine (french) (einecs)
104. Cis-retinoic Acid
105. Acide Retinoique (french) (dsl)
106. Refissa
107. Nexret
108. Vitamin A Acid, Trans-
109. Retisol-a
110. Acid A Vit (belgium, Netherlands)
111. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
112. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2e,4e,6e,8e-tetraenoic Acid
113. (11z)-retinoic Acid
114. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
115. [3h]retinoic Acid
116. Renova (tn)
117. Ccris 3294
118. Avita (tn)
119. Hsdb 2169
120. Sr-01000000239
121. Einecs 206-129-0
122. Nsc 122758
123. Brn 2057223
124. Retinoicacid
125. Tretinoin (jan/usp/inn)
126. Retinoic Acid, Cis-9,trans-13-
127. Tretinion
128. Tnp00194
129. Unii-5688utc01r
130. Bml2-e05
131. Dtxsid7021239
132. 1cbr
133. [3h]tretinoin
134. [all-e]-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
135. Tretinoin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
136. Cas-302-79-4
137. Prestwick_424
138. All-(e)-retinoate
139. Tretinoine (french)
140. Altreno
141. Retinoic Acid, Cis-
142. (5e)-retinoic Acid
143. [3h]vitamin A Acid
144. 1n4h
145. Cpd000058245
146. Retinoic Acid All Trans
147. Tretinoin [inn]
148. Tretinoin [jan]
149. 6-s-trans-retinoic Acid
150. Tretinoin [hsdb]
151. Tretinoin [usan]
152. Vitamin-a-sa Currencyure
153. Opera_id_1055
154. Prestwick2_000257
155. Prestwick3_000257
156. Spectrum5_001746
157. Spectrum5_001933
158. Tretinoin [vandf]
159. Acide Retinoique (french)
160. Vesanoid (tn) (roche)
161. Tretinoin - Retinoic Acid
162. Bmse000562
163. Tretinoin [mart.]
164. Upcmld-dp097
165. R 2625
166. Renova (0.02% Cream)
167. Retinoic Acid [mi]
168. Schembl3145
169. Tretinoin [usp-rs]
170. Tretinoin [who-dd]
171. (9z,13z)-retinoic Acid
172. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-2,4,6,8-all-trans-tetraenoic Acid
173. Altreno (0.05% Lotion)
174. Bidd:pxr0081
175. Lopac0_001061
176. Avita (0.025% Gel)
177. Bspbio_000074
178. Bspbio_001500
179. Retinoic Acid [inci]
180. Mls001076515
181. Mls002207234
182. Mls002222211
183. Mls002548861
184. Mls006010222
185. Bidd:gt0483
186. Spectrum1502016
187. 9-cis-retinoic Acid (9cra)
188. [3h]ra
189. Bpbio1_000082
190. Cid_444795
191. Gtpl2644
192. .beta.-all-trans-retinoic Acid
193. Tretinoin [orange Book]
194. Ziana Component Tretinoin
195. All-trans-retinoic Acid (atra)
196. Schembl19091395
197. Tretinoin [ep Monograph]
198. Bdbm31883
199. Hms502n05
200. Solage Component Tretinoin
201. Twyneo Component Tretinoin
202. Veltin Component Tretinoin
203. Tretinoin [usp Monograph]
204. Bcpp000036
205. Bdbm323588
206. Hms1361k22
207. Hms1568d16
208. Hms1791k22
209. Hms1921d14
210. Hms1989k22
211. Hms2089d20
212. Hms2092n11
213. Hms2095d16
214. Hms2236n03
215. Hms3259e11
216. Hms3263e04
217. Hms3402k22
218. Hms3411b09
219. Hms3675b09
220. Hms3712d16
221. Pharmakon1600-01502016
222. Retinoic Acid, All-trans- (8ci)
223. 124510-04-9
224. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2e,4e,6z,8e)-
225. Act00012
226. Bcp01405
227. Tretinoin Component Of Ziana
228. Tri-luma Component Tretinoin
229. Us10188615, At-ra
230. Tox21_110812
231. Tox21_202330
232. Tox21_300305
233. Tox21_501061
234. Tretinoin Component Of Solage
235. Tretinoin Component Of Twyneo
236. Tretinoin Component Of Veltin
237. All-trans Retinoic Acid (tretinoin)
238. Ccg-39912
239. Lmpr01090019
240. Nsc759631
241. S1653
242. Zinc12358651
243. Akos000280845
244. Tox21_110812_1
245. Ac-6824
246. Cs-1269
247. Db00755
248. Gs-3578
249. Lp01061
250. Nc00481
251. Nsc-759631
252. Sdccgsbi-0051031.p004
253. Tretinoin Component Of Tri-luma
254. Idi1_000903
255. Idi1_033970
256. Ncgc00017280-05
257. Ncgc00017280-06
258. Ncgc00017280-07
259. Ncgc00017280-08
260. Ncgc00017280-09
261. Ncgc00017280-12
262. Ncgc00017280-15
263. Ncgc00017280-16
264. Ncgc00017280-17
265. Ncgc00017280-18
266. Ncgc00017280-19
267. Ncgc00017280-20
268. Ncgc00017280-23
269. Ncgc00017280-38
270. Ncgc00021808-04
271. Ncgc00021808-05
272. Ncgc00021808-06
273. Ncgc00021808-07
274. Ncgc00021808-09
275. Ncgc00021808-11
276. Ncgc00021808-14
277. Ncgc00021808-15
278. Ncgc00254179-01
279. Ncgc00259879-01
280. Ncgc00261746-01
281. Bp-20401
282. Br164493
283. Hy-14649
284. Retinoic Acid, >=98% (hplc), Powder
285. Sbi-0051031.p003
286. Eu-0101061
287. Isotretinoin Impurity A [ep Impurity]
288. R0064
289. Sw203749-4
290. 02t794
291. C00777
292. D00094
293. Q29417
294. Ab00052318-15
295. Ab00052318-16
296. Ab00052318-17
297. Ab00052318_18
298. Ab00052318_19
299. A899883
300. L000833
301. Q-200610
302. Sr-01000000239-3
303. Sr-01000000239-4
304. Sr-01000000239-6
305. Sr-01000000239-7
306. Brd-k06926592-001-01-7
307. Brd-k71879491-001-15-0
308. Brd-k71879491-001-22-6
309. Sr-01000000239-12
310. Sr-01000000239-13
311. Sr-01000000239-14
312. Sr-01000000239-15
313. Wln: L6utj A1 B1u1y1&u2u1y1&u1vq C1 C1
314. Tretinoin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
315. Wln: L6utj A1 B1u1y1 & U2u1y1 & U1vq C1 C1
316. Tretinoin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
317. 3,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
318. Tretinoin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
319. (2e,4e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
320. (4e,6e,8e)-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
321. (all-e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate
322. 2,4,6,8-nonatetranoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-
323. 2,6,8-nonatetranoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-
324. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate
325. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2e,4e,6e,8e,-nonatetraenoic Acid
326. All-trans-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
327. 2,4, 6,8-nonatetranoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6, 6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2e, 4e, 6e, 8e)-
328. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)--, (all Trans)-
329. 2,4,6,8-nonatetranoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all Trans)-
330. 2,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all-e)-
331. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid-, (all Trans)-
332. 97950-17-9
| Molecular Weight | 300.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 567 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atralin |
| Drug Label | Atralin (tretinoin) Gel, 0.05% is a translucent to opaque, pale yellow gel containing 0.05% tretinoin, by weight for topical administration. Chemically, tretinoin is all-trans-retinoic acid, also known as (all-E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyc... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Dow Pharm |
| 2 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Renova |
| Drug Label | RENOVA (tretinoin cream) 0.02% contains the active ingredient tretinoin in a cream base. Tretinoin is a yellow- to light-orange crystalline powder having a characteristic floral odor. Tretinoin is soluble in dimethylsulfoxide, slightly soluble in p... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.02% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl |
| 3 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Retin-a |
| PubMed Health | Tretinoin |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Antineoplastic Agent, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | RETIN-A Gel, Cream and Liquid, containing tretinoin are used for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris. RETIN-A Gel contains tretinoin (retinoic acid, vitamin A acid) in either of two strengths, 0.025% or 0.01% by weight, in a gel vehicle of butylat... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Gel; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.1%; 0.025%; 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl; Valeant Bermuda |
| 4 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Retin-a micro |
| PubMed Health | Fluocinolone/Hydroquinone/Tretinoin (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid Combination, Dermatological Agent, Hypopigmentation Agent, Retinoid Combination |
| Drug Label | Retin-A Micro (tretinoin gel) microsphere, 0.1% and 0.04%, is a formulation containing 0.1% or 0.04%, by weight, tretinoin for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. This formulation uses patented methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.1%; 0.04% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl |
| 5 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tretinoin |
| PubMed Health | Tretinoin |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Antineoplastic Agent, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Tretinoin, USP is a retinoid that induces maturation of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells in culture. It is available in a 10 mg gelatin capsule for oral administration. Each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydro... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Capsule; Gel |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.1%; 0.025%; 0.0375%; 10mg; 0.01%; 0.04%; 0.075% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Anchen Pharms; Suneva Medcl; Spear Pharms; Barr Labs; Precision Dermat |
| 6 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tri-luma |
| Active Ingredient | tretinoin; Fluocinolone acetonide; hydroquinone |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 4%; 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Galderma Labs |
| 7 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atralin |
| Drug Label | Atralin (tretinoin) Gel, 0.05% is a translucent to opaque, pale yellow gel containing 0.05% tretinoin, by weight for topical administration. Chemically, tretinoin is all-trans-retinoic acid, also known as (all-E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyc... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Dow Pharm |
| 8 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Renova |
| Drug Label | RENOVA (tretinoin cream) 0.02% contains the active ingredient tretinoin in a cream base. Tretinoin is a yellow- to light-orange crystalline powder having a characteristic floral odor. Tretinoin is soluble in dimethylsulfoxide, slightly soluble in p... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.02% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl |
| 9 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Retin-a |
| PubMed Health | Tretinoin |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Antineoplastic Agent, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | RETIN-A Gel, Cream and Liquid, containing tretinoin are used for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris. RETIN-A Gel contains tretinoin (retinoic acid, vitamin A acid) in either of two strengths, 0.025% or 0.01% by weight, in a gel vehicle of butylat... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Gel; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.1%; 0.025%; 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl; Valeant Bermuda |
| 10 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Retin-a micro |
| PubMed Health | Fluocinolone/Hydroquinone/Tretinoin (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid Combination, Dermatological Agent, Hypopigmentation Agent, Retinoid Combination |
| Drug Label | Retin-A Micro (tretinoin gel) microsphere, 0.1% and 0.04%, is a formulation containing 0.1% or 0.04%, by weight, tretinoin for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. This formulation uses patented methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.1%; 0.04% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Intl |
| 11 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tretinoin |
| PubMed Health | Tretinoin |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Antineoplastic Agent, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Tretinoin, USP is a retinoid that induces maturation of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells in culture. It is available in a 10 mg gelatin capsule for oral administration. Each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydro... |
| Active Ingredient | Tretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Capsule; Gel |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.1%; 0.025%; 0.0375%; 10mg; 0.01%; 0.04%; 0.075% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Anchen Pharms; Suneva Medcl; Spear Pharms; Barr Labs; Precision Dermat |
| 12 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tri-luma |
| Active Ingredient | tretinoin; Fluocinolone acetonide; hydroquinone |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 4%; 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Galderma Labs |
Antineoplastic Agents Keratolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Tretinoin. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. trans-Retinoic acid is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Tretinoin gel and cream are indicated for topical application in the treatment of acne vulgaris. The safety and efficacy of the long-term use of this product in the treatment of other disorders have not been established. /Included in US product labeling; Tretinoin, topical/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Gel (Updated: January 3, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4889c7f8-37d0-4f1a-9829-bca107806586
Tretinoin is used topically as a 0.05 or 0.1% cream for palliative therapy to improve dermatologic changes (e.g., fine wrinkling, mottled hyperpigmentation, roughness) associated with photodamage. /NOT included in US product labeling; Tretinoin, topical/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for all-trans-Retinoic acid (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ Experienced Physician and Institution. Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) are at high risk in general and can have severe adverse reactions to tretinoin capsules. Tretinoin capsules should therefore be administered only to patients with APL under the strict supervision of a physician who is experienced in the management of patients with acute leukemia and in a facility with laboratory and supportive services sufficient to monitor drug tolerance and protect and maintain a patient compromised by drug toxicity, including respiratory compromise. Use of tretinoin capsules requires that the physician concludes that the possible benefit to the patient outweighs the following known adverse effects of the therapy. /Tretinoin, systemic/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
/BOXED WARNING/ Retinoic Acid-APL Syndrome. About 25% of patients with APL treated with tretinoin capsules have experienced a syndrome called the retinoic acid-APL (RA-APL) syndrome characterized by fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress, weight gain, radiographic pulmonary infiltrates, pleural and pericardial effusions, edema, and hepatic, renal, and multi-organ failure. This syndrome has occasionally been accompanied by impaired myocardial contractility and episodic hypotension. It has been observed with or without concomitant leukocytosis. Endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation have been required in some cases due to progressive hypoxemia, and several patients have expired with multi-organ failure. The syndrome generally occurs during the first month of treatment, with some cases reported following the first dose of tretinoin capsules. The management of the syndrome has not been defined rigorously, but high-dose steroids given at the first suspicion of the RA-APL syndrome appear to reduce morbidity and mortality. At the first signs suggestive of the syndrome (unexplained fever, dyspnea and/or weight gain, abnormal chest auscultatory findings or radiographic abnormalities), high-dose steroids (dexamethasone 10 mg intravenously administered every 12 hours for 3 days or until the resolution of symptoms) should be immediately initiated, irrespective of the leukocyte count. The majority of patients do not require termination of tretinoin capsules therapy during treatment of the RA-APL syndrome. However, in cases of moderate and severe RA-APL syndrome, temporary interruption of tretinoin capsules therapy should be considered. /Tretinoin, systemic/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
/BOXED WARNING/ During tretinoin capsules treatment about 40% of patients will develop rapidly evolving leukocytosis. Patients who present with high WBC at diagnosis (>5x10 9/L) have an increased risk of a further rapid increase in WBC counts. Rapidly evolving leukocytosis is associated with a higher risk of life-threatening complications. If signs and symptoms of the RA-APL syndrome are present together with leukocytosis, treatment with high-dose steroids should be initiated immediately. Some investigators routinely add chemotherapy to tretinoin capsules treatment in the case of patients presenting with a WBC count of >5x10 9/L or in the case of a rapid increase in WBC count for patients leukopenic at start of treatment, and have reported a lower incidence of the RA-APL syndrome. Consideration could be given to adding full-dose chemotherapy (including an anthracycline if not contraindicated) to the tretinoin capsules therapy on day 1 or 2 for patients presenting with a WBC count of >5x10 9/L, or immediately, for patients presenting with a WBC count of <5x10 9/L, if the WBC count reaches >/= 6x10(9)/L by day 5, or >/= 10x10(9)/L by day 10, or >/=15x10(9)/L by day 28. /Tretinoin, systemic/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
/BOXED WARNING/ Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category D. There is a high risk that a severely deformed infant will result if tretinoin capsules are administered during pregnancy. If, nonetheless, it is determined that tretinoin capsules represent the best available treatment for a pregnant woman or a woman of childbearing potential, it must be assured that the patient has received full information and warnings of the risk to the fetus if she were to be pregnant and of the risk of possible contraception failure and has been instructed in the need to use two reliable forms of contraception simultaneously during therapy and for 1 month following discontinuation of therapy, and has acknowledged her understanding of the need for using dual contraception, unless abstinence is the chosen method. Within 1 week prior to the institution of tretinoin capsules therapy, the patient should have blood or urine collected for a serum or urine pregnancy test with a sensitivity of at least 50 mIU/mL. When possible, tretinoin capsules therapy should be delayed until a negative result from this test is obtained. When a delay is not possible, the patient should be placed on two reliable forms of contraception. Pregnancy testing and contraception counseling should be repeated monthly throughout the period of tretinoin capsules treatment. /Tretinoin, systemic/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for all-trans-Retinoic acid (44 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the the induction of remission in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), French-American-British (FAB) classification M3 (including the M3 variant); For the topical treatment of acne vulgaris, flat warts and other skin conditions (psoriasis, ichthyosis congenita, icthyosis vulgaris, lamellar icthyosis, keratosis palmaris et plantaris, epidermolytic hyperkeratosis, senile comedones, senile keratosis, keratosis follicularis (Darier's disease), and basal cell carcinomas.); For palliative therapy to improve fine wrinkling, mottled hyperpigmentation, roughness associated with photodamage. Tretinoin is also indicated in combination with [benzoyl peroxide] for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients aged nine years and older.
FDA Label
Tretinoin, also known as all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), is a naturally occurring derivative of vitamin A (retinol). Retinoids such as tretinoin are important regulators of cell reproduction, proliferation, and differentiation and are used to treat acne and photodamaged skin and to manage keratinization disorders such as ichthyosis and keratosis follicularis. Tretinoin also represents the class of anticancer drugs called differentiating agents and is used in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).
Keratolytic Agents
Agents that soften, separate, and cause desquamation of the cornified epithelium or horny layer of skin. They are used to expose mycelia of infecting fungi or to treat corns, warts, and certain other skin diseases. (See all compounds classified as Keratolytic Agents.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
D10AD51
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10A - Anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AD - Retinoids for topical use in acne
D10AD01 - Tretinoin
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XF - Retinoids for cancer treatment
L01XF01 - Tretinoin
Absorption
Tretinoin applied topically is typically between 1-31% absorbed. When formulated with [benzoyl peroxide], the extent of absorption was examined after 14 days of once-daily application of 1.9 g of the combination product. On Day 14, at steady-state, the mean Cmax for tretinoin and the metabolites 4-keto 13-cis RA and 13-cis RA were 0.15-0.19, 0.27-0.34, and 0.13-0.28 ng/mL, depending on the patient age group. The corresponding ranges for the mean AUC0-24 were 0.63-2.06, 2.39-2.89, and 0.96-1.99 ng\*h/mL.
/MILK/ It is not known whether topically applied tretinoin is excreted in human milk.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
Studies with radiolabeled drug have demonstrated that after the oral administration of 2.75 and 50 mg doses of tretinoin, greater than 90% of the radioactivity was recovered in the urine and feces. Based upon data from 3 subjects, approximately 63% of radioactivity was recovered in the urine within 72 hours and 31% appeared in the feces within 6 days.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
A single 45 mg/sq m (approximately 80 mg) oral dose to APL /acute promyelocytic leukemia/ patients resulted in a mean +/- SD peak tretinoin concentration of 347 +/- 266 ng/mL. Time to reach peak concentration was between 1 and 2 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
The apparent volume of distribution of tretinoin has not been determined. Tretinoin is greater than 95% bound in plasma, predominately to albumin. Plasma protein binding remains constant over the concentration range of 10 to 500 ng/mL.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for all-trans-Retinoic acid (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic
Evidence suggests that tretinoin induces its own metabolism. In patients with APL receiving 45 mg/sq m tretinoin daily, urinary excretion of 4-oxo trans retinoic acid glucuronide increased approximately tenfold over the course of 2-6 weeks of continuous therapy, suggesting that increased metabolism of tretinoin may be the primary mechanism leading to the decreased plasma drug concentrations observed during continued administration. Possible mechanisms for the increased clearance of tretinoin with continuous daily dosing of the drug include induction of CYP enzymes or oxidative cofactors and increased expression of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins. Increasing the dosage of tretinoin to compensate for the apparent autoinduction has not been shown to increase therapeutic response. Reduced plasma retinoid concentrations have been associated with relapse and clinical resistance, and some investigators suggest that the clinical failure of tretinoin may be related to a lack of sustained effective concentrations of the drug during prolonged treatment.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1392
Tretinoin metabolites have been identified in plasma and urine. Cytochrome P450 enzymes have been implicated in the oxidative metabolism of tretinoin. Metabolites include 13- cis retinoic acid, 4-oxo trans retinoic acid, 4-oxo cis retinoic acid, and 4-oxo trans retinoic acid glucuronide. In APL /acute promyelocytic leukemia/ patients, daily administration of a 45 mg/SQ m dose of tretinoin resulted in an approximately tenfold increase in the urinary excretion of 4-oxo trans retinoic acid glucuronide after 2 to 6 weeks of continuous dosing, when compared to baseline values.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tretinoin Capsule (Updated: January 11, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9c4ae9d9-c2a0-4995-a27a-e3f0f0284db9
Ethanol fed rats showed enhanced microsomal retinoic acid metabolism (50%) accompanied by increased microsomal cytochrome P450 content (34%). The increased hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 dependent metabolism of retinoic acid after chronic ethanol consumption may contribute to the accelerated catabolism of retinoic acid in vivo.
PMID:6803674 Sato M et al; Arch Biochem Biophys 213 (2): 557-64 (1982)
Following ip administration of high doses of 15-(14)C- and 10,11-(3)H-labeled retinoic acid to rats, 3 major metabolites were isolated from feces in microgram amounts by column, thin-layer and high-pressure liquid chromatography. Mass spectrometry provided identification as all-trans-4-oxoretinoic acid, all-trans-5'-hydroxy-retinoic acid and 7-trans-9-cis-11-trans-13-trans-5'-hydroxyretinoic acid.
PMID:863728 Hanni R et al; HELV CHIM ACTA 60 (3): 881 (1977)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for all-trans-Retinoic acid (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Tretinoin has known human metabolites that include 18-Hydroxyretinoic acid, 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid, 5,6-Epoxy-retinoic acid, and All-trans-retinoyl glucuronide.
Tretinoin is a known human metabolite of retinal.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
0.5-2 hours
In patients with APL /acute promyelocytic leukemia/ receiving tretinoin orally, a terminal elimination half-life of 0.5-2 hours has been reported following initial dosing.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1392
Tretinoin binds to alpha, beta, and gamma retinoic acid receptors (RARs). RAR-alpha and RAR-beta have been associated with the development of acute promyelocytic leukemia and squamous cell cancers, respectively. RAR-gamma is associated with retinoid effects on mucocutaneous tissues and bone. Although the exact mechanism of action of tretinoin is unknown, current evidence suggests that the effectiveness of tretinoin in acne is due primarily to its ability to modify abnormal follicular keratinization. Comedones form in follicles with an excess of keratinized epithelial cells. Tretinoin promotes detachment of cornified cells and the enhanced shedding of corneocytes from the follicle. By increasing the mitotic activity of follicular epithelia, tretinoin also increases the turnover rate of thin, loosely-adherent corneocytes. Through these actions, the comedo contents are extruded and the formation of the microcomedo, the precursor lesion of acne vulgaris, is reduced. Tretinoin is not a cytolytic agent but instead induces cytodifferentiation and decreased proliferation of APL cells in culture and in vivo. When Tretinoin is given systemically to APL patients, tretinoin treatment produces an initial maturation of the primitive promyelocytes derived from the leukemic clone, followed by a repopulation of the bone marrow and peripheral blood by normal, polyclonal hematopoietic cells in patients achieving complete remission (CR). The exact mechanism of action of tretinoin in APL is unknown.
Although the precise mechanism(s) of action of tretinoin has not been fully elucidated, it is known that the drug is not a cytolytic agent. Tretinoin induces cellular differentiation and decreases the proliferation of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells. The PML/RAR-a fusion protein resulting from the chromosomal translocation appears to block myeloid differentiation at the promyelocyte stage, possibly by complexing and inactivating wild-type PML or by inhibiting the normal retinoic acid signaling pathway. In patients with APL who achieve a complete remission with tretinoin therapy, the drug causes an initial maturation of the primitive promyelocytes derived from the cellular leukemic clone followed by a repopulation of the bone marrow and peripheral blood by normal, polyclonal hematopoietic cells. Observations supporting cellular differentiation effects as a mechanism of tretinoin include the absence of bone marrow hypoplasia during induction, the appearance of immunophenotypically unique "intermediate cells" expressing both mature and immature cell surface antigens, and the presence of both Auer rods and the translocation in morphologically mature granulocytes until a late stage of induction. The mechanism by which the population of malignant cells is eliminated is not fully understood but appears to involve apoptosis (programmed cell death). Following induction therapy, the PML/RAR-a fusion protein can be detected in the majority of patients, suggesting that tretinoin alone does not eradicate the leukemic clone.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1391