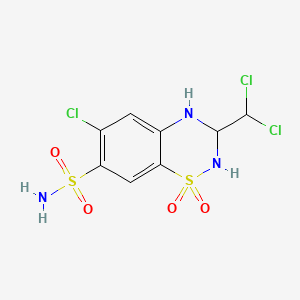

1. Aquazide
2. Naqua
3. Triazide
4. Trichloromethiazide
1. 133-67-5
2. Trichloromethiazide
3. Naqua
4. Metahydrin
5. Trichlormetazid
6. Achletin
7. Trichlormethiazid
8. Diu-hydrin
9. Chlopolidine
10. Hydrotrichlorothiazide
11. Aponorin
12. Cretonin
13. Diurazida
14. Diuroral
15. Fluitran
16. Gangesol
17. Intromene
18. Isestran
19. Schebitran
20. Triflumen
21. Diurese
22. Esmarin
23. Flutra
24. Nakva
25. Triclordiuride
26. Anistadin
27. Carvacron
28. Kubacron
29. Tachionin
30. Tolcasone
31. Eurinol
32. Triclormetiazide
33. Trichloromethiadiazide
34. Triclormetiazida
35. Ciba 7057-su
36. Trichlormethiazidum
37. 3-dichloromethylhydrochlorothiazide
38. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide
39. Nsc 61560
40. Brn 0629145
41. 3-dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
42. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
43. Trichlormas
44. Nsc-61560
45. 3-dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
46. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
47. Mls000028705
48. Chebi:9683
49. Q58c92tun0
50. Trichlordiuride
51. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
52. Salurin (wadel)
53. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
54. Naquasone
55. Smr000058712
56. Dsstox_cid_3699
57. Triclormetiazide [dcit]
58. Dsstox_rid_77154
59. Dsstox_gsid_23699
60. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
61. Triclormetiazide [italian]
62. Trichlormethiazidum [inn-latin]
63. Naqua (tn)
64. Triclormetiazida [inn-spanish]
65. Hsdb 3406
66. Trichloromethiazide, 6
67. Sr-01000000284
68. Einecs 205-118-8
69. Unii-q58c92tun0
70. Ncgc00016398-01
71. Trichlormethiazide [usp:inn:jan]
72. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
73. Cas-133-67-5
74. Prestwick_1020
75. 3-dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine1,1-dioxide
76. 6-chloro-3-dichloromethyl-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine1,1-dioxide
77. Spectrum_000520
78. Opera_id_1588
79. Prestwick0_000825
80. Prestwick1_000825
81. Prestwick2_000825
82. Prestwick3_000825
83. Spectrum2_000948
84. Spectrum3_001373
85. Spectrum4_000367
86. Spectrum5_001074
87. 3-(dichloromethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
88. 6-chloro-3-dichloromethyl-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
89. Chembl1054
90. Nciopen2_007750
91. Trichlormethiazide, >=98%
92. Schembl25492
93. Bspbio_000749
94. Bspbio_002926
95. Kbiogr_000833
96. Kbioss_001000
97. Trichlormethiazide (achletin)
98. (+-)-6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
99. Mls001076545
100. Divk1c_000366
101. Spectrum1500590
102. Spbio_000916
103. Spbio_002670
104. Trichlormethiazide [mi]
105. Bpbio1_000825
106. Gtpl7314
107. Trichlormethiazide [inn]
108. Trichlormethiazide [jan]
109. Dtxsid7023699
110. Bdbm26998
111. Hms501c08
112. Kbio1_000366
113. Kbio2_001000
114. Kbio2_003568
115. Kbio2_006136
116. Kbio3_002146
117. Trichlormethiazide [hsdb]
118. Trichlormethiazide [vandf]
119. Ninds_000366
120. Hms1570f11
121. Hms1921g13
122. Hms2090g08
123. Hms2092o19
124. Hms2097f11
125. Hms2235k21
126. Hms3371b09
127. Hms3655i17
128. Hms3714f11
129. Pharmakon1600-01500590
130. Trichlormethiazide [mart.]
131. Trichlormethiazide [usp-rs]
132. Trichlormethiazide [who-dd]
133. Hy-b0235
134. Nsc61560
135. Tox21_110421
136. Mfcd00057315
137. Nsc757368
138. S1667
139. Trichlormethiazide (jp17/usp/inn)
140. Akos024374993
141. Tox21_110421_1
142. Ccg-212834
143. Db01021
144. Nsc-757368
145. Trichlormethiazide [green Book]
146. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
147. Idi1_000366
148. Trichlormethiazide [orange Book]
149. Ncgc00018302-02
150. Ncgc00018302-03
151. Ncgc00018302-04
152. Ncgc00018302-07
153. Ncgc00018302-08
154. Ncgc00089756-02
155. Ncgc00089756-03
156. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide, (+-)-
157. As-56976
158. Trichlormethiazide [usp Monograph]
159. Sbi-0051544.p002
160. Naquival Component Trichlormethiazide
161. Wln: T66 Bswm Em Dhj Dygg Hg Iszw
162. Ab00052117
163. Ft-0746865
164. Sw197095-3
165. T1318
166. Metatensin Component Trichlormethiazide
167. Trichlormethiazide Metahydrin Naqua Trichlorex
168. C07767
169. C72338
170. D00658
171. Trichlormethiazide Component Of Naquival
172. Ab00052117-15
173. Ab00052117_16
174. Ab00052117_17
175. Trichlormethiazide Component Of Metatensin
176. A908323
177. Q-201860
178. Q2072745
179. Sr-01000000284-2
180. Sr-01000000284-4
181. Brd-a28940325-001-05-9
182. Brd-a28940325-001-15-8
183. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
184. Trichlormethiazide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
185. 3-(dichloromethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
186. 3-(dichloromethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
187. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide
188. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamid
189. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
190. (+/-)-6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
191. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide, (+/-)-
192. 2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide
193. 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1??,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 380.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H8Cl3N3O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 378.902181 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 378.902181 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 571 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
ORALLY EFFECTIVE & LONG-ACTING DIURETIC & ANTIHYPERTENSIVE OF THIAZIDE CLASS. ... ON MG BASIS, IT IS APPROX 250 TIMES MORE ACTIVE THAN CHLOROTHIAZIDE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
THIAZIDE DRUGS...USUALLY FIRST DRUG TO BE EMPLOYED IN TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION. SINCE THIAZIDES INDUCE ONLY LIMITED (10%) REDN IN BLOOD PRESSURE THEY ARE USEFUL EITHER IN MILD CASES OF HYPERTENSION OR AS ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY TO OTHER DRUGS. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE EFFECTIVE AS ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY IN EDEMA ASSOC WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS, & CORTICOSTEROID & ESTROGEN THERAPY, AS WELL AS EDEMA DUE TO VARIOUS FORMS OF RENAL DYSFUNCTION...& SEVERE EDEMA DUE TO PREGNANCY. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE...COULD BE GIVEN LESS FREQUENTLY /THAN MOST OF THIAZIDES/, SINCE...DURATION OF ACTION LONGER THAN 24 HR.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
PERIODIC SERUM ELECTROLYTE DETERMINATION SHOULD BE DONE ON ALL PATIENTS IN ORDER TO DETECT ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE SUCH AS HYPONATREMIA, HYPOCHLOREMIC ALKALOSIS, & HYPOKALEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, PATIENTS HYPERSENSITIVE TO THESE & OTHER SULFONAMIDE DRUGS, & IN OTHERWISE HEALTHY PREGNANT WOMEN WITH OR WITHOUT MILD EDEMA. ...SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE, SINCE THEY MAY PPT AZOTEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
PLASMA POTASSIUM CONCN SHOULD BE DETERMINED PERIODICALLY IN PATIENTS WHO RECEIVE THIAZIDE DIURETICS FOR EXTENDED PERIODS. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
Used in the treatment of oedema (including that associated with heart failure) and hypertension.
Trichloromethiazide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Trichloromethiazide has also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomer-ulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. Trichloromethiazide is also indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension. Like other thiazides, Trichloromethiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). They inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA06 - Trichlormethiazide
Trichlormethiazide is absorbed from the GI tract. Little information is available on the extent of absorption and the fate of trichlormethiazide in the body, although it is believed to be excreted principally as unchanged drug in urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2178
MOST CMPD ARE RAPIDLY EXCRETED WITHIN 3-6 HR. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
DIURESIS OCCURS WITHIN 2 HR, REACHES PEAK IN 6 HR, & LASTS MORE THAN 24 HR.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
THIAZIDES ARE ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT & OWE THEIR USEFULNESS LARGELY TO THEIR EFFECTIVENESS BY ORAL ROUTE. ABSORPTION IS RELATIVELY RAPID. MOST AGENTS SHOW DEMONSTRABLE DIURETIC EFFECT WITHIN HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
IN GENERAL, THIAZIDES WITH RELATIVELY LONG DURATIONS OF ACTION SHOW PROPORTIONATELY HIGH DEGREE OF BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEINS & ARE REABSORBED... BY RENAL TUBULES. ... DRUG PASSES READILY THROUGH PLACENTAL BARRIER TO FETUS. ALL THIAZIDES PROBABLY UNDERGO ACTIVE SECRETION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
Half-life is 2-7 hr. /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 703
Trichlormethiazide seemingly appears to inhibit the active reabsorption of chloride in the ascending loop of Henle. Additionally, it may also do the same for sodium. These actions subsequently alter electrolyte transfer in the proximal tubule. This results in excretion of sodium, chloride, and water and, hence, diuresis. As a diuretic, Trichloromethiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the Na-Cl cotransporter, resulting in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like Trichloromethiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of Trichloromethiazide is less well understood although it may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
...BENZOTHIADIAZIDES HAVE DIRECT EFFECT ON RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE...INDEPENDENT OF ANY EFFECT ON CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
THIAZIDES INHIBIT REABSORPTION OF SODIUM &...CHLORIDE IN DISTAL SEGMENT. ... AS CLASS...HAVE IMPORTANT ACTION ON EXCRETION OF POTASSIUM THAT RESULTS FROM INCR SECRETION OF CATION BY DISTAL TUBULE. ... GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE MAY BE REDUCED BY THIAZIDES, PARTICULARLY WITH IV ADMIN FOR EXPTL PURPOSES. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
...MAY DECR EXCRETION OF URIC ACID IN MAN, THUS INCR ITS CONCN IN PLASMA. HYPERURICEMIC EFFECT RESULTS PRIMARILY FROM INHIBITION OF TUBULAR SECRETION OF URATE. ... UNLIKE MOST OTHER NATRIURETIC AGENTS...DECR RENAL EXCRETION OF CALCIUM RELATIVE TO THAT OF SODIUM... /ENHANCE/ EXCRETION OF MAGNESIUM... /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
NATURE OF CHEM INTERACTION BETWEEN THIAZIDES & SPECIFIC RENAL RECEPTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR CHLORURETIC EFFECT IS NOT KNOWN; NO CRITICAL ENZYMATIC REACTIONS HAVE BEEN IDENTIFIED. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.