

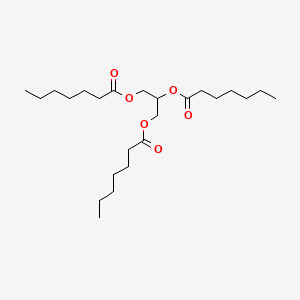

1. Glyceroltriheptanoate
2. Glyceryl Triheptanoate
1. 620-67-7
2. Propane-1,2,3-triyl Triheptanoate
3. Trienanthoin
4. Trioenanthoin
5. Glyceryl Triheptanoate
6. Glycerol Triheptanoate
7. Triheptanoic Glyceride
8. Heptanoin, Tri-
9. Ux007
10. Dermofeel Tc 7
11. Dojolvi
12. Propane-1,2,3-triyl Trisheptanoate
13. 2,3-di(heptanoyloxy)propyl Heptanoate
14. Dub Thg
15. Heptanoic Acid, 1,2,3-propanetriyl Ester
16. Dermofeel Tc-7
17. Ux-007
18. Radiamuls 2375
19. Lanol 37 T
20. Triheptanoin [usan]
21. 2p6o7cfw5k
22. 3-02-00-00769 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
23. Heptanoic Acid, 1,1',1''-(1,2,3-propanetriyl) Ester
24. Triheptanoin (usan)
25. Triheptylin
26. 1,2,3-propanetriyl Triheptanoate
27. Glyceroltriheptanoate
28. Brn 1807724
29. Lanol 37t
30. Einecs 210-647-2
31. Unii-2p6o7cfw5k
32. Trienantin
33. Dojolvi (tn)
34. Glycerol Trienanthate
35. Glyceryl Trienanthate
36. Triheptanoin [mi]
37. Triheptanoin [inn]
38. Ec 210-647-2
39. Triheptanoin [inci]
40. Schembl525618
41. Triheptanoin [who-dd]
42. Glycerol Trienanthate, >=94%
43. Chembl4297585
44. Gtpl11431
45. Dtxsid40862306
46. Propane-1,2,3-triyltriheptanoate
47. Triheptanoin [orange Book]
48. Zinc4521897
49. Ind106011
50. Mfcd00042910
51. Ux 007
52. 1r,2s-(-)-norephedrinehydrochloride
53. Cs-w013852
54. Db11677
55. Hy-w013136
56. Ind 106011
57. Ind-106011
58. Ind106011; Ux007
59. Ls-15081
60. Ft-0757070
61. D11465
62. A868568
63. Q414576
64. W-109093
| Molecular Weight | 428.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H44O6 |
| XLogP3 | 7.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 23 |
| Exact Mass | 428.31378912 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 428.31378912 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 78.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 421 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Triheptanoin is a medium chain triglyceride indicated to provide calories and fatty acids to treat long chain fatty acid oxidation disorders (lc-FAODs).
FDA Label
Triheptanoin is a source of medium chain fatty acids for patients with lc-FAODs. It has a moderate duration of action and a wide therapeutic window. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of feeding tube dysfunction and intestinal malabsorption due to pancreatic insufficiency.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX - Various alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX17 - Triheptanoin
Absorption
A single 0.3 g/kg dose of triheptanoin reaches a Cmax of 178.9 mol/L, with a Tmax 0.5 h, and an AUC of 336.5 mol\*h/L. A single 0.4 g/kg dose of triheptanoin reaches a Cmax of 259.1 mol/L, with a Tmax 0.8 h, and an AUC of 569.1 mol\*h/L.
Route of Elimination
Triheptanoin is minimally eliminated in the urine.
Clearance
A single dose of 0.3 g/kg results in a mean apparent clearance of 6.05 L/h/kg for heptanoate. A single dose of 0.4 g/kg results in a mean apparent clearance of 4.31 L/h/kg for heptanoate.
Triheptanoin is hydrolysed to heptanoate, which can be further metabolized to -hydroxypentanoate or -hydroxybutyrate.
Due to multiple peak concentrations of the heptanoate metabolite, the half life of triheptanoin could not be determined.
Triheptanoin is a source of heptanoate fatty acids, which can be metabolized without the enzymes of long chain fatty acid oxidation. In clinical trials, patients with lc-FAODs treated with triheptanoin experienced improvements in hypoglycemia, cardiomyopathy, and rhabdomyolysis.
