

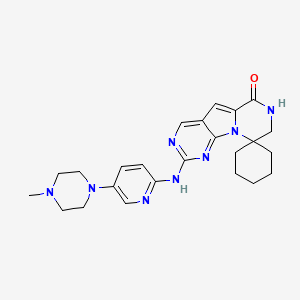

1. 2'-((5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'h-spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one
2. Cosela
3. Spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'(6'h)-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one, 7',8'-dihydro-2'-((5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-
1. 1374743-00-6
2. G1t28
3. Cosela
4. Trilaciclib [usan]
5. U6072do9xg
6. 2'-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'h-spiro[cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino[1',2':1,5]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin]-6'-one
7. Spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'(6'h)-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one, 7',8'-dihydro-2'-((5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-
8. 2'-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'h-spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one
9. G1t28(trilaciclib)
10. G1t28 Di-hcl
11. Trilaciclib [inn]
12. Trilaciclib (usan/inn)
13. Unii-u6072do9xg
14. Trilaciclib [who-dd]
15. Gtpl9626
16. Chembl3894860
17. Schembl10082028
18. Bdbm253928
19. Dtxsid601337125
20. Bcp25013
21. Ex-a4297
22. Nsc816987
23. Db15442
24. Nsc-816987
25. Sb19783
26. Ac-36547
27. Us9464092, T
28. Hy-101467
29. Cs-0021431
30. A17084
31. D11130
32. 2'-((5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'h-spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one
33. 2'-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'hspiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one
34. 2-[[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]spiro[7,8-dihydropyrazino[5,6]pyrrolo[1,2-d]pyrimidine-9,1'-cyclohexane]-6-one
35. 4-[[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]spiro[1,3,5,11-tetrazatricyclo[7.4.0.02,7]trideca-2,4,6,8-tetraene-13,1'-cyclohexane]-10-one
| Molecular Weight | 446.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H30N8O |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 446.25425761 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 446.25425761 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 91.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 707 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. It has a short duration of action of approximately 16 hours, and a narrow therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of injection site reactions, hypersensitivity, and interstitial lung disease.
V - Various
V03 - All other therapeutic products
V03A - All other therapeutic products
V03AF - Detoxifying agents for antineoplastic treatment
V03AF12 - Trilaciclib
Absorption
Cmax and AUC of trilaciclib increase proportionally with dose.
Route of Elimination
79.1% of a radiolabelled dose is recovered in the feces, 7% as the unchanged parent compound. 14% of a radiolabelled dose is recovered in the urine, 2% as the unchanged parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of trilaciclib at steady state is 1130 L.
Clearance
The clearance of trilaciclib is 158 L/h.
Data regarding the metabolism of trilaciclib are not readily available, however it is expected to be extensively metabolised.
The mean terminal half life of trilaciblib is approximately 14 h.
Trilaciclib is inhibits cyclin-dependant kinase 4 (CDK4) at a concentration of 1 nmol/L and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) at 4 nmol/L. Inhibition of CDK2, CDK5, and CDK7 is over 1000-fold less at these concentrations and inhibition of CDK9 is 50-fold less. CDK4 and CDK5 are expressed in hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells. They are capable of phosphorylating and inactivating the retinoblastoma protien; a tumor suppressor. When trilaciclib is given to patients with retinoblastoma protein-null small cell lung cancer, it does not interfere with the intended chemotherapy induced cytotoxicity of cancer cells. Inhibition of CDK4 and CDK5 leads to a reversible pause in the cell cycle in the G1 phase for approximately 16 hours. The temporary cell cycle arrest prevents chemotherapy induced DNA damage in healthy cells, reducing the activity of caspases 3 and 7, which reduces apoptosis of healthy cells. Other studies have shown inhibitors of CDK4 and CDK6 enhance T-cell activation, upregulating major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II, and stabilize programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). Together these activities increase T-cell activity, increase antigen presentation, and sensitize cells to immune checkpoint inhibitors.