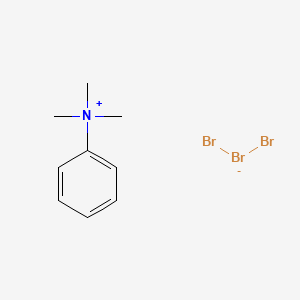
1. Hydroxide Of Phenyltrimethylammonium
2. Iodide Of Phenyltrimethylammonium
3. Phenyltrimethylammonium
4. Phenyltrimethylammonium Acetate
5. Phenyltrimethylammonium Benzenesulfonate
6. Phenyltrimethylammonium Bromide
7. Phenyltrimethylammonium Chloride
8. Phenyltrimethylammonium Tosylate
9. Phenyltrimethylammonium, Tri(methyl-3(2)h)-labeled Cpd
10. Trimethyl-d9-anilinium Hydroxide
11. Trimethylanilinium
12. Trimethylanilinium Iodide
13. Trimethylphenylammonium Hydroxide
14. Trimethylphenylammonium Iodide
15. X-tractelute
1. 4207-56-1
2. Mono(n,n,n-trimethylbenzenaminium) Tribromide
3. Trimethylphenylammonium Tribromide
4. Jacques Reagent
5. 9v4e7j2mss
6. Trimethylphenylammoniumtribromide
7. Nsc-87897
8. Nsc-138640
9. Nsc-173340
10. Ammonium, (tribromide)
11. Benzenaminium, N,n,n-trimethyl-, (tribromide)
12. Benzenaminium, N,n,n-trimethyl-, (tribromide) (1:1)
13. Benzenaminium,n,n-trimethyl-, (tribromide)
14. Einecs 224-127-8
15. Nsc 87897
16. Nsc 138640
17. Nsc 173340
18. Ammonium, Trimethylphenyl-, (tribromide)
19. Mono(n,n,n-trimethylbenzenaminium)tribromide
20. Unii-9v4e7j2mss
21. Schembl17007192
22. Nsc87897
23. Mfcd00011789
24. Nsc138640
25. Nsc173340
26. Trimethylphenylammonium Perbromide
27. Trimethylphenylammonium Tribromide, 97%
28. Phenyltrimethylammonium Bromide-perbromide
29. As-11338
30. P0928
31. A825752
| Molecular Weight | 375.93 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H14Br3N |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 374.86559 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 372.86764 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 95.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Indicators and Reagents
Substances used for the detection, identification, analysis, etc. of chemical, biological, or pathologic processes or conditions. Indicators are substances that change in physical appearance, e.g., color, at or approaching the endpoint of a chemical titration, e.g., on the passage between acidity and alkalinity. Reagents are substances used for the detection or determination of another substance by chemical or microscopical means, especially analysis. Types of reagents are precipitants, solvents, oxidizers, reducers, fluxes, and colorimetric reagents. (From Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed, p301, p499) (See all compounds classified as Indicators and Reagents.)
