

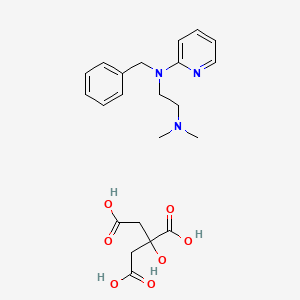

1. Azaron
2. Histantin
3. Pyribenzamine
4. Tripelennamine
5. Tripelennamine Citrate (1:1)
6. Tripelennamine Hydrochloride
7. Tripelennamine Maleate
8. Tripelennamine Maleate (1:1)
9. Tripelennamine Monohydrochloride
10. Vetibenzamin
1. 6138-56-3
2. Tripelennamine (citrate)
3. Nsc-757360
4. 2-(benzyl(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)pyridine Citrate (1:1)
5. 30oc46a3j9
6. 1,2-ethanediamine, N,n-dimethyl-n'-(phenylmethyl)-n'-2-pyridinyl-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
7. Ncgc00095775-01
8. Dsstox_cid_25989
9. Dsstox_rid_81276
10. Dsstox_gsid_45989
11. N'-benzyl-n,n-dimethyl-n'-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic Acid
12. Pyribenzamine Citrate
13. Cas-6138-56-3
14. Einecs 228-121-6
15. Tripelennamine Citrate [usp]
16. Unii-30oc46a3j9
17. Pbz (tn)
18. Schembl99166
19. Spectrum1500597
20. Chembl1200769
21. Dtxsid8045989
22. Hms501k16
23. Hms2092a14
24. Pharmakon1600-01500597
25. Tripelennamine Citrate [mi]
26. Tox21_111518
27. Ccg-39053
28. Hy-17428b
29. Nsc757360
30. Pyridine, 2-(benzyl(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)-, Citrate (1:1)
31. Tripelennamine Citrate [vandf]
32. Tox21_111518_1
33. Tripelennamine Citrate [mart.]
34. Nsc 757360
35. Tripelennamine Citrate [who-dd]
36. Ncgc00018125-05
37. Ncgc00095775-02
38. Tripelennamine Citrate [orange Book]
39. Cs-0030834
40. D06246
41. Sr-01000003013-4
42. Q27255968
43. 1,2-ethanediamine, N,n-dimethyl-n'-(phenylmethyl)-n'-2-pyridinyl-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1) (salt)
44. 1,2-ethanediamine, N1,n1-dimethyl-n2-(phenylmethyl)-n2-2-pyridinyl-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
45. N\'-benzyl-n,n-dimethyl-n\'-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine,2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 447.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H29N3O7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 447.20055027 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 447.20055027 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 152 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 464 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anti-Allergic Agents
Agents that are used to treat allergic reactions. Most of these drugs act by preventing the release of inflammatory mediators or inhibiting the actions of released mediators on their target cells. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p475) (See all compounds classified as Anti-Allergic Agents.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)