
1. Blue, Diamine
2. Blue, Niagara
3. Blue, Trypan
4. Diamine Blue
5. Niagara Blue
6. Visionblue
1. Direct Blue 14
2. 72-57-1
3. C.i. Direct Blue 14
4. Niagara Blue
5. Visionblue
6. Benzamine Blue
7. Dianil Blue
8. Diamine Blue
9. Benzo Blue
10. Congo Blue
11. Naphthylamine Blue
12. Diphenyl Blue
13. C.i. 23850
14. Niagara Blue 3b
15. Trypan-blue
16. Diamineblue
17. Dianilblau
18. Pyrotropblau
19. Parkibleu
20. Parkipan
21. Bleu Diamine
22. Chloramine Blue
23. Trypane Blue
24. Tripan Blue
25. Benzaminblau 3b
26. Chloramiblau 3b
27. Bleu Trypane N
28. Benzanil Blue R
29. Diaminblau 3b
30. Directblau 3b
31. Triazolblau 3bx
32. Benzoblau 3b
33. Congoblau 3b
34. Dianilblau H3g
35. Renolblau 3b
36. Bleu Directe 3b
37. Azidine Blue 3b
38. Diamine Blue 3b
39. Diazine Blue 3b
40. Pyrazol Blue 3b
41. Trypan Blue Bpc
42. Bleue Diretto 3b
43. Bencidal Blue 3b
44. Dianil Blue H3g
45. Diazol Blue 3b
46. Diphenyl Blue 3b
47. Direct Blue 3b
48. Direct Blue 3bx
49. Direct Blue D3b
50. Direct Blue H3g
51. Direct Blue M3b
52. Paramine Blue 3b
53. Azurro Diretto 3b
54. Benzo Blue 3b
55. Benzo Blue 3bs
56. Blue Emb
57. Naphthaminblau 3bx
58. Orion Blue 3b
59. Benzamine Blue 3b
60. Chlorazol Blue 3b
61. Cresotine Blue 3b
62. Amanil Sky Blue R
63. Benzanil Blue 3bn
64. Centraline Blue 3b
65. Chloramine Blue 3b
66. Hispamin Blue 3bx
67. I2zwo3ls3m
68. Diaphtamine Blue Th
69. Bleu Diazole N 3b
70. Blue 3b
71. Pontamine Blue 3bx
72. Brasilamina Blue 3b
73. Brasilazina Blue 3b
74. Directakol Blue 3bl
75. Naphthamine Blue 3bx
76. C.i. Direct Blue 14, Tetrasodium Salt
77. Chrome Leather Blue 3b
78. Trianol Direct Blue 3b
79. Sodium Ditolyl-diazobis-8-amino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulfonate
80. Chebi:78897
81. Trypanblau
82. Nsc-11247
83. Sodium Ditolyldisazobis-8-amino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulfonate
84. Sodium Ditolyldisazobis-8-amino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulphonate
85. Diaminine Blue
86. Vision Blue
87. Azidinblau 3b
88. Directblue14
89. Trypanblau [german]
90. Trypan (congo) Blue
91. Modr Trypanova [czech]
92. Ncgc00167554-01
93. Modr Prima 14 [czech]
94. Rcra Waste No. U236
95. Rcra Waste Number U236
96. Membraneblue
97. Ccris 616
98. Azul Tripano
99. Bleu Trypan
100. Modr Trypanova
101. Trypan Blue (commercial Grade)
102. Hsdb 2945
103. Nci C61289
104. Einecs 200-786-7
105. Modr Prima 14
106. Mfcd00003969
107. Nsc 11247
108. Trypan Blue Solution
109. Ai3-26698
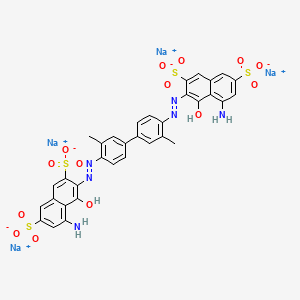
110. 2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid,3,3'-[(3,3'-dimethyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)bis(azo)]bis[5-amino-4-hydroxy-, Tetrasodium Salt
111. Unii-i2zwo3ls3m
112. Dsstox_cid_6268
113. Trypan Blue [mi]
114. Trypan Blue [hsdb]
115. Trypan Blue [iarc]
116. Chembl1640
117. Dsstox_rid_78083
118. Trypan Blue [vandf]
119. Dsstox_gsid_26268
120. Trypan Blue [mart.]
121. Trypan Blue [who-dd]
122. Chembl177987
123. Trypan Blue, Dye Content 60%
124. Dtxsid4026268
125. Trypan Blue [orange Book]
126. Amy22430
127. Tox21_112549
128. Akos015902434
129. Akos030228627
130. Cas-72-57-1
131. 2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diyl)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-, Tetrasodium Salt
132. As-83614
133. Tetrasodium 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diyl)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulphonate)
134. Ft-0690008
135. T0556
136. C19307
137. Sodium Ditolyl-diazobis-8-amino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulphonate
138. 2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diyl)bis(2,1-diazenediyl))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-, Sodium Salt (1:4)
139. 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diyl)bis(azo))bis-(5-amino-4-hydroxy)-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid Tetrasodium Salt
140. 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl-4,4'-biphenylene)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid) Tetrasodium Salt
141. Sodium 3,3'-(1e,1'e)-(3,3'-dimethylbiphenyl-4,4'-diyl)bis(diazene-2,1-diyl)bis(5-amino-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate)
142. Tetrasodium 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diyl)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulphonate
143. Tetrasodium 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl-4,4'-biphenylene)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonate)
144. Tetrasodium 3,3'-((3,3'-dimethyl-4,4'-biphenylene)bis(azo))bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulphonate)
145. Tetrasodium 3,3'-[(3,3'-dimethylbiphenyl-4,4'-diyl)didiazene-2,1-diyl]bis(5-amino-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate)
| Molecular Weight | 960.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C34H24N6Na4O14S4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 20 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 959.9824113 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 959.9824113 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 404 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 62 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1790 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
A diazo-naphthalene sulfonate that is widely used as a stain.
NLM; Medical Subject Headings (2010 MeSH) for trypan blue, RN 72-57-1. Available from, as of June 17, 2010: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2010/MB_cgi?term=72-57-1&rn=1
A therapeutic agent in the treatment of sleeping sickness. /Former use/
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V8 269 (1975)
MembraneBlue 0.15% is indicated for use as an aid in ophthalmic surgery by staining the epiretinal membranes during ophthalmic surgical vitrectomy procedures, facilitating removal of the tissue.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for MEMBRANEBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2010). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15868
/Experimental Therapy/ Trypan blue can be used to stain the superior oblique tendon for easy identification and delineation of it at its insertion, making the current surgical technique less difficult.
PMID:17274335 Saxena R et al; J Pediatr Opthalmol Strabusmus 44 (1): 45-6 (2007)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Trypan blue (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adverse reactions reported following use of VisionBlue include discoloration of high water content hydrogen intraocular lenses (see Contraindications) and inadvertent staining of the posterior lens capsule and vitreous face. Staining of the posterior lens capsule or staining of the vitreous face is generally self limited, lasting up to one week.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VISIONBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2006). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15897
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when trypan blue is administered to a nursing woman.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VISIONBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2006). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15897
VisionBlue is contraindicated when a non-hydrated (dry state), hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lens is planned to be inserted into the eye because the dye may be absorbed by the intraocular lens and stain theintraocular lens.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VISIONBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2006). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15897
It is recommended that after injection all excess VisionBlue be immediately removed from the eye by thorough irrigation of the anterior chamber.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VISIONBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2006). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15897
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VISIONBLUE (trypan blue) injection, solution (March 2006). Available from, as of June 28, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=15897
Coloring Agents
Chemicals and substances that impart color including soluble dyes and insoluble pigments. They are used in INKS; PAINTS; and as INDICATORS AND REAGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Coloring Agents.)
Trypan blue ... was observed in animals to pass from bloodstream through walls of vessels of iris & choroid, but not through walls of retinal vessels.
Grant, W.M. Toxicology of the Eye. 3rd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher, 1986., p. 959
Following sc or ip injections into mice or rats, trypan blue is rapidly absorbed & widely distributed throughout the body. Max serum concentrations are ... within 2 hr; it appears bound to serum proteins with ... rapid excretion in urine & uptake by the reticulo-endothelial system.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V8 272 (1973)
Trypan blue never reaches the rat embryo, but accumulates in maternal reticuloendothelial system and in the placenta.
Doull, J., C.D. Klaassen, and M. D. Amdur (eds.). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1980., p. 168
Experiments with ring-labelled radioactive trypan blue did not give evidence of any embryonic incorporation of the (14)C. The absence of teratogenic action after the initiation of chorio-allantoic placentation also indicated that yolk sac function was important in pathogenesis. The dye can be visualized in the cells of the visceral yolk sac.
Shepard, T.H. Catalog of Teratogenic Agents. 5th ed. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1986., p. 584
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Trypan blue (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/Trypan blue/ is reduced in vitro by a rat liver enzyme to ortho-tolidine & 2,8-diamino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulfonic acid.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V8 273 (1975)
Six azo dyes, including trypan blue, were reduced, N-acetylated, and N-conjugated. No N,N'-diacetylated metabolites were detected in rat urine.
KENNALLY JC ET AL; CARCINOGENESIS (LONDON) 3 (8): 947 (1982)
Azo dyes based on beta-diketone coupling components exist preferentially as the tautomeric hydrazones. A series of hydrazone dyes based on benzidine and benzidine congeners ... was prepared. The hydrazone dyes were resistant to enzymatic reduction by FMN supplemented hamster liver post-mitochondrial supernatant (S-9); under identical conditions, azo dyes such as trypan blue were rapidly reduced.
PMID:3957165 De France BF et al; Food Chem Toxicol 24 (2): 165-9 (1986)
Metabolism experiments were conducted with rats dosed with 9 azo dyes based on dimethyl-, dimethoxy-, or dichlorobenzidine to determine whether the free amine congeners, their monoacetyl or diacetyl metabolites, or alkaline hydrolyzable conjugates were excreted in the urine. 2-mg doses were administered and urine samples were collected at intervals up to 96 hr. Peak levels of metabolites were excreted either 0-12 or 12-24 hr after administration and, in 7 of 9 instances, no metabolites persisted in the urine after 48 hr. Minimum detectable levels of all metabolites were 12 ppb or less. All 9 dyes were converted to measurable levels of their benzidine-congener-based metabolites in rats.
PMID:6834800 Bowman MC et al; J Anal Toxicol 7 (l): 55-60 (1983)
The ability of rat liver microsomes from phenobarbitone pretreated animals to reduce the azo groups of amaranth, sunset yellow, congo red, trypan blue, chloramine sky blue FF and direct black 38 was measured in vitro. The dyes amaranth and sunset yellow acted as positive controls. Of the dyes derived from (the carcinogen) benzidine or its congeners, only direct black 38 was reduced to an appreciable extent; the rate of reduction was 10% of that for amaranth. The dyes were tested for mutagenicity in the Salmonella/microsome assay, the only active compound being direct black 38. Mutagenicity of this dye may be due in part to the mutagen 1,2,4-triaminobenzene. Mutagenic activity and azo-reduction of direct black 38 was independent of the presence of oxygen. Mammalian liver may play only a minor or negligible role in the azo-reduction of dyes derived from benzidine or its congeners.
Martin CN, Kennelly JC; Carcinogenesis (Lond) 2 (4): 307-12 (1981)
A dose of 50 mg per kg /of trypan blue/ appears to be the optimum teratogenic dose. A characteristic observation with trypan blue is that with treatment after the 9th day of gestation defects are rare. This fact has supported other evidence that the mechanism of action was dependent on disruption of yolk sac nutrition. ... Studies have produced evidence indicating a possible action of trypan blue on a nutritive function of the visceral yolk sac. The failure of the trypan blue to act directly upon the embryo is generally held ... .
Shepard, T.H. Catalog of Teratogenic Agents. 5th ed. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1986., p. 584
The absence of teratogenic action after the initiation of chorio-allantoic placentation also indicated that yolk sac function was important in pathogenesis. The dye can be visualized in the cells of the visceral yolk sac. ... . The protein-trypan blue complex is concentrated in lysosomes. Through disruption of the enzymatic digestive process in the yolk sac lysosome, trypan blue may interfere with normal embryonic nutritive processes.
Shepard, T.H. Catalog of Teratogenic Agents. 5th ed. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1986., p. 584