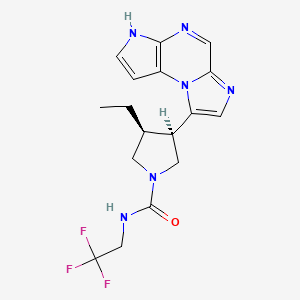

1. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide
2. Abt-494
3. Rinvoq
1. 1310726-60-3
2. Abt-494
3. Rinvoq
4. Upadacitinib Anhydrous
5. 4ra0kn46e0
6. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(1,5,7,10-tetrazatricyclo[7.3.0.02,6]dodeca-2(6),3,7,9,11-pentaen-12-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
7. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide
8. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo[1,2-a]pyrrolo[2,3-e]pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
9. 1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide, 3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-, (3s,4r)-
10. Mfcd30502663
11. Upadacitinib [usan]
12. Upadacitinib [mi]
13. Upadacitinib, Abt-494
14. Upadacitinib (usan/inn)
15. Upadacitinib [inn]
16. Upadacitinib [usan:inn]
17. Upadacitinib (abt-494)
18. Unii-4ra0kn46e0
19. Upadacitinib [who-dd]
20. Gtpl9246
21. Schembl9991056
22. Chembl3622821
23. Abt 494
24. Dtxsid901027919
25. Upadacitinib [orange Book]
26. Amy16528
27. Bcp19011
28. Ex-a1628
29. Bdbm50503287
30. S8162
31. Cs-6150
32. Db15091
33. Abbv-599 Component Upadacitinib
34. Abt494;abt-494;abt 494
35. Ncgc00588874-01
36. Ac-30326
37. As-56379
38. Hy-19569
39. Upadacitinib Component Of Abbv-599
40. J3.590.729g
41. C72237
42. D10994
43. Q27074125
44. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin- 8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
45. (3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2- Trifluoroethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
46. Rel-(-)-(3s,4r)-3-ethyl-4-(3h-imidazo(1,2-a)pyrrolo(2,3-e)pyrazin-8-yl)-n-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 380.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H19F3N6O |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 380.15724374 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 380.15724374 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 78.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 561 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Upadacitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis or active psoriatic arthritis in adult patients who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate or TNF blockers. For these indications, upadacitinib may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate. Upadacitinib is also indicated for the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis in adult patients who have an inadequate response to conventional therapy and for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in patients aged 12 years and older who are candidates for systemic therapy. Combining upadacitinib with other JAK inhibitors, biologic DMARDs, or other potent immunosuppressive agents is not recommended.
FDA Label
Rheumatoid arthritis
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis in adult patients who have responded inadequately to, or who are intolerant to one or more disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). RINVOQ may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Psoriatic arthritis
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis in adult patients who have responded inadequately to, or who are intolerant to one or more DMARDs. RINVOQ may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Axial spondyloarthritis
Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA)
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in adult patients with objective signs of inflammation as indicated by elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), who have responded inadequately to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS, radiographic axial spondyloarthritis )
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis in adult patients who have responded inadequately to conventional therapy.
Atopic dermatitis
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents 12 years and older who are candidates for systemic therapy.
Ulcerative colitis
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who have had an inadequate response, lost response or were intolerant to either conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Treatment of ulcerative colitis
Treatment of Crohn's disease
Treatment of vasculitides
Treatment of vasculitides
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
Treatment of chronic idiopathic arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis , psoriatic arthritis , spondyloarthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis )
Upadacitinib is a DMARD that works by inhibiting the Janus Kinases (JAKs), which are essential downstream cell signalling mediators of pro-inflammatory cytokines. It is believed that these pro-inflammatory cytokines play a role in many autoimmune inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In clinical trials, upadacitinib decreased the activity of pro-inflammatory interleukins, transiently increased the levels of lymphocytes, and insignificantly decreased the levels of immunoglobulins from the baseline.
Antirheumatic Agents
Drugs that are used to treat RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. (See all compounds classified as Antirheumatic Agents.)
Janus Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit JANUS KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Janus Kinase Inhibitors.)
L04AA
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AA - Selective immunosuppressants
L04AA44 - Upadacitinib
Absorption
Upadacitinib displays a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile over the therapeutic dose range. Following oral administration, the median time to reach Cmax (Tmax) ranges from 2 to 4 hours. The steady-state plasma concentrations of upadacitinib are reached within 4 days following multiple once-daily administrations, with minimal accumulation. Food intake has no clinically relevant effect on the AUC, Cmax, and Cmin of upadacitinib from the extended-release formulation.
Route of Elimination
Following administration of a single radio-labelled dose from the immediate-release formulation, approximately 53% of the total dose was excreted in the feces where 38% of the excreted dose was an unchanged parent drug. About 43% of the total dose was excreted in the urine, where 24% of that dose was in the unchanged parent drug form. Approximately 34% of the total dose of upadacitinib dose was excreted as metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of upadacitinib in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and a body weight of 74 kg is estimated to be 224 L following oral administration of an extended-release formula. In a pharmacokinetic study consisting of healthy volunteers receiving the extended-release formulation, the steady-state volume of distribution was 294 L. Upadacitinib partitions similarly between plasma and blood cellular components with a blood to plasma ratio of 1.0.
Clearance
The apparent oral clearance of upadacitinib in healthy volunteers receiving the extended-release formulation was 53.7 L/h.
Upadacitinib predominantly undergoes CYP3A4-mediated metabolism; however, upadacitinib is a nonsensitive substrate of CYP3A4. It is also metabolized by CYP2D6 to a lesser extent. In a human radio-labelled study, about 79% of the total plasma radioactivity accounted for the parent drug, and about 13% of the total plasma radioactivity accounted for the main metabolite produced from mono-oxidation, followed by glucuronidation. There are no known active metabolites of upadacitinib.
The mean terminal elimination half-life of upadacitinib ranged from 8 to 14 hours following administration of the extended-release formulation. In clinical trials, approximately 90% of upadacitinib in the systemic circulation was eliminated within 24 hours of dosing.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease that involves the interplay of several mediators, including the immune cells (mainly T- and B-lymphocytes) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as the tumour necrosis factor (TNF), transforming growth factor (TGF), and interleukin 6 (IL-6). The Janus Kinase (JAK) family plays an essential role in the normal physiological functions (such as erythropoiesis), but also the signalling of pro-inflammatory cytokines that are implicated in many immune-mediated diseases. The JAK family consists of four isoforms (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and Tyrosine Kinase 2) that each interacts with different cytokine receptors and uniquely associates with the intracellular domains of Type I/II cytokine receptors. JAK1 is primarily involved in the signalling transduction pathways of IL-6, IFN and the common -chain cytokines, including IL-2 and IL-15. IL-6 has been closely studied in particular, as it is a major cytokine involved in B- and T-cell differentiation and the acute phase response in inflammation. Upon interaction of cytokines with their cytokine receptors, the JAKs mediate the JAK-STAT signal transduction pathway in response to receptor activation. JAKs are tyrosine kinases that cause phosphorylation of several proteins, including cytokine receptors and JAKs themselves. Phosphorylation of JAKs promotes the phosphorylation and activation of the signalling molecules called STATs, leading to their nuclear translocation, binding to DNA promoters, and target gene transcription. JAK1-mediated signalling pathways ultimately promote pro-inflammatory events, such as increased proliferation and survival of immune cells, T cell differentiation, and macrophage activation. Upadacitinib is a selective JAK1 inhibitor that has a negligible effect on JAK3, leading to an improved drug safety profile. Upadacitinib blocks the cellular processes that contribute to the inflammatory conditions in rheumatoid arthritis. In human leukocytes cellular assays, upadacitinib inhibited JAK1/3-induced phosphorylation of STAT3/5 mediated by IL-6/7.