

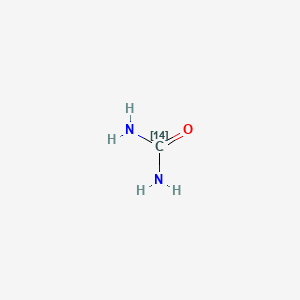

1. Urea-14c
2. 14c-urea
3. Urea C-14
4. Urea C 14
5. Carbon 14 Urea
6. Carbon-14 Urea
7. Urea ((sup 14)c)
8. Urea (14c)
9. 594-05-8
10. Urea 14 C
11. Diamino(114c)methanone
12. Wbz6m63tee
13. Pytest
14. Unii-wbz6m63tee
15. Urea C 14 [usp]
16. Pytest (tn)
17. Urea C14 (usp)
18. Chembl2096635
19. Urea 14 C [who-dd]
20. Urea, [14c]
21. Chebi:134711
22. Dtxsid701026303
23. Urea C 14 [usp Impurity]
24. Urea, C-14 [orange Book]
25. Db09513
26. D10496
27. Q27098010
| Molecular Weight | 62.048 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CH4N2O |
| XLogP3 | -1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 62.03560474 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 62.03560474 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 29 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 1 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pytest |
| PubMed Health | 14C-Urea (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Diagnostic Agent, Helicobactor Pylori, Breath Test |
| Active Ingredient | Urea, c-14 |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1uci |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Avent |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pytest |
| PubMed Health | 14C-Urea (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Diagnostic Agent, Helicobactor Pylori, Breath Test |
| Active Ingredient | Urea, c-14 |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1uci |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Avent |
14C-urea is intended for use in the detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in the human stomach. The test utilizes a liquid scintillation counter for the measurement of 14CO2 in breath samples.
FDA Label
14C-urea that is not hydrolyzed by H. pylori is excreted in the urine with a half-life of approximately 12 hours. About 10% of the 14C remains in the body at 72 hours and is gradually excreted with a biological half-life of 40 days.
The urease enzyme is not present in mammalian cells, so the presence of urease in the stomach is evidence that bacteria are present. The presence of urease is not specific for H. pylori, but other bacteria are not usually found in the stomach. To detect H. pylori, urea labeled with 14C is swallowed by the patient. If gastric urease from H. pylori is present, urea is split to form CO2 and NH3 at the interface between the gastric epithelium and lumen and 14CO2 is absorbed into the blood and exhaled in the breath. Following ingestion of the capsule by a patient with H. pylori, 14CO2 excretion in the breath peaks between 10 and 15 minutes and declines thereafter with a biological half-life of about 15 minutes. Therefore, the detection of isotope-labelled carbon dioxide in exhaled breath indicates that urease is present in the stomach, and hence that H. pylori bacteria are present.
