
1. Basodexan
2. Carbamide
3. Carmol
1. Carbamide
2. 57-13-6
3. Carbonyldiamide
4. Isourea
5. Ureophil
6. Carbonyldiamine
7. Ureaphil
8. Carbamimidic Acid
9. Pseudourea
10. Urevert
11. Alphadrate
12. Aquadrate
13. Calmurid
14. Carbaderm
15. Keratinamin
16. Carbonyl Diamide
17. Pastaron
18. Urepearl
19. Carbamide Resin
20. Ultra Mide
21. Varioform Ii
22. Aqua Care
23. Prespersion, 75 Urea
24. B-i-k
25. Basodexan
26. Carmol
27. Harnstoff
28. Mocovina
29. Nutraplus
30. Supercel 3000
31. Aqua Care Hp
32. Ureacin-20
33. Ureacin-10 Lotion
34. Ureacin-40 Creme
35. Onychomal
36. Panafil
37. Polyurea
38. Hyanit
39. Caswell No. 902
40. Carbonyl Diamine
41. Nci-c02119
42. Ccris 989
43. Aminoketone
44. Aquacare
45. Hsdb 163
46. Carbamimic Acid
47. Bubber Shet
48. Elaqua Xx
49. Keratinamin Kowa
50. Nsc 34375
51. Benural 70
52. Urea Ammonium Nitrate Solution
53. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 085702
54. Ur
55. Ai3-01202
56. Carbamide;carbonyldiamide
57. Mfcd00008022
58. Nsc-34375
59. Azodicarboxylic Acid-diamide
60. Ins No.927a
61. E927b
62. (nh2)2co
63. Ins-927a
64. 37955-36-5
65. Helicosol
66. Chebi:16199
67. Urea Solution
68. E-927a
69. 8w8t17847w
70. 4744-36-9
71. Ncgc00090892-01
72. Dsstox_cid_1426
73. Dsstox_rid_76155
74. Mocovina [czech]
75. Dsstox_gsid_21426
76. Ure
77. Harnstoff [german]
78. Urea [jan]
79. Ureum
80. Antisepsis Bolus
81. Sterile Urea
82. Cas-57-13-6
83. Urea [usp:jan]
84. Urea, Acs
85. Einecs 200-315-5
86. Uree
87. Isoharnstoff
88. Cerovel
89. Karbamid
90. Urepeal
91. Uroderm
92. Amino Ketone
93. Amino-ketone
94. Urea Perhydrate
95. Pastaron Soft
96. Urea, Ultrapure
97. E-cardamoni
98. Aquacare Hp
99. Unii-8w8t17847w
100. Urepeal L
101. Carbamide Solution
102. Urea, Homopolymer
103. Beta-i-k
104. Pastaron 10
105. Pastaron 20
106. Pastaron (tn)
107. Pastaron 20 Soft
108. Carbonamidimidic Acid
109. Carmol 40
110. Cerovel (salt/mix)
111. Panafil (salt/mix)
112. Rubinol St 010
113. Urea, P.a.
114. Optigen 1200
115. Urea, 2m
116. Urea,(s)
117. Spectrum_000672
118. Urea [vandf]
119. Wln: Zvz
120. Carbamimidic Acid (van)
121. Spectrum2_001192
122. Spectrum3_001791
123. Spectrum4_001168
124. Spectrum5_001862
125. Urea (jp17/usp)
126. Urea, Analytical Standard
127. Urea, For Electrophoresis
128. Urea [hpus]
129. Urea [hsdb]
130. Urea [inci]
131. Urea (8ci,9ci)
132. Urea [fcc]
133. Urea [usp-rs]
134. Urea [who-dd]
135. Eucerin 10% Urea Lotion
136. Chembl985
137. Urea [ii]
138. Urea [mart.]
139. Urea [mi]
140. Ec 200-315-5
141. Urea [orange Book]
142. H2n-co-nh2
143. H2nc(o)nh2
144. Urea [ep Monograph]
145. Urea [usp Impurity]
146. Urea A.c.s. Reagent Grade
147. H2n-c(oh)=nh
148. Bspbio_003341
149. Kbiogr_001775
150. Kbioss_001152
151. U-cort Component Urea
152. Urea [usp Monograph]
153. Urea, Puriss., 99.5%
154. Mls001076688
155. Divk1c_000086
156. H2n-c(=nh)-oh
157. Ho-c(=nh)-nh2
158. Spectrum1500604
159. Urea, Ar, >=99%
160. Urea, Lr, >=99%
161. Spbio_001263
162. Alphaderm Component Urea
163. Gtpl4539
164. Carmol Hc Component Urea
165. Dtxsid4021426
166. Urea Component Of U-cort
167. Urea, >=99.0%
168. Urea, Molecular Biology Reagent
169. Bdbm24961
170. Chebi:48376
171. Hms500e08
172. Kbio1_000086
173. Kbio2_001152
174. Kbio2_003720
175. Kbio2_006288
176. Kbio3_002843
177. Calmurid Hc Component Urea
178. Urea 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
179. Ninds_000086
180. Hms1921i17
181. Hms2092c08
182. Hms2232p21
183. Pharmakon1600-01500604
184. Urea Component Of Alphaderm
185. Component Of Artra Ashy Skin Cream
186. Urea Component Of Carmol Hc
187. Amy37159
188. Bcp30439
189. Cs-b1800
190. Hy-y0271
191. Nsc34375
192. Str00449
193. Urea, Tested According To Ph.eur.
194. Zinc8214514
195. Tox21_111036
196. Tox21_202158
197. Tox21_300035
198. C0165
199. Ccg-40265
200. Nsc757375
201. S3687
202. Stl194286
203. Urea Component Of Calmurid Hc
204. Urea, Reagentplus(r), >=99.5%
205. Akos009031424
206. Urea, Nist(r) Srm(r) 2141
207. Urea, Saj First Grade, >=98.0%
208. Db03904
209. Nsc-757375
210. Urea, Jis Special Grade, >=99.0%
211. Urea, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
212. Urea, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
213. Idi1_000086
214. Urea Solution, 40 % (w/v) In H2o
215. Basodexan Pound>>carmol Pound>>carbamide
216. Ncgc00090892-02
217. Ncgc00090892-03
218. Ncgc00090892-04
219. Ncgc00090892-05
220. Ncgc00090892-06
221. Ncgc00254181-01
222. Ncgc00259707-01
223. Urea Solution, Bioultra, ~8 M In H2o
224. Smr000499585
225. Urea, Acs Reagent, 99.0-100.5%
226. 4,4-(3-oxapentanediyldioxy)dibenzaldehyde
227. Allantoin Impurity B [ep Impurity]
228. Sbi-0051552.p002
229. Urea, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
230. B7781
231. Fluorouracil Impurity G [ep Impurity]
232. Ft-0645129
233. Ft-0675737
234. Ft-0675738
235. U0073
236. U0077
237. Urea, Reagentplus(r), >=99.5%, Pellets
238. Urea Solution, For Microbiology, 40% In H2o
239. C00086
240. Component Of Artra Ashy Skin Cream (salt/mix)
241. D00023
242. D70446
243. M02656
244. Q48318
245. Urea, P.a., Acs Reagent, 99.0-100.5%
246. Ab00052123_05
247. Sr-01000762961
248. Urea, Nist(r) Srm(r) 912a, Clinical Standard
249. Sr-01000762961-2
250. Urea, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
251. Urea, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
252. F0001-1490
253. Urea, Bioultra, For Molecular Biology, >=99.5% (t)
254. Urea, Bioxtra, Ph 7.5-9.5 (20 C, 5 M In H2o)
255. Urea, Nist Srm 2152, Combustion Calorimetric Standard
256. Z230747540
257. Urea, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
258. 6e4eb293-4363-4d38-bf3b-1397372c31e5
259. Urea, 8 M (after Reconstitution With 16 Ml High Purity Water)
260. Urea, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Ph. Eur., >=99.5%
261. Urea, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
262. Urea, Powder, Bioreagent, For Molecular Biology, Suitable For Cell Culture
263. Urea, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Usp, 99.0-100.5%, 99.0-101.0% (calc. On Dry Substance)
| Molecular Weight | 60.056 g/mol |
|---|---|
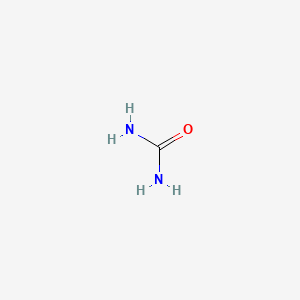
| Molecular Formula | CH4N2O |
| XLogP3 | -1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 60.032362755 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 60.032362755 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 29 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Dermatologic Agents; Diuretics, Osmotic
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
UREA IS /USED LESS COMMONLY THAN OTHER OSMOTIC AGENTS/ FOR THE SHORT-TERM REDUCTION OF INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE & VITREOUS VOL ... IN ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA .. PRIOR TO SURGERY ... IN CHRONIC GLAUCOMA ... PRE- AND POSTOPERATIVE TREATMENT.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 1825
DOSE--USUAL, IV INFUSION, 100 MG TO 1 G/KG DAILY, AS 30% SOLN IN DEXTROSE INJECTION @ RATE NOT EXCEEDING 4 ML/MIN.
GENNARO. REMINGTON'S PHARM SCI 17TH ED 1985 p 935
USED TOPICALLY IN THE TREATMENT OF PSORIASIS, ICHTHYOSIS, ATOPIC DERMATITIS, AND OTHER DRY, SCALY CONDITIONS.
GENNARO. REMINGTON'S PHARM SCI 17TH ED 1985 p 785
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for UREA (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
UREA SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PATIENTS WITH SEVERELY IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 936
UREA IS OFTEN RECONSTITUTED WITH INVERT SUGAR SOLN. INVERT SUGAR CONTAINS FRUCTOSE, WHICH CAN CAUSE SEVERE REACTION (HYPOGLYCEMIA, NAUSEA, VOMITING, TREMORS, COMA, & CONVULSIONS) IN PATIENTS WITH HEREDITARY FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE (ALDOLASE DEFICIENCY).
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 936
In general osmotic diuretics are contraindicated in patients who are anuric due to severe renal disease or who are unresponsive to test doses of the drugs. Urea may cause thrombosis or pain if extravasation occurs, and it should not be admin to patients with impaired liver function because of the risk of elevation of blood ammonia levels. Both mannitol and urea are contraindicated in patients with active cranial bleeding.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 696
In ruminants unaccustomed to urea, ingestion of 0.3-0.5 g urea/kg may be toxic ... The toxic dose of urea in (presumably unaccustomed) cattle is 0.45 g/kg (50 g total dose) but that animals can ingest more urea than this if the dose is increased gradually.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 1029
As a humectant, urea draws water into the striatum corneum.
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05B - I.v. solutions
B05BC - Solutions producing osmotic diuresis
B05BC02 - Carbamide
D - Dermatologicals
D02 - Emollients and protectives
D02A - Emollients and protectives
D02AE - Carbamide products
D02AE01 - Carbamide
SOME SMALL, WATER SOL, BUT NONIONIZABLE COMPD SUCH AS UREA READILY TRAVERSE MAMMALIAN MEMBRANES, PROBABLY ALONG WITH WATER, BY WAY OF THE PORES. THIS FILTRATION PROCESS IS PARTICULARLY RAPID BETWEEN CAPILLARIES & EXTRACELLULAR FLUID.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology Volume 1. General Principles. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 127
... UREA ... PENETRATES OTHER CELLS RAPIDLY, ENTERS THE BRAIN ONLY VERY SLOWLY ...
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 51
... DISTRIBUTED APPROX IN TOTAL BODY WATER ... HAVE BEEN USED FOR MEASUREMENT OF TOTAL BODY WATER.
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 53
EXCRETION OF UREA DURING SWEATING IN MAN: 1.84 SWEAT/PLASMA RATIO WITH PKA @ 13.8. /FROM TABLE/
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 143
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for UREA (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... The primary mechanism of ammonia toxicosis appears to be inhibition of the citric acid cycle. There is an increase in anaerobic glycolysis, blood glucose, and blood lactate ... . Acidosis is manifested. The exact means by which ammonia blocks the citric acid cycle is not known. It is postulated that ammonia saturation of the glutamine-synthesizing system causes a backing-up in the citrate cycle, a decrease in its intermediates, and a decrease in energy production and cellular respiration, which leads to convulsions ... . The decrease of citrate cycle intermediates is postulated to result from reamination of pyruvic, ketoglutaric, and oxaloacetic acids.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 1031