

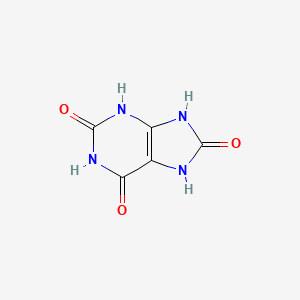

1. 2,6,8-trihydroxypurine
2. Acid Urate, Ammonium
3. Acid Urate, Sodium
4. Acid, Uric
5. Ammonium Acid Urate
6. Monohydrate, Monosodium Urate
7. Monohydrate, Sodium Urate
8. Monosodium Urate
9. Monosodium Urate Monohydrate
10. Potassium Urate
11. Sodium Acid Urate
12. Sodium Acid Urate Monohydrate
13. Sodium Urate
14. Sodium Urate Monohydrate
15. Trioxopurine
16. Urate
17. Urate Monohydrate, Monosodium
18. Urate Monohydrate, Sodium
19. Urate, Ammonium Acid
20. Urate, Monosodium
21. Urate, Potassium
22. Urate, Sodium
23. Urate, Sodium Acid
1. 69-93-2
2. Urate
3. Lithic Acid
4. 2,6,8-trioxypurine
5. 2,6,8-trihydroxypurine
6. 8-hydroxyxanthine
7. 7,9-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6,8(3h)-trione
8. 2,6,8-trioxopurine
9. 1h-purine-2,6,8-triol
10. 1h-purine-2,6,8(3h)-trione, 7,9-dihydro-
11. Purine-2,6,8(1h,3h,9h)-trione
12. 7,9-dihydro-3h-purine-2,6,8-trione
13. Uricum Acidum
14. Ai3-15432
15. 2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-1h-purine-2,6,8-trione
16. Nsc 3975
17. 1h-purine-2,6,8(3h,7h,9h)-trione
18. Nsc-3975
19. Mfcd00005712
20. Idelalisib Metabolite M54
21. Chembl792
22. 9h-purine-2,6,8-triol
23. Chebi:17775
24. 268b43mj25
25. 2,6-dihydroxy-7,9-dihydropurin-8-one
26. Ncgc00181032-01
27. 8-hydroxy-3,9-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
28. 6,8-dioxo-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-1h-purin-2-olate
29. Trioxopurine
30. Urc
31. Einecs 200-720-7
32. Lithate
33. Hypoxanthinediol
34. Uric-acid
35. Unii-268b43mj25
36. 2,8-trioxopurine
37. 2,8-trioxypurine
38. 8hx
39. Uric Acid (8ci)
40. 2,8-trihydroxypurine
41. 1l5s
42. 2,6,8-trihydroxypurin
43. Purine-2,6,8-triol
44. 1h-purine-2,8-triol
45. Uric Acid, 99.0%
46. Uric Acid [mi]
47. Uric Acid [inci]
48. Bmse000126
49. Schembl7933
50. 7h-purine-2,6,8-triol
51. Dsstox_cid_22508
52. Dsstox_rid_80044
53. Dsstox_gsid_42508
54. Uricum Acidum [hpus]
55. (s)-3-aminoquinuclidine Hcl
56. Gtpl4731
57. Dtxsid3042508
58. Schembl15777793
59. Schembl17081907
60. Chebi:46811
61. Chebi:46814
62. Chebi:46817
63. Chebi:46823
64. Chebi:62589
65. Nsc3975
66. Uric Acid, >=99%, Crystalline
67. Hms3604n17
68. Amy23430
69. Bcp28980
70. Hy-b2130
71. Purine-2,8(1h,3h,9h)-trione
72. Zinc2041003
73. Tox21_113563
74. Bdbm50325824
75. S3955
76. Stl185577
77. Akos000118731
78. Purine-3,6,8(1h,3h,9h)-trione
79. Ccg-339700
80. Db08844
81. Uric Acid, Nist(r) Srm(r) 913b
82. Cas-69-93-2
83. Purine-2,6,8-(1h,3h,9h)-trione
84. Uric Acid, Bioxtra, >=99% (hplc)
85. As-56119
86. Sy057305
87. 6-hydroxy-1h-purine-2,8(7h,9h)-dione
88. Db-055359
89. 2,6,8-trioxypurine;2,6,8-trihydroxypurine
90. 2,6-dihydroxy-7,9-dihydro-8h-purin-8-one
91. Cs-0020287
92. Ft-0631301
93. U0018
94. 1h-purine-2,8(3h)-trione, 7,9-dihydro-
95. 7,9-dihydro-3h-purine-2,6,8-trione(urate)
96. C00366
97. U-6050
98. 1h-purine-2,6,8-triol 2,6,8-trihydroxypurine
99. 7,9-dihydro-3h-purine-2,6,8-trione(uric Acid)
100. A866713
101. Q105522
102. Sr-01000945208
103. Sr-01000945208-1
104. 565ff3af-8afa-4ee9-9fc4-6b119784a5bb
105. 1h-purine-2,6,8(3h)-trione, 7,9-dihydro- (9ci)
106. Z1318255135
| Molecular Weight | 168.11 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | -1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 168.02834000 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 168.02834000 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 99.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 332 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
At present (August 2013), there is no approved indication for uric acid. The potential therapeutic use for uric acid is as an adjunct in acute ischemic stroke.
Uric acid is a strong reducing agent (donates electrons) and an antioxidant. Normally in humans, one of the main antioxidants in plasma is uric acid. Several animal studies have found that animals given exogenous uric acid within 3 hours after a stroke had decreased infarct volume, improved neurologic function, and diminished inflammatory responses providing evidence for the neuroprotective effects of uric acid. In some early human studies, uric acid has so far shown similar neuroprotective effects, in both the cortex and subcortex areas, due to its antioxidant effects such as decreased lipid peroxidation, and there appears to be no significant toxicities.
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Route of Elimination
Uric acid is eliminated by the kidneys.
In higher primates and humans, the enzyme, uricase, is absent, and thus uric acid is not further metabolized and is excreted. In all other mammals, uric acid is metabolized by uricase to allantoin, which is then excreted.
The exact mechanism of action for uric acid's antioxidant effects have not yet been elucidated.
