


1. 1360457-46-0
2. Rpx7009
3. Rpx-7009
4. Vaborbactam [inn]
5. Chembl3317857
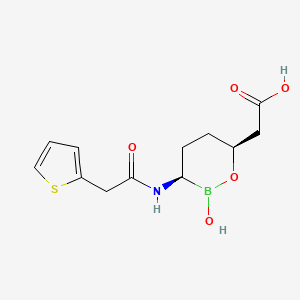
6. 2-[(3r,6s)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]oxaborinan-6-yl]acetic Acid
7. 1c75676f8v
8. 1,2-oxaborinane-6-acetic Acid, 2-hydroxy-3-((2-(2-thienyl)acetyl)amino)-, (3r,6s)-
9. 2-((3r,6s)-2-hydroxy-3-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido)-1,2-oxaborinan-6-yl)acetic Acid
10. Rpx 7009
11. Unii-1c75676f8v
12. Vaborbactam [mi]
13. Vaborbactam. Rpx7009
14. Vaborbactam (usan/inn)
15. Vaborbactam [usan:inn]
16. Vaborbactam [usan]
17. Vaborbactam [who-dd]
18. Schembl620289
19. Gtpl10871
20. Vaborbactam [orange Book]
21. Dtxsid901027690
22. Vabomere (vaborbactam + Meropenem)
23. Ex-a2589
24. Bdbm50089084
25. Mfcd28502176
26. Vabomere Component Vaborbactam
27. Akos032961376
28. Carbavance Component Vaborbactam
29. Cs-6445
30. Db12107
31. Compound 9f [pmid: 25782055]
32. Ncgc00510003-01
33. (3r,6s)-
34. 1575712-03-6
35. Bv163750
36. Hy-19930
37. Vaborbactam Component Of Carbavance
38. 2-hydroxy-3-((2-(2-thienyl)acetyl)amino)-
39. D10998
40. Q27252228
41. {(3r,6s)-2-hydroxy-3-[(thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]-1,2-oxaborinan-6-yl}acetic Acid; 2-((3r,6s)-2-hydroxy-3-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido)-1,2-oxaborinan-6-yl)acetic Acid; 2-[(3r,6s)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]oxaborinan-6-yl]acetic Acid; 1,2-oxaborinane-6-acetic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 297.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H16BNO5S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 297.0842240 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 297.0842240 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 124 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 370 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated in combination with meropenem for the treatment of patients 18 years of age and older with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) including pyelonephritis caused by the following susceptible microorganisms: _Escherichia coli_, _Klebsiella pneumoniae_, and _Enterobacter cloacae_ species complex.
FDA Label
Treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections
Vaborbactam shows no antibacterial activity alone; it serves to restore the antibacterial activity of other antibacterial agents such as meropenem by attenuating their degradation by inhibiting certain serine beta-lactamases of microorganisms. Vaborbactam does not decrease the activity of meropenem against meropenem-susceptible organisms. Vaborbactam in combination with meropenem, which is a penem antibacterial drug, potentiates the bactericidal actions of meropenem against carbapenem-resistant KPC-containing _Escherichia coli_, _Klebsiella pneumoniae_, and _Enterobacter cloacae_ in a concentration-dependent manner. It restored the antimicrobial activity of meropenem in animal models of infection caused by some meropenem non-susceptible KPC-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
beta-Lactamase Inhibitors
Endogenous substances and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of BETA-LACTAMASES. (See all compounds classified as beta-Lactamase Inhibitors.)
Absorption
The peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and AUC of vaborbactam increase in a dose-proportional manner. In healthy adult subjects, the Cmax following administration of multiple 2 g dose as a 3-hour infusion was 55.6 mg/L and AUC was 588 mgh/L. In patients with the same dosing regimen, the Cmax was 71.3 mg/L and AUC was 835 mgh/L at steady state. The exposure of vaborbactam in terms of Cmax and AUC are not expected to change with repeated dosing, and there was no evidence of accumulation of vaborbactam in plasma in a repeated dosing study.
Route of Elimination
Vaborbactam predominantly undergoes renal excretion, where about 75 to 95% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine over a 24 to 48 hour period.
Volume of Distribution
The steady-state volume of distribution of vaborbactam in patients was 18.6 L.
Clearance
The mean renal clearance for vaborbactam was 8.9 L/h. The mean non-renal clearance for vaborbactam was 2.0 L/h indicating nearly complete elimination of vaborbactam by the renal route. The clearance of vaborbactam in healthy subjects following administration of multiple doses of 2 g as a 3-hour infusion was 10.9 L/h. The clearance of vaborbactam in patients following administration of 2 g by 3 hour infusion was 7.95 L/h.
Vaborbactam does not undergo metabolism.
The half life of vaborbactam in healthy subjects following multiple 2 g dose administration as a 3-hour infusion was 1.68 hours. The half life of vaborbactam following administration of 2 g by 3 hour infusion was 2.25 hours.
Vaborbactam is a cyclic boronic acid pharmacophore -lactamase inhibitor that elicits potent inhibition of _Klebsiella pneumoniae_ carbapenemase (KPC) enzymes and other Ambler class A and C enzymes such as serine -lactamases that confer resistance to commonly-used antibiotics such as Carbapenems. Vaborbactam is a potent inhibitor of class A carbapenemases, such as KPC, as well as an inhibitor of other class A (CTX-M, SHV, TEM) and class C (P99, MIR, FOX) beta-lactamases. Vaborbactam interacts with -lactamases of Ambler classes A and C via precovalent and covalent binding. It exerts no inhibitory actions on class D or class B carbapenemases. The production of contemporary -lactamase by bacterial isolates potentiate the degradation of -lactam antibiotic agents, rendering them clinically ineffective and posing challenges for patients receiving the standard antibiotic therapy. In combination with meropenem, varborbactam acts as a non-suicidal beta-lactamase inhibitor that protects meropenem from degradation mediated by serine beta-lactamases such as _Klebsiella pneumoniae_ carbapenemase (KPC).