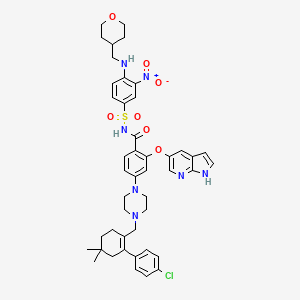

1. 4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-n-((3-nitro-4-((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylmethyl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
2. Abt-199
3. Benzamide, 4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)methyl)-1-piperazinyl)-n-((3-nitro-4-(((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-5-yloxy)-
4. Gdc-0199
5. Rg-7601
6. Rg7601
7. Venclexta
1. 1257044-40-8
2. Abt-199
3. Venclexta
4. Gdc-0199
5. Abt199
6. Abt 199
7. Rg7601
8. Venetoclax (abt199)
9. Gdc 0199
10. Rg-7601
11. Venetoclax; Abt-199
12. 4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]piperazin-1-yl]-n-[3-nitro-4-(oxan-4-ylmethylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
13. Venetoclax (abt-199)
14. N54aic43pw
15. Abt-199 (gdc-0199)
16. 2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)-4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-n-(3-nitro-4-((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methy
17. 4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-n-((3-nitro-4-((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylmethyl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
18. 4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]-1-piperazinyl]-n-[[3-nitro-4-[[(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl]amino]phenyl]sulfonyl]-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)-benzamide
19. Benzamide, 4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)methyl)-1-piperazinyl)-n-((3-nitro-4-(((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-5-yloxy)-
20. Venclyxto
21. Bdbm189459
22. Unii-n54aic43pw
23. 4-(4-{[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]methyl}piperazin-1-yl)-n-({3-nitro-4-[(oxan-4-ylmethyl)amino]benzene}sulfonyl)-2-{1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy}benzamide
24. 4-(4-{[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]methyl}piperazin-1-yl)-n-({3-nitro-4-[(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylmethyl)amino]phenyl}sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
25. 4-{4-[(4'-chloro-5,5-dimethyl[3,4,5,6-tetrahydro[1,1'-biphenyl]]-2-yl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}-n-(3-nitro-4-{[(oxan-4-yl)methyl]amino}benzene-1-sulfonyl)-2-[(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)oxy]benzamide
26. Venetoclax [usan:inn]
27. Venclexta (tn)
28. Benzamide, 4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]-1-piperazinyl]-n-[[3-nitro-4-[[(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl]amino]phenyl]sulfonyl]-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)-
29. Venetoclax [mi]
30. Venetoclax(abt-199)
31. Venetoclax [inn]
32. Venetoclax [jan]
33. Venetoclax [usan]
34. Venetoclax [who-dd]
35. Mls006010298
36. Schembl523816
37. Venetoclax (jan/usan/inn)
38. Amy343
39. Gtpl8318
40. Chembl3137309
41. Schembl19236295
42. Venetoclax [orange Book]
43. Bdbm60828
44. Dtxsid30154863
45. Ex-a168
46. Chebi:133021
47. Hms3653j06
48. Hms3745e07
49. Bcp06811
50. Bdbm50162774
51. Mfcd23160052
52. Nsc766270
53. Akos025289539
54. Zinc150338755
55. Ccg-270543
56. Cs-1155
57. Db11581
58. Ks-1470
59. Nsc-766270
60. Sb16499
61. Ncgc00345789-01
62. Ncgc00345789-05
63. Ncgc00345789-10
64. Ncgc00345789-11
65. Ac-28754
66. Da-35360
67. Hy-15531
68. Smr004701366
69. Ft-0699586
70. S8048
71. Sw219672-1
72. J3.516.625d
73. D10679
74. Us9174982, 5
75. A850921
76. Us9174982, 369
77. J-005269
78. Q23671272
79. 2-((1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)oxy)-4-(4-((4'-chloro-5,5-dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-n-((3-nitro-4-(((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)benzamide
80. 4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-n-((3-nitro-4-((tetrahydro-2hpyran-4-ylmethyl) Amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)-2-(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
81. 4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]-1-piperazinyl]-n-[[3-nitro-4-[[(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)methyl]amino]phenyl]sulfonyl]-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
82. 4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-cyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]piperazin-1-yl]-n-[3-nitro-4-(tetrahydropyran-4-ylmethylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl-2-(1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
83. 4-{4-[(4'-chloro-5,5-dimethyl[3,4,5,6-tetrahydro[1,1'-biphenyl]]-2-yl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}-n-[(3-nitro-4-{[(oxan-4-yl
| Molecular Weight | 868.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C45H50ClN7O7S |
| XLogP3 | 8.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 867.3180958 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 867.3180958 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 183 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 61 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1640 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
A BCL-2 inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy.
FDA Label
Venclyxto in combination with obinutuzumab is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) (see section 5. 1).
Venclyxto in combination with rituximab is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with CLL who have received at least one prior therapy.
Venclyxto monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of CLL:
- in the presence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation in adult patients who are unsuitable for or have failed a B cell receptor pathway inhibitor, or
- in the absence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation in adult patients who have failed both chemoimmunotherapy and a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor.
Venclyxto in combination with a hypomethylating agent is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) who are ineligible for intensive chemotherapy.
Venetoclax induces rapid and potent onset apoptosis of CLL cells, powerful enough to act within 24h and to lead to tumor lysis syndrome,,. Selective targeting of BCL2 with venetoclax has demonstrated a manageable safety profile and has been shown to induce significant response in patients with relapsed CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) or SLL (small lymphocytic leukemia), including patients with poor prognostic features. This drug is not expected to have a significant impact on the cardiac QT interval. Venetoclax has demonstrated efficacy in various types of lymphoid malignancies, including relapsed/ refractory CLL harboring deletion 17p, with an overall response rate of approximately 80%.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
L01XX52
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX52 - Venetoclax
Absorption
Following several oral administrations after a meal, the maximum plasma concentration of venetoclax was reached 5-8 hours after the dose. Venetoclax steady state AUC (area under the curve) increased proportionally over the dose range of 150-800 mg. After a low-fat meal, venetoclax mean ( standard deviation) steady-state Cmax was 2.1 1.1 g/mL and AUC0-24 was 32.8 16.9 gh/mL at the 400 mg once daily dose. When compared with the fasted state, venetoclax exposure increased by 3.4 times when ingested with a low-fat meal and 5.2 times with a high-fat meal. When comparing low versus high fat, the Cmax and AUC were both increased by 50% when ingested with a high-fat meal. The FDA label indicataes that venetoclax should be taken with food,.
Route of Elimination
After single oral administration of 200 mg radiolabeled [14C]-venetoclax dose to healthy subjects, >99.9% of the dose was found in feces and <0.1% of the dose was excreted in urine within 9 days, suggesting that hepatic elimination is responsible for the clearance of venetoclax from systemic circulation. Unchanged venetoclax accounted for 20.8% of the radioactive dose excreted in feces.
Volume of Distribution
The population estimate for apparent volume of distribution (Vdss/F) of venetoclax ranged from 256-321 L.
Clearance
Mainly hepatic.
In vitro studies demonstrated that venetoclax is predominantly metabolized as a substrate of CYP3A4/5,,.
The half-life of venetoclax is reported to be 19-26 hours, after administration of a single 50-mg dose,.
Proteins in the B cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) family are necessary regulators of the apoptotic (anti-cell programmed death) process. This family comprises proapoptotic and prosurvival proteins for various cells. Cancer cells evade apoptosis by inhibiting programmed cell death (apoptosis). The therapeutic potential of directly inhibiting prosurvival proteins was unveiled with the development of navitoclax, a selective inhibitor of both BCL-2 and BCL-2-like 1 (BCL-X(L)), which has demonstrated clinical efficacy in some BCL-2-dependent hematological cancers. Selective inhibition of BCL-2 by venetoclax, sparing BCL-xL enables therapeutic induction of apoptosis without the negative effect of thrombocytopenia,. Venetoclax helps restore the process of apoptosis by binding directly to the BCL-2 protein, displacing pro-apoptotic proteins, leading to mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and the activation of caspase enzymes. In nonclinical studies, venetoclax has shown cytotoxic activity in tumor cells that overexpress BCL-2.