


1. Rsd 1235
2. Rsd-1235
3. Rsd1235
1. 794466-70-9
2. Vemakalant
3. Rsd1235
4. Rsd-1235
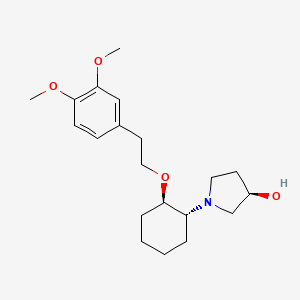
5. (3r)-1-((1r,2r)-2-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethoxy)cyclohexyl)pyrrolidin-3-ol
6. 9g468c8b13
7. (3r)-1-[(1r,2r)-2-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethoxy]cyclohexyl]pyrrolidin-3-ol
8. 3-pyrrolidinol, 1-((1r,2r)-2-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethoxy)cyclohexyl)-, (3r)-
9. 3-pyrrolidinol,1-[(1r,2r)-2-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethoxy]cyclohexyl]-, (3r)-
10. Vernakalant [inn]
11. Vernakalant [inn:ban]
12. Unii-9g468c8b13
13. Vernakalant [mi]
14. Vernakalant [who-dd]
15. Schembl410062
16. Chembl2111112
17. Dtxsid60229659
18. Chebi:135956
19. Ex-a2465
20. Zinc22010910
21. Cs-0276
22. Db06217
23. Ncgc00378872-01
24. Ac-35850
25. As-56235
26. Hy-14182
27. A864860
28. Q665725
29. J-513102
30. (r)-1-((1r,2r)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenethoxy)cyclohexyl)pyrrolidin-3-ol
31. (r,r)-1-{2-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethoxy]-cyclohexyl}-pyrrolidin-3-(r)-ol
| Molecular Weight | 349.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H31NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 349.22530847 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 349.22530847 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 51.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 394 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for the rapid conversion of recent onset of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm in adults for non-surgery patients that lasts for less than 7 days of duration and post-cardiac surgery patients with atrial fibrillation lasting less than 3 days of duration.
Vernakalant blocks currents in all phases of atrial action potential including atria-specific potassium currents (the ultra-rapid delayed rectifier and the acetylcholine dependent potassium currents) and prolongs the refractory period. It dose-dependently prolongs atrial refractoriness, prolongs AV nodal conduction and refractoriness, and slightly prolongs QRS duration without significantly affecting ventricular refractory period. Vernakalant has a high affinity to ion channels specifically involved in repolarization of atrial tissue and is thought to have a low proarrhythmic potential.
C01BG11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01B - Antiarrhythmics, class i and iii
C01BG - Other antiarrhythmics, class i and iii
C01BG11 - Vernakalant
Absorption
In patients, average peak plasma concentrations of vernakalant were 3.9 g/ml following a single 10 minute infusion of 3 mg/kg vernakalant hydrochloride, and 4.3 g/ml following a second infusion of 2 mg/kg with a 15 minute interval between doses.
Route of Elimination
Mainly eliminated via renal excretion.
Volume of Distribution
Approximately 2L/kg.
Clearance
The typical total body clearance of vernakalant was estimated to be 0.41 l/hr/kg.
Vernakalant is mainly eliminated by CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation in CYP2D6 extensive metabolisers. Glucuronidation is the main metabolism pathway in CYP2D6 poor metabolisers.
Elimination half life in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers is 3 hours and 5.5 hours in poor metabolizers.
Vernakalant blocks atrial voltage-gated sodium channels in a dose and frequency-dependent manner and inhibits late sodium current (INa)which confers its effect on intra-atrial conduction. This current blockade enhance and onset of drug action accelerates in higher heart rate as the affinity of vernakalant for INa also increases. Its binding offset is quick once the heart rate slows. It also blocks Kv 1.5 channel and its early activating potassium channels (IKur) and inhibits acetylcholine-activated potassium channels (IKAch), which are specific to the atrium and cause prolongation of atrial refractoriness. Vernakalant also blocks Kv4.3 channel and its cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito), which is involved more with atrial than ventricular refractoriness. Vernakalant minimally blocks hERG channels and its rapidly activating/delayed rectifying potassium current (IKr) which accounts for mild QT prolongation. QRS widening due to INa blockade also contributes to QT prolongation.
