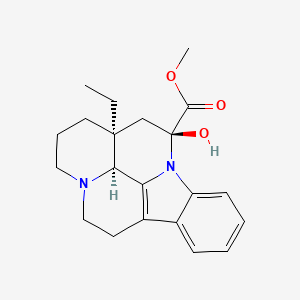

1. Cerebroxine
2. Devincan
3. Pervincamine
4. Vincapront
5. Vincimax
1. 1617-90-9
2. Pervincamine
3. Devincan
4. Angiopac
5. Arteriovinca
6. Minorine
7. Vincamidol
8. Novicet
9. Equipur
10. Monorin
11. Oxygeron
12. Vincafor
13. Vincagil
14. (+)-vincamine
15. Methyl Vincaminate
16. Anasclerol
17. Perval
18. Vincimax
19. Vincasaunier
20. Decincan
21. Devinkan
22. Tripervan
23. Vincadar
24. Vincafolina
25. Vincamin
26. Vincapront
27. Vinkametrin
28. Vraap
29. Cetal Retard
30. Minorin
31. Pervone
32. Vincachron
33. Vincapan
34. Vinodrel Retard
35. Ocu-vinc
36. Vinca-ecobi
37. Vinca-minor
38. Alkaloid Obtained From Vinca Minor
39. Anasclerol (base)
40. 14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxyeburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
41. 996xvd0jht
42. Chebi:9985
43. Vincamine (inn)
44. Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid, 14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxy-, Methyl Ester, (3alpha,14beta,16alpha)-
45. Vincamine [inn]
46. Dsstox_cid_20134
47. Dsstox_rid_79448
48. Dsstox_gsid_40134
49. Vincamina [dcit]
50. Vincaminum
51. Vincamina
52. Vincaminum [inn-latin]
53. Nsc-91998
54. Methyl 14beta-hydroxy-14,15-dihydro-3alpha,16alpha-eburnamenine-14alpha-carboxylate
55. Vincamine [inn:ban:dcf]
56. Methyl (15s,17s,19s)-15-ethyl-17-hydroxy-1,11-diazapentacyclo[9.6.2.02,7.08,18.015,19]nonadeca-2,4,6,8(18)-tetraene-17-carboxylate
57. Hsdb 7150
58. Einecs 216-576-3
59. Nsc 91998
60. Unii-996xvd0jht
61. Oxybral
62. (3?,14?,16?)-14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxyeburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
63. Vincamine (fp)
64. Ncgc00094824-01
65. Prestwick_495
66. Cas-1617-90-9
67. Cetal Retard (tn)
68. Mfcd00078054
69. Vincamine, 98%
70. Vincamine [mi]
71. Vincamine [hsdb]
72. Prestwick0_000271
73. Prestwick1_000271
74. Prestwick2_000271
75. Prestwick3_000271
76. Vincamine [mart.]
77. Vincamine [who-dd]
78. Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid, 14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxy-, Methyl Ester, (3alpha,14beta,16.)
79. Bspbio_000142
80. Gtpl349
81. Mls002154249
82. Schembl147179
83. Spbio_002361
84. Bpbio1_000158
85. Chembl1165342
86. Dtxsid9040134
87. Vincamine [ep Monograph]
88. Bcbcmap01_000080
89. Hms1568h04
90. Hms2095h04
91. Hms2268c20
92. Hms3712h04
93. Amy39091
94. Bcp05837
95. Hy-b1021
96. Zinc1069082
97. Tox21_111342
98. Tox21_301968
99. S3891
100. Akos015896471
101. Tox21_111342_1
102. Ccg-208544
103. Cs-4536
104. Db13374
105. Ks-5179
106. Methyl (3alpha,14beta,16alpha)-14-hydroxy-14,15-dihydroeburnamenine-14-carboxylate
107. Smp1_000314
108. Vincamine, Analytical Reference Material
109. Ncgc00184983-01
110. Ncgc00184983-03
111. Ncgc00255542-01
112. Ac-22625
113. Smr000112509
114. C09251
115. D08677
116. 617v909
117. A851579
118. Q416225
119. Q-100193
120. Brd-k40902647-001-03-7
121. Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid, 14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxy-, Methylester, (3a,14b,16a)-
122. (3.alpha.,14.beta.,16.alpha.)-14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxyeburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
123. (3alpha,14beta,16alpha)-14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxyeburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acidmethyl Ester
124. Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic Acid, 14,15-dihydro-14-hydroxy-,methyl Ester, (3alpha,14beta,16alpha)-
125. Methyl (15s,17s,19s)-15-ethyl-17-hydroxy-1,11-diazapentacyclo[9.6.2.0?,?.0?,??.0??,??]nonadeca-2,4,6,8(18)-tetraene-17-carboxylate
126. Methyl (15s,17s,19s)-15-ethyl-17-hydroxy-1,11-diazapentacyclo[9.6.2.0^{2,7}.0^{8,18}.0^{15,19}]nonadeca-2,4,6,8(18)-tetraene-17-carboxylate
127. Methyl (41s,12s,13as)-13a-ethyl-12-hydroxy-2,3,41,5,6,12,13,13a-octahydro-1h-indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridine-12-carboxylate
128. Methyl(41s,12s,13as)-13a-ethyl-12-hydroxy-2,3,41,5,6,12,13,13a-octahydro-1h-indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridine-12-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 354.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 354.19434270 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 354.19434270 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 54.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 598 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Periwinkle is used for circulatory disorders, cerebral circulatory impairment, support for the metabolism of the brain and its improved oxygen supply, prophylaxis of memory and concentration impairment, improvement of memory and thinking capacity, mental productivity, prevention of premature aging of brain cells, for geriatric support, as a sedative and as a blood pressure-lowering remedy, for catarrhs, feebleness, and for improvement of the immune function, for diarrhea, vaginal flux, throat aliments, tonsillitis and angina, sore throat, intestinal inflammation, toothache, dropsy, as a diuretic and blood-purifying remedy, for promotion of wound healing, as a hemostatic remedy, and a bitter principle.
Blumenthal M, ed; The Complete German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Guide to Herbal Medicines p. 364-365 (1998)
Its use is recommended as a cerebral vasodilator in neonatal calves for cerebral anoxia.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
/VET:/ Vincamine is widely used in human medicine to increase global and regional blood flow in patients suffering from acute or subchronic cerebral ischemia.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
/VET:/ It is mostly used in combination with heptaminol (a central nervous system stimulant) and papaverine (a vasodilator).
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
...Vincamine and vincamine derivatives, ...are able to prevent the occurrence of an edematous reaction.
PMID:6500773 Borzeix MG, Cahn J; Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 4 (4): 259-261 (1984)
In animal experiments, administration of periwinkle caused destruction of blood components, manifested as leukocytopenia, lymphocytopenia, and lowering of the a a2-, and g-globulin level.
Blumenthal M, ed; The Complete German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Guide to Herbal Medicines p. 365 (1998)
Arrhythmia was observed in rabbits and dogs after intravenous administration of doses of 0.5 to 2.5 mg/kg bw. However, this effect was not only a function of the dose but also of the speed of the infusion. When the speed of the infusion was higher than the rate of metabolic transformation, the effect on the heart increased even up to the death of the animal. The effect was linear with the dose and was present at all speeds of infusion used.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Sedative effects were established in mice after subcutaneous administration of doses of 2.5 to 10 mg/kg bw.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Other observed effects of vincamine include cardiovascular effects (e.g. hypotension, proarrhythmogenic effect) and effects on central nervous system (sedation).
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C04 - Peripheral vasodilators
C04A - Peripheral vasodilators
C04AX - Other peripheral vasodilators
C04AX07 - Vincamine
In a crossover study of six healthy volunteers the pharmacokinetics and the bioavailability of vincamine were studied after administration of two oral forms. All subjects received an oral dose of 60 mg vincamine. ...The drug generally follows a one-compartment kinetic model. The average value of Tmax is 1.4 +/- 0.5/hr with the tablets and 1 +/- 0.6/hr with the solution; the Cmax are, respectively, 155 +/- 82 micrograms . 1(-1) and 133 +/- 104 micrograms . 1(-1). The AUC are 443 +/- 156 micrograms . 1(-1) hr with the tablets and 315 +/- 178 micrograms . 1(-1) hr with the solution.
PMID:6654533 Millart H et al; Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 21 (11): 581-586 (1983)
Vincamine HCl was biopharmaceutically and pharmacokinetically evaluated. For biopharmaceutical characterization of the drug the apparent lipoid/water partition coefficient (APC), pKa, extent of protein (bovine) binding and the erythrocyte (human) uptake were determined. Vincamine has an APC of 2.05, a pKa of 6.17, is 64% bound to plasma proteins, and is about 6% bound to erythrocytes. Because the gerbil was used as model in pharmacodynamic studies, the pharmacokinetic drug disposition was determined in this species and compared to parameters reported in the literature for other species. The terminal half-life is about 1 hour, the apparent volume of distribution 2.9 L/kg, and the total clearance is about 33.3 mL/min/kg. The parameters are comparable to other species including man. The brain concentration is about 5-fold that in plasma. A therapeutic steady state concentration for effectiveness in gerbils has been estimated to be 0.02 ug/mL.
PMID:4010386 Ritschel WA, Agrawala P; Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 7 (3): 129-36 (1985)
Pharmacokinetic parameters of vincamine in rats were measured after oral administration of 20 mg base/kg bw and intravenous injection of 10 mg vincamine hydrochloride/kg bw. After oral administration, a bioavailability of 58% was found and the concentration/time curve showed a two-compartment open model. The following parameters were observed: an elimination half-life of 1.71 hours, a t-max of 1.27 hours, a C-max of 0.87 ug/ml, a total clearance of 0.818 1/h (higher than the plasma perfusion volume, which indicates a very quick metabolism in other organs in addition to the liver), and a volume of distribution of 2.018 liters. The amount of unchanged vincamine excreted was very low with 3 to 11% in urine and 2 to 5% in bile. Vincamine is taken up in high concentrations into the different organs resulting in the following ratios: lung/plasma 21, brain/plasma 14.6, kidneys/plasma 14.3, liver/plasma 8.9, heart/plasma 7.6. However, elimination from these organs was significantly more rapid than from plasma. After intravenous injection the pharmacokinetic parameters observed were an elimination half-life of 1.68 hours, a C-max of 5.46 ug/ml, a total clearance of 0.866 1/hour, and a volume of distribution of 2.104 liters. The values for elimination half-life, volume of distribution and total clearance did not differ significantly between oral and intravenous administration.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Pharmacokinetics of vincamine in dogs also followed a two-compartment open model. Doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg intravenously showed dose-dependent half-life and clearance rate. After oral administration of 20 mg vincamine hydrochloride, bioavailability ranged between 23 and 58%. Vincamine could be detected in the urine at up to 9.5% depending on urinary pH.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for VINCAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The metabolism of vincamine hydrochloride was studied in the rat after oral administration of the drug. Vincamine is almost completely metabolized, only a small fraction of the original compound being excreted in the urine. The metabolites detected in blood, urine and tissues were purified by preparative thin layer and column chromatography in several solvent systems, and analyzed by mass spectrometry. It was found that the main urinary metabolites were vincamine conjugates (sulphates and glucuronides). Two new metabolites were detected in all the biological fluids and specimens analyzed: these compounds are more polar than vincamine and their structure was characterized by mass spectrometry, I.R. and U.V. spectroscopy and confirmed by synthesis in our laboratory.[Vigano V et al; Farmaco
PMID:744256 Sci] 33 (8): 583-94 (1978)
Vincamine is very extensively metabolised with only a small percentage of unchanged compound detectable in the urine. Radiolabel studies in rats after an oral dose of 10 mg/kg bw demonstrate the metabolic pathway of vincamine. On the one hand it is hydrolysed by the plasma esterases to the unstable vincaminic acid. The latter is quickly decarboxylised and oxidised to eburnamenine. On the other hand vincamine is hydroxylated to the major metabolite 6-beta-hydroxy-vincamine, which accounts for 40% of total urinary and biliary radioactivity, followed by 6-alpha-hydroxy-vtncamine (8%) and 6-keto-vincamine, the oxidized metabolite of both previous metabolites (about 10% of the administered dose). 6-Keto-vincamine is eliminated by conjugation. The same metabolites (hydroxy.-keto) could also be detected in the urine of rabbits, dogs and man. Within 72 hours 40% of the total radioactivity are excreted in twine and 23% in the feces.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
After intravenous injection /of vincamine hydrochloride to rats/ the pharmacokinetic parameters observed were an elimination half-life of 1.68 hours /Vincamine hydrochloride/.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
The following parameters were observed /after oral administration of 20 mg/kg vincamine (base) to rats/: an elimination half-life of 1.71 hours...
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
After oral administration of 4 mg vincamine hydrochloride/kg bw /in dogs/ an elimination half-life of 4.5 hours (longer than for rats) and a total clearance of 0.52 1/hour were observed. /vincamine hydrochloride/
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Half-life of elimination for the solution was 0.57 to 1.07 hours/for 169 mg vincamine hydrochloride and 33.81 mg vincamine hydrochloride control-released tablets respectively/.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.
Vincamine HCl was biopharmaceutically and pharmacokinetically evaluated. ...The terminal half-life is about 1 hour... .
PMID:4010386 Ritschel WA, Agrawala P; Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 7 (3): 129-36 (1985)
... At concentrations of 1, 10 and 100 microM, a five-minute perfusion with vincamine did not affect the synaptically-mediated activation of pyramidal neurons evoked by stimulation of the Schaffer-commissural fiber system. The effect of vincamine on the excitability of the pyramidal neurons was investigated by studying its effect on the antidromically-elicited field potential and the input-output relation of Schaffer-commissural fiber input. No effect on either of the two parameters was seen at a concentration of 100 microM of vincamine. Vincamine ... attenuate both the post-tetanic (PTP) and long-term potentiation (LTP) evoked by repetitive stimulation of the Schaffer-commissural fiber system. At a concentration of 100 microM of vincamine, PTP was significantly reduced and LTP was almost completely suppressed.
PMID:7176804 Olpe HR et al; Life Sci. 31(18): 1947-53 (1982)
Vincamine's function and therapeutic use as a vasodilating agent, especially at the level of the central nervous system, has been proven after an intravenous administration of 30 mg over a period of 20 minutes in Mongolian gerbils by an increase of cerebral blood flow of approximately 10% and of regional cerebral blood flow in areas with insufficient blood supply by approximately 15%. The mechanism of this vascular action, while not fully clear, seems to be partly due to a reserpine-like noradrenaline depleting effect. Hence, its sedative effects are similar to reserpine
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit; Summary Report for Vincamine (1617-90-9). EMEA/MRL/587/99 (April 1999). Available from: www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/vet/mrls/058799en.pdf as of December 2, 2003.