

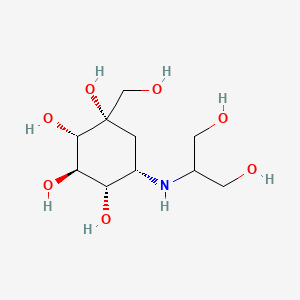

1. 3,4-dideoxy-4-((2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)amino)-2-c-(hydroxymethyl)-d-epi-inositol
2. Basen
3. N-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propyl)valiolamine
1. 83480-29-9
2. Basen
3. Glustat
4. Ao-128
5. Ao 128
6. A-71100
7. (1s,2s,3r,4s,5s)-5-((1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl)amino)-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetraol
8. Chembl476960
9. S77p977ag8
10. 3,4-dideoxy-4-((2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)amino)-2-c-(hydroxymethyl)-d-epi-inositol
11. Dsstox_cid_1442
12. Dsstox_rid_76161
13. Dsstox_gsid_21442
14. (1s,2s,3r,4s,5s)-5-(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-ylamino)-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetraol
15. (1s,2s,3r,4s,5s)-5-[(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl)amino]-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol
16. Voglibosum
17. Basen Od
18. Voglibose [inn]
19. 3,4-dideoxy-4-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino]-2-c-(hydroxymethyl)-d-epinositol
20. Cas-83480-29-9
21. Basen (tn)
22. Voglibose [usan:inn]
23. Voglibosum [inn-latin]
24. Voglibosa [inn-spanish]
25. N-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propyl)valiolamine
26. Unii-s77p977ag8
27. Ccris 4540
28. Ncgc00164595-01
29. Voglibose- Bio-x
30. 3,4-dideoxy-4-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino]-2-c-(hydroxymethyl)-d-epi-inositol
31. Vog
32. Voglibose [jan]
33. Voglibose [mi]
34. Voglibose [usan]
35. Voglibose [mart.]
36. Schembl5882
37. Voglibose [who-dd]
38. A 71100
39. (1s,2s,3r,4s,5s)-5-(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-ylamino)-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol
40. Mls003882582
41. Voglibose (jp17/usan/inn)
42. Dtxsid2021442
43. Chebi:32300
44. Bcpp000020
45. Dtxsid501031239
46. Hms3414a17
47. Hms3678a17
48. Voglibose, >=97.0% (tlc)
49. 112653-29-9
50. Hy-b0025
51. Zinc3788703
52. Tox21_112220
53. Bdbm50263044
54. S4101
55. Akos015950839
56. Tox21_112220_1
57. Ccg-267119
58. Db04878
59. Ncgc00164595-02
60. (1s,2s,3r,4s,5s)-5-{[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino}-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol
61. Bv164530
62. Smr002530327
63. A25630
64. D01665
65. Ab01566929_01
66. 480v299
67. Sr-01000883931
68. Q-101310
69. Q7939403
70. Sr-01000883931-1
71. Brd-k66850609-001-01-7
72. Brd-k66850609-001-07-4
73. (1r,2r,3s,4r,5r)-5-(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-ylamino)-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetraol
74. D-epi-inositol, 3,4-dideoxy-4-((2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)amino)-2-c-(hydroxymethyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 267.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H21NO7 |
| XLogP3 | -4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 267.13180201 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.13180201 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 154 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 263 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of diabetes. It is specifically used for lowering post-prandial blood glucose levels thereby reducing the risk of macrovascular complications.
Voglibose, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, is a synthetic compound with potent and enduring therapeutic efficacies against disorders of sensory, motor and autonomic nerve systems due to diabetes mellitus. The drug was approved in Japan in 1994 for the treatment of diabetes, and it is under further investigation by Takeda for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are oral anti-diabetic drugs used for diabetes mellitus type 2 that work by preventing the digestion of complex carbohydrates (such as starch). Complex carbohydrates are normally converted into simple sugars (monosaccharides) which can be absorbed through the intestine. Hence, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors reduce the impact of complex carbohydrates on blood sugar.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
Glycoside Hydrolase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit or block the activity of GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES such as ALPHA-AMYLASES and ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASES. (See all compounds classified as Glycoside Hydrolase Inhibitors.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BF - Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
A10BF03 - Voglibose
Absorption
Slowly and poorly absorbed. The reported pharmacokinetic parameters of voglibose with metformin are Cmax corresponds to 1.38 mcg/ml while AUC is 8.17 mcg.h/ml and tmax is of 2.5 hours.
Little metabolism occurs and no metabolites have as yet been identified.
The half-life of voglibose is very similar to the one found for metformin and it is reported to be of 4.08 hours.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are saccharides that act as competitive inhibitors of enzymes needed to digest carbohydrates: specifically alpha-glucosidase enzymes in the brush border of the small intestines. The membrane-bound intestinal alpha-glucosidases hydrolyze oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and disaccharides to glucose and other monosaccharides in the small intestine. Acarbose also blocks pancreatic alpha-amylase in addition to inhibiting membrane-bound alpha-glucosidases. Pancreatic alpha-amylase hydrolyzes complex starches to oligosaccharides in the lumen of the small intestine. Inhibition of these enzyme systems reduces the rate of digestion of complex carbohydrates. Less glucose is absorbed because the carbohydrates are not broken down into glucose molecules. In diabetic patients, the short-term effect of these drugs therapies is to decrease current blood glucose levels: the long term effect is a small reduction in hemoglobin-A1c level. (From Drug Therapy in Nursing, 2nd ed)
