
1. Uk 109,496
2. Uk 109496
3. Uk-109,496
4. Uk-109496
5. Uk109,496
6. Uk109496
7. Vfend
1. 137234-62-9
2. Vfend
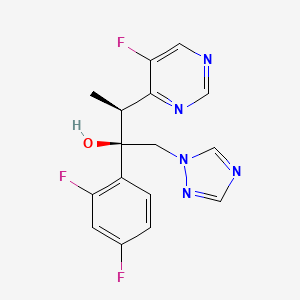
3. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoropyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
4. Uk-109496
5. (+/-)-voriconazole
6. Voriconazole Vfend
7. Uk-109,496
8. Uk 109496
9. Voriconzole
10. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoropyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
11. Vcz
12. Voriconazole, (+/-)-
13. Chembl638
14. Nsc-759888
15. Jfu09i87tr
16. Usg4b1cd29
17. Cpd000466350
18. (r-(r*,s*))-alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-pyrimidineethanol
19. 4-pyrimidineethanol, Alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (alphar,betas)-
20. Chebi:10023
21. 173967-54-9
22. Vrc
23. Voriconazol
24. Dsstox_cid_26485
25. Dsstox_rid_81656
26. Dsstox_gsid_46485
27. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoro-4-pyrimidinyl)-1-((1h)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-butan-2-ol
28. (alphar,betas)-alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-pyrimidineethanol
29. 4-pyrimidineethanol, Alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (r-(r*,s*))-
30. Voriconazole Related Compound A
31. 188416-29-7
32. Voriconazolum
33. Vorikonazole
34. Voriconazole [usan:inn:ban]
35. Drg-0301
36. Smr000466350
37. Cas-137234-62-9
38. Vfend (tn)
39. Vfend I.v.
40. Unii-jfu09i87tr
41. Pfizer
42. Ncgc00164622-01
43. Voriconazole Solution
44. Voriconazole- Bio-x
45. Voriconazole - Vfend
46. (alphar,betas)-alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-pyrimidineethanol
47. Voriconazole In Combination With Mgcd290
48. Voriconazole [mi]
49. Voriconazole [inn]
50. Voriconazole [jan]
51. Unii-usg4b1cd29
52. Voriconazole [usan]
53. Voriconazole [vandf]
54. Schembl36233
55. Voriconazole [mart.]
56. Mls000759464
57. Mls001424082
58. Mls006010028
59. Voriconazole [usp-rs]
60. Voriconazole [who-dd]
61. Voriconazole [ema Epar]
62. Dtxsid5046485
63. Voriconazole (jp17/usp/inn)
64. Zinc14864
65. Amy8903
66. Voriconazole, >=98% (hplc)
67. Bcpp000019
68. Dtxsid201019420
69. Hms2051n09
70. Hms3260m22
71. Hms3713f12
72. Pharmakon1600-01502346
73. Voriconazole [orange Book]
74. Voriconazole [ep Monograph]
75. Tox21_112241
76. Tox21_500150
77. Voriconazole [usp Monograph]
78. Voriconazole 2.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
79. Ac-823
80. Bdbm50333117
81. Nsc759888
82. S1442
83. Akos005145705
84. Tox21_112241_1
85. Ccg-100941
86. Cs-1227
87. Db00582
88. Hy-w337569
89. Ks-1157
90. Nc00191
91. Nsc 759888
92. Ncgc00164622-02
93. Ncgc00164622-04
94. Ncgc00164622-06
95. Ncgc00260835-01
96. Bv164532
97. Hy-76200
98. ( Inverted Exclamation Marka)-voriconazole
99. Voriconazole Related Compound A Rs [usp]
100. Cs-0448910
101. Sw197571-2
102. V0116
103. C07622
104. D00578
105. Ab00639948-04
106. Ab00639948-06
107. Ab00639948_07
108. Ab00639948_08
109. Voriconazole Related Compound A [usp-rs]
110. Voriconazole, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
111. 234v629
112. A807215
113. Q412236
114. J-006986
115. Voriconazole Related Compound A [usp Impurity]
116. Z2616414875
117. Voriconazole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
118. Voriconazole, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
119. (2r,3s)-2,3-bis(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
120. 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoropyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) Butan-2-ol
121. 4-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methylene]-1-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-5-one
122. Voriconazole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard: Certified Reference Material
123. (.alpha.r,.beta.s)-a-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-.beta.-methyl-.alpha.-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-pyrimidineethanol
124. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluoro-phenyl)-3-(5-fluoro-pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-[1,2,4]triazol-1-yl-butan-2-ol
125. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoro-4-pyrimidinyl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) Butan-2-ol
126. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoro-4-pyrimidinyl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-butanol
127. (2r,3s)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoro-4-pyrimidinyl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
128. 2r,3s-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(5-fluoropyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol-4-pyrimidineethanol, ?-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-?-methyl-?-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-,?(?r,?s)-
129. 4-pyrimidineethanol, .alpha.-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-.beta.-methyl-.alpha.-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (.alpha.r,.beta.s)-rel-
130. 4-pyrimidineethanol, A-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-.beta.-methyl-.alpha.-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (.alpha.r,.beta.s)-
131. 4-pyrimidineethanol, Alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-fluoro-beta-methyl-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (alphar,betas)-rel-
| Molecular Weight | 349.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H14F3N5O |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 349.11504457 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 349.11504457 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 448 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vfend |
| PubMed Health | Voriconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | VFEND (voriconazole), a triazole antifungal agent, is available as a lyophilized powder for solution for intravenous infusion, film-coated tablets for oral administration, and as a powder for oral suspension. The structural formula is:Voriconazole... |
| Active Ingredient | Voriconazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; For suspension |
| Route | injection; oral; Iv (infusion); Oral; iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 200mg/5ml; 200mg; 200mg/vial; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Voriconazole |
| PubMed Health | Voriconazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | VFEND (voriconazole), a triazole antifungal agent, is available as a lyophilized powder for solution for intravenous infusion, film-coated tablets for oral administration, and as a powder for oral suspension. The structural formula is:Voriconazole... |
| Active Ingredient | Voriconazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; For suspension |
| Route | Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 200mg/5ml; 200mg; 200mg/vial; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Sandoz; Teva Pharms |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vfend |
| PubMed Health | Voriconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | VFEND (voriconazole), a triazole antifungal agent, is available as a lyophilized powder for solution for intravenous infusion, film-coated tablets for oral administration, and as a powder for oral suspension. The structural formula is:Voriconazole... |
| Active Ingredient | Voriconazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; For suspension |
| Route | injection; oral; Iv (infusion); Oral; iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 200mg/5ml; 200mg; 200mg/vial; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Voriconazole |
| PubMed Health | Voriconazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | VFEND (voriconazole), a triazole antifungal agent, is available as a lyophilized powder for solution for intravenous infusion, film-coated tablets for oral administration, and as a powder for oral suspension. The structural formula is:Voriconazole... |
| Active Ingredient | Voriconazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; For suspension |
| Route | Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 200mg/5ml; 200mg; 200mg/vial; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Sandoz; Teva Pharms |
For the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, cadidemia, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and serious fungal infections caused by Scedosporium apiospermum and Fusarium spp.
FDA Label
Voriconazole is a broad spectrum, triazole antifungal agent and is indicated in adults and children aged 2 years and above as follows:
- treatment of invasive aspergillosis;
- treatment of candidaemia in non-neutropenic patients;
- treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive Candida infections (including C. krusei);
- treatment of serious fungal infections caused by Scedosporium spp. and Fusarium spp.
Voriconazole should be administered primarily to patients with progressive, possibly life-threatening infections.
Prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in high risk allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)
recipients.
Voriconazole, is a broad spectrum, triazole antifungal agent and is indicated in adults and children aged 2 years and above as follows:
- treatment of invasive aspergillosis;
- treatment of in candidaemianon-neutropenic patients;
- treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive Candida infections (including C. krusei);
- Treatment of serious fungal infections caused by Scedosporium spp. and Fusarium spp.
Vfend should be administered primarily to patients with progressive, possibly life-threatening infections.
Prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in high risk allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients.
Voriconazole is a broad-spectrum, triazole antifungal agent and is indicated in adults and children aged two years and above as follows:
- treatment of invasive aspergillosis;
- treatment of candidaemia in non-neutropenic patients;
- treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive Candida infections (including C. krusei);
- Treatment of serious fungal infections caused by Scedosporium spp. and Fusarium spp.
Voriconazole Accord should be administered primarily to patients with progressive, possibly life-threatening infections.
Treatment of candidaemia in non-neutropenic patients, Treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive Candida infections (including C. krusei), Treatment of invasive aspergillosis, Treatment of serious fungal infections caused by Scedosporium spp. and Fusarium spp.
Voriconazole is a fungistatic triazole antifungal used to treat infections by inhibiting fungal growth. It is known to cause hepatotoxic and photosensitivity reactions in some patients.
14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit STEROL 14-DEMETHYLASE. A variety of azole-derived ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS act through this mechanism. (See all compounds classified as 14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors.)
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP3A Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP3A. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP3A Inhibitors.)
J02AC03
J02AC03
J02AC03
J02AC03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J02 - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02A - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02AC - Triazole and tetrazole derivatives
J02AC03 - Voriconazole
Absorption
The oral bioavailability is estimated to be 96% in healthy adults. Population pharmacokinetic studies report a reduced bioavailability pediatric patients with a mean of 61.8% (range 44.664.5%) thought to be due to differences in first-pass metabolism or due to differences in diet. Of note, transplant patients also have reduced bioavailability but this is known to increase with time after transplantation and may be due in part to gastrointestinal upset from surgery and some transplant medications. Tmax is 1-2 hours with oral administration. When administered with a high-fat meal Cmax decreases by 34% and AUC by 24%. pH does not have an effect on absorption of voriconazole. Differences in Cmax and AUC have been observed between healthy adult males and females with Cmax increasing by 83% and AUC by 113% although this has not been observed to significantly impact medication safety profiles.
Route of Elimination
Voriconazole is eliminated via hepatic metabolism with less than 2% of the dose excreted unchanged in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The estimated volume of distribution of voriconazole is 4.6 L/kg. Population pharmacokinetic studies estimate the median volume of distribution to be 77.6 L with the central compartment estimated at 1.07 L/kg Voriconazole is known to achieve therapeutic concentrations in many tissues including the brain, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, and heart.
Clearance
The clearance of voriconazole is estimated to be a mean of 5.25-7 L/h in healthy adults for the linear portion of the drug's kinetics.
Voriconazole undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism through cytochrome enzymes CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4. CYP2C19 mediates N-oxidation with an apparent Km of 14 M and an apparent Vmax of 0.22 nmol/min/nmol CYP2C19. Voriconazole N-oxide is the major circulating metabolite, accounting for 72% of radiolabeled metabolites found. CYP3A4 contributes to N-oxidation with a Km of 16 M and Vmax of 0.05 nmol/min/nmol CYP3A4 as well as 4-hydroxylation with a Km of 11 M and a Vmax of 0.10 nmol/min/nmol CYP3A4. CYP3A5 and CYP3A7 provide minor contributions to N-oxidation and 4-hydroxylation. The N-oxide and 4-hydroxylated metabolites undergo glucuronidation and are excreted through the urine with other minor glucuronidated metabolites.
Voriconazole has known human metabolites that include Hydroxymethyl Voriconazole and Voriconazole N-Oxide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Voriconazole follows non-linear kinetics and has a terminal half-life of elimination which is dose-dependent.
Voriconazole is used to treat fungal infections caused by a variety of organisms but including _Aspergillus spp._ and _Candida spp_. Voriconazole is a triazole antifungal exhibiting fungistatic activity against fungal pathogens. Like other triazoles, voriconazole binds to 14-alpha sterol demethylase, also known as CYP51, and inhibits the demethylation of lanosterol as part of the ergosterol synthesis pathway in yeast and other fungi. The lack of sufficient ergosterol disrupts fungal cell membrane function and limits fungal cell growth. With fungal growth limited, the host's immune system is able to clear the invading organism.