

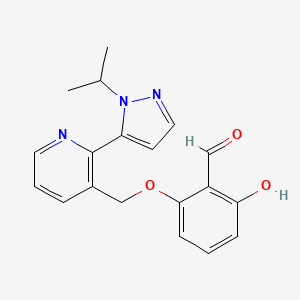

1. 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
2. Gbt440
3. Oxbryta
1. 1446321-46-5
2. Oxbryta
3. Gbt440
4. Gbt 440
5. Gbt-440
6. Gtx-011
7. Hemoglobin Modulators-1
8. Voxelotor [usan]
9. 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
10. 2-hydroxy-6-[[2-(2-propan-2-ylpyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl]methoxy]benzaldehyde
11. Chembl4101807
12. 3zo554a4q8
13. Voxelotor (usan)
14. 2-hydroxy-6-({2-[1-(propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrazol-5-yl]pyridin-3-yl}methoxy)benzaldehyde
15. Benzaldehyde, 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-(1-methylethyl)-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)methoxy)-
16. 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-(propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
17. Oxbryta (tn)
18. Voxelotor [inn]
19. Gbt-440(voxelotor)
20. Voxelotor [mi]
21. Voxelotor [who-dd]
22. Unii-3zo554a4q8
23. Voxelotor [orange Book]
24. Schembl15065529
25. Gtpl10559
26. Voxelotor(gbt440, Gtx011)
27. Dtxsid801027954
28. Bcp20182
29. Ex-a2980
30. Bdbm50235297
31. Zinc145969085
32. Ccg-267884
33. Cs-5317
34. Db14975
35. Sb19656
36. 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
37. Compound 36 [pmid: 28337324]
38. Ac-36867
39. As-57911
40. Da-44587
41. Hy-18681
42. Ft-0702904
43. S8540
44. D11330
45. Gbt-440;gbt440;voxelotor;gtx-011;gtx011;gtx 011
46. 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy) Benzaldehyde
| Molecular Weight | 337.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H19N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 337.14264148 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 337.14264148 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 434 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Voxelotor is indicated to treat sickle cell disease in both adult and pediatric patients aged 4 years and older.
Oxbryta is indicated for the treatment of haemolytic anaemia due to sickle cell disease (SCD) in adults and paediatric patients 12 years of age and older as monotherapy or in combination with hydroxycarbamide.
Voxelotor modifies hemoglobin to prevent painful and dangerous sickle cell crises that normally lead to organ damage, hospitalization, and sometimes death. It prevents low hemoglobin, which is normally associated with the destruction of sickled blood cells in sickle cell disease. Voxelotor has led to up to a 40% increase in hemoglobin in clinical trials.
Hematologic Agents
Drugs that act on blood and blood-forming organs and those that affect the hemostatic system. (See all compounds classified as Hematologic Agents.)
B06AX03
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B06 - Other hematological agents
B06A - Other hematological agents
B06AX - Other hematological agents
B06AX03 - Voxelotor
Absorption
Voxelotor is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a plasma Tmax of 2 hours. Tmax in the red blood cells ranges from 17-24 hours. The Cmax, on average in whole blood and red blood cells occur 6 and 18 hours after an oral dose, respectively. Consumption of a high fat meal with voxelotor significantly increased exposure to the drug during clinical trials. After a daily dose of either 300, 600, or 900 mg for a period of 15 days, when steady-state concentrations were reached, the average RBC Cmax for the respective doses were measured to be 4950, 9610 and 14 000 g*h mL1, respectively.
Route of Elimination
62.6% of the voxelotor dose administered orally as well as its metabolites are found in the feces (with 33.3% as unchanged drug) and 35.5% in urine (with only 0.08% unchanged drug).
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of voxelotor in the central compartment is 338L and 72.2L in the plasma.
Clearance
The apparent oral clearance of voxelotor is approximately 6.7 L/h.
Voxeletor is heavily metabolized via 2 phases. Phase I consists of oxidation and reduction, while phase II consists of glucuronidation. Voseletor is oxidized mainly by CYP3A4, and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 hepatic cytochrome enzymes.
The plasma elimination half-life of voxelotor in sickle cell disease patients is about 35.5 hours, according to the FDA label. The mean half-life in the red blood cell is 60 days. The average plasma half-life of voxelotor was 50 hours in patients with sickle cell disease, compared with 6185 hours in healthy patients, in one clinical study.
Deoxygenated sickle hemoglobin (HbS) polymerization is the causal factor for sickle cell disease. The genetic mutation associated with this disease leads to the formation of abnormal, sickle shaped red blood cells that aggregate and block blood vessels throughout the body, causing vaso-occlusive crises. Voxelotor binds irreversibly with the Nterminal valine of the chain of hemoglobin, leading to an allosteric modification of Hb20, which increases the affinity for oxygen. Oxygenated HbS does not polymerize. By directly blocking HbS polymerization, voxelotor can successfully treat sickle cell disease by preventing the formation of abnormally shaped cells, which eventually cause lack of oxygenation and blood flow to organs.
