
1. 2,3-didehydro-2,4-dideoxy-4-guanidino-n-acetyl-d-neuraminic Acid
2. 2,3-didehydro-2,4-dideoxy-4-guanidinyl-n-acetylneuraminic Acid
3. 4 Guanidino 2 Deoxy 2,3 Didehydro N Acetylneuraminic Acid
4. 4 Guanidino Neu5ac2en
5. 4-guanidino-2,4-dideoxy-2,3-didehydro-n-acetylneuraminic Acid
6. 4-guanidino-2-deoxy-2,3-didehydro-n-acetylneuraminic Acid
7. 4-guanidino-neu5ac2en
8. 5-acetylamino-2,6-anhydro-4-guanidino-3,4,5-trideoxy-d-galacto-non-enoic Acid
9. Acid, 4-guanidino-2-deoxy-2,3-didehydro-n-acetylneuraminic
10. Gg 167
11. Gg-167
12. Gg167
13. Relenza
1. 139110-80-8
2. Relenza
3. 4-guanidino-neu5ac2en
4. Gana
5. Zanamavir
6. Gg167
7. Gg-167
8. Gr 121167x
9. Gr-121167x
10. 4-guanidino-2,4-dideoxy-2,3-dehydro-n-acetylneuraminic Acid
11. Zanamivir (relenza)
12. Relenza (tn)
13. 5-acetamido-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-4-guanidino-d-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid
14. Chembl222813
15. L6o3xi777i
16. (2r,3r,4s)-3-acetamido-4-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
17. Zmr
18. Chebi:50663
19. 139110-80-8 (free Base)
20. Modified Sialic Acid
21. Gr-121167
22. Dsstox_cid_3749
23. Zanamivirhydrate
24. Dsstox_rid_77184
25. Dsstox_gsid_23749
26. 5-(acetylamino)-2,6-anhydro-4-carbamimidamido-3,4,5-trideoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid
27. Gg 167
28. (2r,3r,4s)-3-(acetylamino)-4-carbamimidamido-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
29. Gana (inhibitor)
30. Cas-139110-80-8
31. 4-guanidino-neueac2en
32. Unii-l6o3xi777i
33. Zanamivi
34. Zanamivir [usan:inn:ban]
35. Hsdb 7437
36. 2qwe
37. Ncgc00164561-01
38. (2r,3r,4s)-3-acetamido-4-guanidino-2-((1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
39. (2r,3r,4s)-3-acetamido-4-guanidino-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
40. D-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid, 5-(acetylamino)-4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-
41. D-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid, 5-(acetylamino)-4-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-
42. Zanamivir (hydrate)
43. Gr121167x
44. Mfcd00866966
45. 1a4g
46. Zanamivir (usp/inn)
47. Zanamivir [inn]
48. Zanamivir [mi]
49. Zanamivir [hsdb]
50. Zanamivir [usan]
51. Zanamivir [vandf]
52. Zanamivir [mart.]
53. Schembl9501
54. Zanamivir [usp-rs]
55. Zanamivir [who-dd]
56. Gna
57. Bidd:gt0349
58. Bdbm4934
59. Zanamivir [orange Book]
60. Dtxsid0023749
61. Zanamivir, >=98% (hplc)
62. Zanamivir [usp Monograph]
63. Zinc3918138
64. Tox21_112190
65. Bdbm50330326
66. S3007
67. Akos015841013
68. Akos015994539
69. Tox21_112190_1
70. Bs-1017
71. Ccg-267828
72. Cs-0631
73. Db00558
74. Ncgc00164561-02
75. Ncgc00164561-08
76. Ncgc00164561-11
77. (2r,3r,4s)-3-acetamido-4-((diaminomethylene)amino)-2-((1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
78. 5-(acetylamino)-4-{[amino(imino)methyl]amino}-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid
79. Hy-13210
80. Z0023
81. C08095
82. C72554
83. D00902
84. Ab01566897_01
85. 110z808
86. A807485
87. Q146075
88. Q-201942
89. Zanamivir, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
90. Zanamivir For Assay, Europepharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
91. Zanamivir For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
92. (2r,3r,4s)-4-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-3-acetamido-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
93. (2r,3r,4s)-4-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-3-acetamido-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid Hydrate
94. (2r,3r,4s)-4-carbamimidamido-3-acetamido-2-[(1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-6-carboxylic Acid
95. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetamido-4-(diaminomethyleneamino)-6-((1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
96. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-((1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxy-propy)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
97. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-((1r,2r)-1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
98. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-((1r,3r)-1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
99. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-((r)-1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
100. (4s,5r,6r)-5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
101. 4-diaminomethylamino-3-methylcarboxamido-2-(1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-(3r)-3,4-dihydro-2h-6-pyrancarboxylic Acid(zanamivir)
102. 4-guanidino-2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-n-acetyl-neuraminic Acid; 4-guanidino-neu5ac2en; Modified Sialic Acid
103. 5-acetamido-2,6-anhydro-4-carbamimidamido-3,4,5-trideoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid
104. 5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
105. 5-acetylamino-4-guanidino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid(zanamivir)
106. 5-formylamino-4-guanidino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxy-propyl)-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyran-2-carboxylic Acid
107. D-glycero-d-galacto-non-2-enonic Acid, 5-(acetylamino)-4-(aminoiminomethyl)amino)-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-
| Molecular Weight | 332.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H20N4O7 |
| XLogP3 | -3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 332.13319899 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 332.13319899 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 201 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 518 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Relenza |
| PubMed Health | Zanamivir (By breathing) |
| Drug Classes | Antiviral |
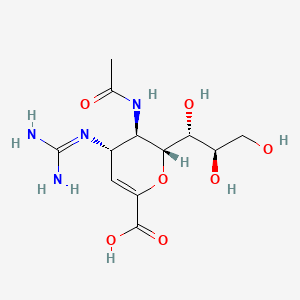
| Drug Label | The active component of RELENZA is zanamivir. The chemical name of zanamivir is 5-(acetylamino)-4-[(aminoiminomethyl)-amino]-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-enonic acid. It has a molecular formula of C12H20N4O7 and a molecular we... |
| Active Ingredient | Zanamivir |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Glaxosmithkline |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Relenza |
| PubMed Health | Zanamivir (By breathing) |
| Drug Classes | Antiviral |
| Drug Label | The active component of RELENZA is zanamivir. The chemical name of zanamivir is 5-(acetylamino)-4-[(aminoiminomethyl)-amino]-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-enonic acid. It has a molecular formula of C12H20N4O7 and a molecular we... |
| Active Ingredient | Zanamivir |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Glaxosmithkline |
Antiviral Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Zanamivir (139110-80-8), MESH Heading. Available from, as of March 15, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
At this time, CDC recommends the use of oseltamivir or zanamivir for the treatment of infection with swine influenza (H1N1) viruses.
CDC; Interim Guidance on Antiviral Recommendations for Patients with Confirmed or Suspected Swine Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection and Close Contacts; Available at https://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/recommendations.htm as of April 27, 2009-04-27. CDC; Health Advisory - Investigation and Interim Recommendations: Swine Influenza (H1N1); Available at https://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/pdf/HAN_042509.pdf as of April 27, 2009
MEDICATION: Antiviral; Influenza viral neuraminidase inhibitor
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1807
Zanamivir is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated acute illness due to influenza A virus in adults and children 7 years and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 2 days. Zanamivir must be started within 48 hours after the onset of influenza symptoms. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ZANAMIVIR (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Swine influenza (H1N1) viruses contain a unique combination of gene segments that have not been reported previously among swine or human influenza viruses in the US or elsewhere. The H1N1 viruses are resistant to amantadine and rimantadine but not to oseltamivir or zanamivir.
CDC; Interim Guidance on Antiviral Recommendations for Patients with Confirmed or Suspected Swine Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection and Close Contacts; Available at https://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/recommendations.htm as of April 27, 2009-04-27. CDC; Health Advisory - Investigation and Interim Recommendations: Swine Influenza (H1N1); Available at https://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/pdf/HAN_042509.pdf as of April 27, 2009
Bronchospasm and decline in lung function have been reported in some patients receiving relenza. Many but not all of these patients had underlying airways disease such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Because of the risk of serious adverse events and because efficacy has not been demonstrated in this population, /zanamivir/ is not generally recommend for treatment of patients with underlying airways disease. Some patients with serious adverse events during treatment with /zanamivir/ have had fatal outcomes, although causality was difficult to assess. /Zanamivir/ should be discontinued in any patient who develops bronchospasm or decline in respratory function; immediate treatment and hospitalization may be required. Some patients without prior pulmonary disease may also have respiratory abnormalities from acute respiratory infection that could resemble adverse drug reactions or increase patient vulnerability to adverse drug reactions.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1526
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: B /NO EVIDENCE OF RISK IN HUMANS. Adequate, well controlled studies in pregnant women have not shown increased risk of fetal abnormalities despite adverse findings in animals, or, in the absence of adequate human studies, animal studies show no fetal risk. The chance of fetal harm is remote but remains a possibility./
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
Adverse effects occurring in 1-3% or more of adults and children 12 years of age or older include diarrhea; nausea; vomiting; nasal signs and symptoms; bronchitis; sinusitis; cough; ear, nose, and throat infections; headache; and dizziness. No adverse effect occurred at an incidence greater than 3%. Adverse effects occurring in up to 5% of children 5-12 years of age include ear, nose, and throat infections; vomiting; nausea; and diarrhea. Some adverse effects may be secondary to lactose vehicle inhalation. Bronchospasm and allergic-like reactions, including oropharyngeal edema and serious rash, have been reported. Unlike amantadine and rimantadine, neuraminidase inhibitors like zanamivir do not appear to adversely affect the CNS.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 769
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ZANAMIVIR (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
FDA Label
Dectova is indicated for the treatment of complicated and potentially life-threatening influenza A or B virus infection in adult and paediatric patients (aged 6 months) when:
- The patients influenza virus is known or suspected to be resistant to anti-influenza medicinal products other than zanamivir, and/or
- Other anti-viral medicinal products for treatment of influenza, including inhaled zanamivir, are not suitable for the individual patient.
Dectova should be used in accordance with official guidance.
Prevention of influenza, Treatment of influenza
Zanamivir, an antiviral agent, is a neuraminidase inhibitor indicated for treatment of uncomplicated acute illness due to influenza A and B virus in adults and pediatric patients 7 years and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 2 days. Zanamivir has also been shown to significantly inhibit the human sialidases NEU3 and NEU2 in the micromolar range (Ki 3.7 +/-0.48 and 12.9+/-0.07 microM, respectively), which could account for some of the rare side effects of zanamivir.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
J05AH01
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AH - Neuraminidase inhibitors
J05AH01 - Zanamivir
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability is very low following oral administration (2%). Following oral inhalation, bioavailability is 4% to 17%.
Route of Elimination
It is excreted unchanged in the urine with excretion of a single dose completed within 24 hours. Unabsorbed drug is excreted in the feces.Zanamivir is renally excreted as unchanged drug.
Clearance
2.5 - 10.9 L/h [Following oral inhalation 10 mg]
5.3 L/h [Normal renal function receiving IV single dose of 4 mg or 2 mg]
2.7 L/h [Patients with mild and moderate renal impairement receiving IV single dose of 4 mg or 2 mg]
0.8 L/h [Patients with severe renal impairement receiving IV single dose of 4 mg or 2 mg]
Protein binding: Very low (<10%).
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
Orally inhaled zanamivir is systemically absorbed, approximately 4% to 17%.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
Elimination: Renal: Excreted unchanged in the urine with excretion of a single dose completed within 24 hours. Total clearance ranges from 2.5 to 10.9 L/hr. Fecal: Unabsorbed drug is secreted in the feces.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
Time to peak effect: 72 hours.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ZANAMIVIR (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Not metabolized
Not metabolized.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991
2.5-5.1 hours
The serum half-life of zanamivir following administration by oral inhalation ranges from 2.5 to 5.1 hours.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1526
The proposed mechanism of action of zanamivir is via inhibition of influenza virus neuraminidase with the possibility of alteration of virus particle aggregation and release. By binding and inhibiting the neuraminidase protein, the drug renders the influenza virus unable to escape its host cell and infect others.
Zanamivir is a potent selective competitive inhibitor of the influenza virus neuraminidase, an enzyme essential for viral replication. Neuraminidase cleaves terminal sialic acid residues from glycoconjugates to enable the release of virus from infected cells, prevent the formation of viral aggragates after release from host cells, and possibly decrease viral inactivation by respiratory mucous.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 769
Zanamivir is a selective inhibitor of influenza A and B virus neuraminidase, possibly altering particle aggregation and release.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 2991