
1. 311c90
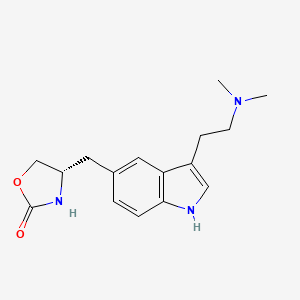
2. 4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
3. Ascotop
4. Flezol
5. Zomig
6. Zomigoro
1. 139264-17-8
2. Zomig
3. Zomigoro
4. 311c90
5. Zomigon
6. Flezol
7. Zomig-zmt
8. C16h21n3o2
9. Bw-311c90
10. (s)-4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)oxazolidin-2-one
11. Zolmitriptan (zomig)
12. (s)-4-[3-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-1h-indol-5-ylmethyl]-oxazolidin-2-one
13. Nsc-760383
14. Cvt-427
15. 2fs66th3yw
16. Chembl1185
17. (s)-4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
18. Chebi:10124
19. (s)-4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
20. (4s)-4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
21. Zomig Nasal Spray
22. Zomig Zmt
23. Ascotopand
24. Ascotop
25. Zolmitriptan [usan]
26. 4-[[3-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]oxazolidin-2-one
27. (4s)-4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]-2-oxazolidinone
28. (s)-4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]-2-oxazolidinone
29. (4s)-4-({3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl}methyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
30. 2-oxazolidinone, 4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-, (s)-
31. Dsstox_cid_25933
32. Dsstox_rid_81232
33. Dsstox_gsid_45933
34. 311-c-90
35. Zipton
36. Zolmitriptane
37. Zolmitriptanum
38. Zominat
39. Rapimelt
40. (4s)-4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
41. Smr000449310
42. Cas-139264-17-8
43. Zomig (tn)
44. Zolmitriptan Rapidfilm
45. Unii-2fs66th3yw
46. 4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
47. Zolmitriptan [usan:inn:ban]
48. Ncgc00095155-01
49. Mfcd00871503
50. Ks-5072
51. Spectrum2_000728
52. Zolmitriptan [mi]
53. Zolmitriptan [inn]
54. Zolmitriptan [jan]
55. Gtpl60
56. (4s)-4-[[3-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
57. Zolmitriptan [vandf]
58. Schembl33336
59. Zolmitriptan [mart.]
60. Mls000758208
61. Mls001424172
62. Bidd:gt0040
63. Spectrum1505281
64. Zolmitriptan [usp-rs]
65. Zolmitriptan [who-dd]
66. Spbio_000656
67. Zolmitriptan (jan/usp/inn)
68. Dtxsid8045933
69. Zinc15515
70. Zolmitriptan, >=98% (hplc)
71. Hms1922b04
72. Hms2052k17
73. Hms2093o14
74. Hms2235i22
75. Hms3714h11
76. Hms3884a06
77. Pharmakon1600-01505281
78. Zolmitriptan [orange Book]
79. Zolmitriptan [ep Monograph]
80. Act04392
81. Bcp10513
82. Hy-b0229
83. Tox21_111455
84. Zolmitriptan [usp Monograph]
85. Bdbm50033383
86. Ccg-38993
87. Nsc760383
88. S1649
89. Akos015850706
90. Tox21_111455_1
91. Db00315
92. Nc00382
93. Nsc 760383
94. (s)-n,n-dimethyl-2-[5-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-4-ylmethyl)-1h-indol-3-yl]ethylamine
95. Ncgc00263884-02
96. Ncgc00263884-03
97. Ncgc00263884-08
98. Bz164590
99. Bw-311c90;311c90
100. Sbi-0206762.p001
101. B2261
102. Sw197762-2
103. Z0024
104. 64z178
105. C07218
106. D00415
107. Ab00698244-05
108. Ab00698244_06
109. Q218820
110. Sr-05000001693
111. J-007257
112. Sr-05000001693-1
113. Zolmitriptan, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
114. (4s)-4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl-2-oxazolidinone
115. (s)-4-{3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-ylmethyl}oxazolidin-2-one
116. (4s)-4-((3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl) -1h-indol-5-yl)methyl)-2-oxazolidinone
117. (s) -n,n-dimethyl-2- [5- (2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-4-ylmethyl) -1h -indol-3-yl]ethylamine
118. (s)-4-({3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl}methyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
119. (s)-n,n-dimethyl-2-[5-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-4-ylmethyl)-1h -indol-3-yl]ethylamine
120. 2-oxazolidinone, 4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1h-indol-5-yl]methyl]-, (4s)-
121. 139264-25-8
122. Zmt
| Molecular Weight | 287.36 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H21N3O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 287.16337692 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 287.16337692 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 57.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 375 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zolmitriptan |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Apotex; Teva Pharms Usa; Invagen Pharms; Sun Pharma Global; Glenmark Generics; Zydus Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zomig |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan (Into the nose) |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Spray |
| Route | Oral; Nasal |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 2.5mg/spray; 5mg; 5mg/spray |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipr; Astrazeneca |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zomig-zmt |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zolmitriptan |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Apotex; Teva Pharms Usa; Invagen Pharms; Sun Pharma Global; Glenmark Generics; Zydus Pharms Usa |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zomig |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan (Into the nose) |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Spray |
| Route | Oral; Nasal |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 2.5mg/spray; 5mg; 5mg/spray |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipr; Astrazeneca |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zomig-zmt |
| PubMed Health | Zolmitriptan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antimigraine |
| Drug Label | ZOMIG (zolmitriptan) Tablets and ZOMIG-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain zolmitriptan, which is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist. Zolmitriptan is chemically designated as (S)-4-[[3-[2-(dime... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolmitriptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
Zolmitriptan is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without auras in patients aged 18 and over.
FDA Label
Zolmitriptan, like other triptans, is a serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) receptor agonist, with enhanced specificity for the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes. It is through the downstream effects of 5-HT1B/1D activation that triptans are proposed to provide acute relief of migraines. Zolmitriptan is also a vasoconstrictor, leading to possible adverse cardiovascular effects such as myocardial ischemia/infarction, arrhythmias, cerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage, stroke, gastrointestinal ischemia, and peripheral vasospastic reactions. In addition, chest/throat/neck/jaw pain, tightness, and/or pressure has been reported, along with the possibility of medication overuse headaches and serotonin syndrome. Patients with phenylketonuria should be advised that ZOMIG-ZMT contains phenylalanine.
Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that specifically stimulate SEROTONIN 5-HT1 RECEPTORS. Included under this heading are agonists for one or more of the specific 5-HT1 receptor subtypes. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists.)
N02CC03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02C - Antimigraine preparations
N02CC - Selective serotonin (5ht1) agonists
N02CC03 - Zolmitriptan
Absorption
Zolmitriptan tablets have a mean absolute oral bioavailability of approximately 40%, with food having no effect on the rate or extent of absorption. The dosing kinetics are linear over a range of 2.5 to 50 mg with 75% of the eventual Cmax being attained within 1 hour of dosing. The median Tmax for the tablet form is 1.5 hours, while for the orally disintegrating tablet form, it is 3 hours. The AUC across studies was in the range of 84.4-173.8 ng/mL*h while the Cmax was between 16 and 25.2 ng/mL. Zolmitriptan administered as a nasal spray is detected in the plasma within 2-5 minutes, compared to 10-15 minutes for the tablet form; the faster kinetics likely reflect fast absorption across the nasal mucosa. The bioavailability compared to the tablet is 102%, and plasma zolmitriptan concentration is maintained for 4-6 hours after intranasal delivery. The active N-desmethyl metabolite of zolmitriptan has a mean plasma concentration that is roughly two-thirds of zolmitriptan, regardless of dosage route or concentration.
Route of Elimination
Zolmitriptan is primarily excreted in urine (approximately 65%) and feces (approximately 30%). Within urine, the most common form is the indole acetic acid metabolite (31%), followed by the N-oxide (7%), and N-desmethyl (4%) metabolites; the majority of zolmitriptan recovered in feces remains unchanged.
Volume of Distribution
Zolmitriptan has a volume of distribution between 7 and 8.4 L/kg.
Clearance
Zolmitriptan has a clearance of 31.5 mL/min/kg for oral tablets and 25.9 mL/min/kg for nasal administration; one-sixth of the clearance is renal.
Zolmitriptan is metabolized in the liver, and studies using cytochrome P450 inhibitors like [cimetidine] suggest that it is likely metabolized by CYP1A2, as well as by monoamine oxidase (MAO). Zolmitriptan metabolism results in three major metabolites: an active N-desmethyl metabolite (183C91) as well as inactive N-oxide (1652W92) and indole acetic acid (2161W92) metabolites.
Zolmitriptan has known human metabolites that include N-Desmethylzolmitriptan and Zolmitriptan N-oxide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Zolmitriptan has a mean elimination half-life of approximately three hours, while its active N-desmethyl metabolite has a slightly longer (approximately 3.5 hours) half-life.
Migraines are complex physiological events characterized by unilateral throbbing headaches combined with photophobia and other aversions to sensory input. Migraine attacks are generally divided into phases: the premonitory phase, which typically involves irritability, fatigue, yawning, and stiff neck; the headache phase, which lasts for between four and 72 hours; and the postdrome phase, which lasts for up to a day following resolution of pain and whose symptoms are similar to those of the premonitory phase. In addition, neurological deficits, collectively termed migraine aura, may precede the headache phase. The underlying pathophysiology of migraines is a matter of active research but involves both neurological and vascular components. The head pain associated with migraine is thought to be a consequence of activation of the nociceptive nerves comprising the trigeminocervical complex (TCC). Terminals of nociceptive nerves that innervate the dura matter release vasoactive peptides, such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), resulting in cranial vasodilation. Finally, when present, migraine aura appears to correlate with a transient wave(s) of cortical depolarization, termed cortical spreading depression (CSD). Triptans, including zolmitriptan, are proposed to act in three ways. The main mechanism is through modulation of nociceptive nerve signalling in the central nervous system through 5-HT1B/1D receptors throughout the TCC and associated areas of the brain. In addition, triptans can enhance vasoconstriction, both through direct 5-HT1B-mediated dilation of cranial blood vessels, as well as through 5-HT1D-mediated suppression of CGRP release. Although triptans are classically described solely in terms of their effects on 5-HT1B/1D receptors, they also act as 5-HT1F agonists as well. This 5-HT subtype is also found throughout the TCC, but is not present appreciably in cerebral vasculature; the significance of triptan-mediated 5-HT1F activation is currently not well described. Additionally, CSD that initiates in the ipsilateral parietal region may exert its effects in a manner that relies on 5-HT1B/1D receptor activation, suggesting that triptans may have some effect on CSD-mediated symptoms.