
1. Ambien
2. Amsic
3. Bikalm
4. Dalparan
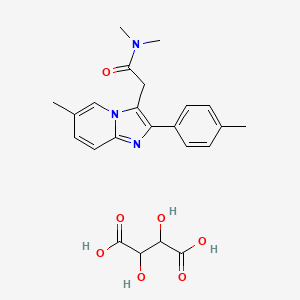
5. Imidazo(1,2-a)pyridine-3-acetamide, N,n,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)-
6. N,n,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo(1,2a)pyridine-3-acetamide Hemitartrate
7. Sl 80.0750
8. Sl 800750 23 N
9. Sl-800750-23-n
10. Stilnoct
11. Stilnox
12. Zodormdura
13. Zoldem
14. Zolirin
15. Zolpi Lich
16. Zolpi-lich
17. Zolpidem
18. Zolpidem 1a Pharma
19. Zolpidem Abz
20. Zolpidem Hemitartrate
21. Zolpimist
22. Zolpinox
1. 99294-93-6
2. Zolpidem Tartarate
3. Schembl40721
4. Mls001401453
5. N,n-dimethyl-2-(6-methyl-2-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetamide 2,3-dihydroxysuccinate
6. Chembl1723343
7. Hms2051h09
8. Hms2232g04
9. Hms3374c07
10. Hms3393h09
11. 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic Acid; N,n-dimethyl-2-[6-methyl-2-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl]acetamide
12. Act03353
13. Bcp28267
14. Bcp28445
15. Mfcd00214408
16. Akos016013007
17. Ab04867
18. Ccg-100938
19. Nc00188
20. Smr000469145
21. Db-057774
22. Sl 80.0750
23. Z-6100
24. Sublinox; Bikalm; Zolpidem Mr;103188-50-7
25. A845992
| Molecular Weight | 457.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H27N3O7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 457.18490021 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 457.18490021 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 153 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 551 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zolpidem tartrate |
| Drug Label | Zolpidem tartrate extended-release tablets, USP contain zolpidem tartrate, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A agonist of the imidazopyridine class. Zolpidem tartrate extended-release tablets are available in 6.25 mg and 12.5 mg strength tablets for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolpidem tartrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 6.25mg; 10mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Synthon Pharms; Wockhardt; Anchen Pharms; Ranbaxy; Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Invagen Pharms; Cipla; Roxane; Hikma; Actavis Elizabeth; Lek Pharms Dd; Vintage; Carlsbad; Mylan |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zolpidem tartrate |
| Drug Label | Zolpidem tartrate extended-release tablets, USP contain zolpidem tartrate, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A agonist of the imidazopyridine class. Zolpidem tartrate extended-release tablets are available in 6.25 mg and 12.5 mg strength tablets for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Zolpidem tartrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 6.25mg; 10mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Synthon Pharms; Wockhardt; Anchen Pharms; Ranbaxy; Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Invagen Pharms; Cipla; Roxane; Hikma; Actavis Elizabeth; Lek Pharms Dd; Vintage; Carlsbad; Mylan |
Zolpidem is indicated for short-term treatment of insomnia. A decrease in sleep latency and increase in the duration of sleep for up to 5 weeks have been demonstrated in controlled clinical studies with zolpidem. Failure of insomnia to remit after 7 to 10 days of treatment may indicate the presence of a primary psychiatric or medical illness. Worsening of insomnia or the emergence of new abnormalities of thinking or behavior may be the consequence of an unrecognized psychiatric or physical disorder. /Included in US product labeling/ /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 2987
Selective benzodiazepine receptor agonist not related chemically to benzodiazepines; sedative; hypnotic. /Salt not specified/
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1816
... A case of antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism that was managed with zolpidem /was reported/. ... A 34-yr-old white man who had had antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism with symptoms of repetitive persistent gross tremors of the hands for numerous years was unresponsive to traditional antiparkinsonian medications. With the initiation of zolpidem ... the tremors decreased significantly. ... When zolpidem was started ..., the motor exam score on the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale decreased from 29 at baseline to a score of 9 after one month of use. After 4 months of zolpidem use, the patient's mental status decompensated, & clozapine was initiated. As the patient experienced excessive sedation, zolpidem was discontinued while clozapine was maintained to help with the psychosis &, potentially, the tremors. The tremors reemerged with a motor exam score of 30. Zolpidem was reinitiated ..., & the patient's tremors have been stable for 2 years. ... Further investigation is needed to study the use of nontraditional medications in patients requiring ...antipsychotic medication who have refractory parkinsonian symptoms. /Salt not specified/
PMID:11302407 Farver DK, Khan MH; Ann Pharmacother 35(4): 435-437 (2001)
1. A new imidazo-pyridine hypnotic (zolpidem 10 mg and 20 mg) was compared with placebo as premedication before general anaesthesia in female patients undergoing minor gynaecological surgery. Efficacy and tolerance before and after anaesthesia were assessed. Psychomotor testing was used to study recovery from anaesthesia. 2 Both doses of zolpidem produced good sedation pre-operatively but only the higher dose was associated with anterograde amnesia. 3 Premorbid anxiety scores were low in the group of patients studied and were unaffected by either dose of zolpidem. 4 There were no significant effects on the course of anaesthesia. However, postoperatively there was a tendency for wake-up to be delayed in those patients who received either dose of zolpidem. 5 Postoperative recovery, as indicated by tests of psychomotor performance, was noticeably delayed with a dose of 20 mg compared with placebo whilst psychomotor performance had returned towards baseline levels 3 h after wake-up in those patients who had received placebo. The zolpidem 10 mg group was intermediate. 6 Zolpidem may be a suitable premedicant when hypnosis and amnesia only are required. /Salt not specified/
PMID:2887188 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1386284 Cashman JN, et al; Br J Clin Pharmacol 24 (1): 85-92 (1987)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Its half-life in plasma is approx 2 hr in individuals with normal hepatic blood flow or function. This value may be increased twofold or more in those with cirrhosis, & it also tends to be greater in older patients; adjustment of dosage often is necessary in both categories of patients. ... The elimination of the drug is slower in patients with chronic renal insufficiency, largely owing to an incr in its apparent volume of distribution. /Salt not specified/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 412
Headache, drowsiness, and dizziness were the most frequent adverse nervous system effects of zolpidem during short-term (up to 10 days) treatment or prolonged therapy (45 weeks) with the drug at recommended doses in clinical trials, and among the most frequent adverse effects requiring discontinuance of the drug. Headache occurred in 7% of patients receiving short-term (up to 10 days) treatment with zolpidem at recommended doses and 6% of those receiving placebo, and in 19% of those receiving prolonged therapy (45 weeks) with the drug at recommended doses and 22% of those receiving placebo. ... Drowsiness occurred in 2% of patients receiving short-term (up to 10 days) treatment with zolpidem at recommended doses, in 8% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (45 weeks) with the drug at recommended doses, and in 5% of those receiving placebo. ... Dizziness occurred in 1% of patients receiving short-term (up to 10 days) treatment with zolpidem at recommended doses, in 5% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (45 weeks) with the drug at recommended doses, and in 1% of those receiving placebo. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2432
Diarrhea was one of the most frequent adverse effects of short-term (up to 10 days) treatment with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials, occurring in 1% of patients. Diarrhea occurred in 3% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (4-5 weeks) with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials and in 2% of those receiving placebo. Nausea occurred in 2 and 6% of patients receiving short-term (up to 10 days) treatment or prolonged therapy (4-5 weeks), respectively, with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials, and in 3 and 6%, respectively, of those receiving placebo. Dry mouth occurred in 3% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (4-5 weeks) with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials and in 1% of those receiving placebo. ... Vomiting occurred in 1% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (4-5 weeks) with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials, the same frequency as in those receiving placebo ... /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2432
Palpitation was reported in 2% of patients receiving prolonged therapy (4-5 weeks) with zolpidem at recommended doses in clinical trials. Cerebrovascular disorder, hypertension, postural hypotension, edema, chest pain, syncope, and tachycardia have been reported in 0.1-1% of patients, and arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia, extrasystoles, arteritis, circulatory failure, hypotension, flushing, aggravated hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, phlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary or facial edema, and varicose veins have been reported in <0.1% of patients receiving zolpidem. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2433
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
GABA-A Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that bind to and activate GABA-A RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as GABA-A Receptor Agonists.)
Sleep Aids, Pharmaceutical
Drugs used to induce SLEEP, prevent SLEEPLESSNESS, or treat SLEEP INITIATION AND MAINTENANCE DISORDERS. (See all compounds classified as Sleep Aids, Pharmaceutical.)
A peak blood level of 200 ng/mL was reached 30 min after oral admin of 20 mg zolpidem. After oral admin zolpidem is rapidly & completely absorbed from the GI tract. Although some first-pass biotransformation of the drug results in a bioavailability of about 70%, after doses of 7-20 mg, zolpidem is 92% bound to plasma proteins. The apparent volume of distribution after a 5 mg iv dose was 0.5 L/kg. Brain concns reach one third to one half of those achieved in the plasma. Zolpidem is completely metabolized. <1% of an admin dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Three metabolites have been identified but have no pharmacologic activity after an 8 mg iv dose. Systemic clearance of zolpidem was 0.26 L/kg/g & the elimination half-life was 1.5 hr. /Salt not specified/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 707
The excretion of zolpidem in breast milk represents 0.004 to 0.019% of an admin dose. /Salt not specified/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 707
Zolpidem is eliminated almost entirely by conversion to inactive products in the liver, largely through oxidation of the methyl groups on the phenyl & imidazopyridine rings to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Its half-life in plasma is approx 2 hr in individuals with normal hepatic blood flow or function. This value may be increased twofold or more in those with cirrhosis, & it also tends to be greater in older patients; adjustment of dosage often is necessary in both categories of patients. Although little or no unchanged zolpidem is found in the urine, the elimination of the drug is slower in patients with chronic renal insufficiency, largely owing to an incr in its apparent volume of distribution. /Salt not specified/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 412
Solid dispersions & physical mixtures of Zolpidem in polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000) & 6000 (PEG 6000) were prepared with the aim to incr its aqueous solubility. ... Physical determinations/revealed/ no drug-polymer interactions ... Both solubility & dissolution rate of the drug in these formulations were increased. Each individual dissolution profile of PEG based formulation fitted Baker-Lonsdale & first order kinetic models. Finally, significant differences in ataxic induction time were observed between Zolpidem orally administered as suspension of drug alone & as solid dispersion or physical mixture. These formulations, indeed, showed almost 2- to 3-fold longer ataxic induction times suggesting that, in the presence of PEG, the intestinal membrane permeability is probably the rate-limiting factor of the absorption process. /Salt not specified/
PMID:10425358 Trapani G, et al; Int J Pharm 184(1): 121-130 (1999)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... Zopiclone & zolpidem are used primarily as hypnotics. Both are extensively metabolized; N-demethylation, N-oxidation, & decarboxylation of zopiclone occur, & zolpidem undergoes oxidation of methyl groups & hydroxylation of a position on the imidazolepyridine ring system. ... Since CYP3A4 has been reported to play an important role in metab of zolpidem, possible interactions with drugs which are substrates &/or inhibitors of that CYP isozyme should be considered. /Salt not specified/
PMID:10379424 Chouinard G, et al; Cell Mol Neurobiol 19(4): 533-552 (1999)
Its half-life in plasma is approx 2 hr in individuals with normal hepatic blood flow or function. This value may be increased twofold or more in those with cirrhosis, & it also tends to be greater in older patients ... . /Salt not specified/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 412
Nursing mothers: Studies in lactating mothers indicate that the half-life of zolpidem is similar to that in young normal volunteers (2.6 + or - 0.3 hr). /Salt not specified/
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference 56th ed p.3193 (2002)
Carvedilol ... has a terminal half-life of 7-10 hr, but most of the drug is eliminated with a half-life of about 2 hr.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 255
Imidazopyridines are thought to interact with the same GABA receptor/chloride channel complex as the benzodiazepines by high affinity with the "central-type" benzodiazepine receptors. Like the benzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, zolpidem appears to potentiate GABAergic transmission, thus increasing the frequency of chloride channel opening, resulting in the inhibition of neuronal excitation. Zolpidem appears to cause only sedation, but is devoid of significant myorelaxant, anxiolytic, & anticonvulsant activity. It also appears to be free of monoaminergic & histaminergic activity. Benzodiazepines exert both their clinical & side effects through nonselective interaction with a family of benzodiazepine recognition sites on neuronal membranes. One of these sites, the so-called benzodiazepine or omega site, appears to mediate sedation, whereas other sites may mediate anticonvulsant anxiolytic & other effects. Zolpidem appears to be relatively selective for the omega site. /Salt not specified/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 707
Mutagenesis: Zolpidem did not have mutagenic activity in several tests including the Ames test, genotoxicity in mouse lymphoma cells in vitro, chromosomal aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes, unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes in vitro, and the micronucleus test in mice. /Salt not specified/
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference 56th ed p.3193 (2002)
... Whereas in the recommended dose range zolpidem almost exclusively binds to the alpha(1) subunit of the GABA(A) receptor associated with sleep promotion, in higher doses it also binds the alpha(2), alpha(3) & alpha(5) subunits typically targeted by benzodiazepines & associated with anxiolytic effects. ... /Salt not specified/
PMID:11753748 Goder R, et al; Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 69(12): 592-596 (2001)