
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
API
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
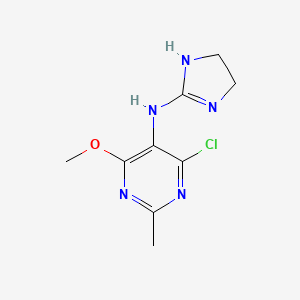

1. 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinamine
2. Be 5895
3. Be-5895
4. Cynt
5. Moxon
6. Moxonidin
7. Normatens
8. Physiotens
1. 75438-57-2
2. Norcynt
3. Nucynt
4. 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidin-5-amine
5. Cynt
6. Be 5895
7. 4-chloro-n-imidazolidin-2-ylidene-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidin-5-amine
8. Bdf5895
9. Bdf 5895
10. Lomox
11. Be-5895
12. 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinamine
13. Ly 326869
14. Bdf5896
15. Be5895
16. Cc6x0l40gw
17. Ly326869
18. 5-pyrimidinamine, 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-
19. Chembl19236
20. Chebi:7009
21. 4-chloro-5-(2-imidazolin-2-ylamino)-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidine
22. 75438-57-2 (free Base)
23. Bdf-5896
24. Ncgc00015649-02
25. Normoxocin
26. Ly-326869
27. Cas-75438-57-2
28. 4-chloro-5-(2-imidazolidinyldeneamino)-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidine
29. Dsstox_cid_25170
30. Dsstox_rid_80720
31. Dsstox_gsid_45170
32. Moxonidinum [latin]
33. Moxonidina [spanish]
34. Moxonidina
35. Moxonidinum
36. 4-chloro-n-(imidazolidin-2-ylidene)-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidin-5-amine
37. Moxonidine Hydrochloride Hydrate
38. Moxonidine [inn]
39. Bdf-5895
40. Unii-cc6x0l40gw
41. Moxonidine [usan:inn:ban]
42. N-(4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)imidazolidin-2-imine
43. Sr-01000075981
44. Cynt (tn)
45. Moxonidine [mi]
46. Moxonidine (usan/inn)
47. Prestwick0_001016
48. Prestwick1_001016
49. Prestwick2_001016
50. Prestwick3_001016
51. Lopac-m-1559
52. Moxonidine [usan]
53. Monoxidine [common Misspelling Of Moxonidine]
54. Moxonidine [mart.]
55. Moxonidine [who-dd]
56. Lopac0_000753
57. Schembl49143
58. Bspbio_001171
59. Mls002222183
60. Spbio_003042
61. Bpbio1_001289
62. Dtxsid5045170
63. Moxonidine [ep Monograph]
64. Hms1571k13
65. Hms2098k13
66. Hms2230b15
67. Hms3373o04
68. Hms3655b17
69. Hms3715k13
70. Hms3747a03
71. Moxonidine 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
72. Albb-022451
73. Bcp23003
74. Ex-a3409
75. Hy-b0374
76. Zinc1854466
77. Tox21_110190
78. 2-(6-chloro-4-methoxy-2-methylpyrimidin-5-ylamino)-2-imidazoline
79. 4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(2-imidazolin-2-yl)aminopyrimidine
80. Ac-637
81. Bdbm50050093
82. Mfcd22689455
83. Pdsp1_000177
84. Pdsp2_000176
85. S2066
86. Stl419983
87. Stl450991
88. Akos015895873
89. Akos015997932
90. Tox21_110190_1
91. Af-0062
92. Ccg-204838
93. Db09242
94. Sdccgsbi-0050731.p002
95. Ncgc00015649-01
96. Ncgc00015649-04
97. Ncgc00015649-05
98. Ncgc00015649-08
99. Ncgc00015649-17
100. Ncgc00092355-02
101. Smr000857402
102. Ab00514003
103. Ft-0601601
104. Ft-0657360
105. M2660
106. Sw196502-4
107. C07451
108. D05087
109. Ab00514003-08
110. Ab00514003_10
111. 438m572
112. A838414
113. Q419944
114. Sr-01000075981-7
115. Brd-k77771411-001-04-4
116. (4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-yl)-imidazolidin-2-ylidene-amine
117. 4-chloro-n-(imidazolin-2-ylidene)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinamine
118. 5-pyrimidinamine, 4-chloro-n-2-imidazolidinylidene-6-methoxy-2-methyl-
119. Bdf5895;bdf-5895;bdf 5895;be 5895; Be-5895; Be5895
120. 2-(4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-ylamino)-4,5-dihydro-3h-imidazol-1-ium
121. 5-pyrimidinamine, 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl- (9ci)
122. (2r,4r)-1-[(2s)-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-1-oxo-2-[[(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8- Quinolinyl)sulfonyl]amino]pentyl]-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid
123. 1008754-16-2
124. 4-chloro-n-(4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-amine Hydrochloride;moxonidine
| Molecular Weight | 241.68 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H12ClN5O |
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 241.0730377 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 241.0730377 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 71.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 275 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of mild to moderate essential or primary hypertension. Effective as most first-line antihypertensives when used as monotherapy.
FDA Label
Treatment of hypertension
Antihypertensive agent whose site of action is the Central Nervous System (CNS), specifically involving interactions with I1- imidazoline and alpha-2-adrenergic rececptors within the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RSV).
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C02AC05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02A - Antiadrenergic agents, centrally acting
C02AC - Imidazoline receptor agonists
C02AC05 - Moxonidine
Absorption
90% of an oral dose is absorbed with negligible interference from food intake or first pass metabolism, resulting in a high bioavailability of 88%.
Route of Elimination
Elimination is nearly entirely via the kidneys with a majority (50 -75%) of overall moxonidine being eliminated unchanged through renal excretion. Ultimately, more than 90% of a dose is eliminated by way of the kidneys within the first 24 hours after administration, with only approximately 1% being eliminiated via faeces.
Volume of Distribution
1.80.4L/kg.
Clearance
Administered twice daily due to short half life. However, lower dosage adjustments and close monitoring is necessary in elderly and renal impairment patients due to reduced clearance. In particular, the exposure AUC can increase by about 50% following a single dose and at steady state in elderly patients and moderately impaired renal function with GFR between 30-60 mL/min can cause AUC increases by 85% and decreases in clearence to 52 %.
Biotransformation is unimportant with 10-20% of moxonidine undergoing oxidation reactions to the primary 4,5-dehydromoxonidine metabolite and a guanidine derivative by opening of the imidazoline ring. The antihypertensive effects of these 4,5-dehydromoxonidine and guanidine metabolites are only 1/10 and 1/100 the effect of moxonidine. Oxidation on either the methyl group (pyrimidine ring) or on the imidazole ring of moxonidine results in the formation of the hydroxylmethyl moxonidine metabolite or the hydroxy moxonidine metabolite. The hydroxy moxonidine metabolite can be further oxidized to the dihydroxy metabolite or it can lose water to form the dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite, which itself can be further oxidized to form an N-oxide. Aside from these Phase I metabolites, Phase II metabolism of moxonidine is also evident with the presence of a cysteine conjugate metabolite minus chlorine. Nevertheless, the identification of the hydroxy moxonidine metabolite with a high level of dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite in human urine samples suggests that dehydrogenation from the hydroxy metabolite to the dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite represents the primary metabolic pathway in humans. The cytochromes P450 responsible for the metabolism of moxonidine in humans have not yet been determined. Ultimately, the parent moxonidine compound was observed to be the most abundant component in different biological matrices of urinary excretion samples, verifying that metabolism only plays a modest role in the clearance of moxonidine in humans.
Plasma elimination half life is 2.2 - 2.3 hours while renal elimination half life is 2.6-2.8 hours.
Stimulation of central alpha 2-adrenergic receptors is associated with sympathoadrenal suppression and subsequent reduction of blood pressure. As this class was further explored it was discovered that sympathoadrenal activity can also be suppressed by a second pathway with a newly discovered drug target specific to imidazolines. Specifically, moxonidine binds the imidazoline receptor subtype 1 (I1) and to a lesser extent lpha-2-adrenoreceptors in the RSV causing a reduction of sympathetic activity, reducing systemic vascular resistance and thus arterial blood pressure. Moreover, since alpha-2-adrenergic receptors are considered the primary molecular target that facilitates the most common side effects of sedation and dry mouth that are elicited by most centrally acting antihypertensives, moxonidine differs from these other centrally acting antihypertensives by demonstrating only low affinity for central alpha-2-adrenoceptors compared to the aforementioned I1-imidazoline receptors.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
75
PharmaCompass offers a list of Moxonidine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Moxonidine manufacturer or Moxonidine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Moxonidine manufacturer or Moxonidine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Moxonidine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Moxonidine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Moxonidine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Moxonidine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Moxon manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Moxon, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Moxon manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Moxon API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Moxon manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Moxon supplier is an individual or a company that provides Moxon active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Moxon finished formulations upon request. The Moxon suppliers may include Moxon API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Moxon suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Moxon DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Moxon active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Moxon DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Moxon USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Moxon DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Moxon USDMF includes data on Moxon's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Moxon USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Moxon suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Moxon CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Moxon Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Moxon CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Moxon EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Moxon to their clients by showing that a Moxon CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Moxon CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Moxon CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Moxon CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Moxon DMF.
A Moxon CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Moxon CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Moxon suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Moxon written confirmation (Moxon WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Moxon manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Moxon active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Moxon APIs or Moxon finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Moxon WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Moxon suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Moxon Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Moxon GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Moxon GMP manufacturer or Moxon GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Moxon CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Moxon's compliance with Moxon specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Moxon CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Moxon CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Moxon may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Moxon EP), Moxon JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Moxon USP).
