
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
FDF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA

1. Arginine Hydrochloride
2. Arginine, L Isomer
3. Arginine, L-isomer
4. Dl Arginine Acetate, Monohydrate
5. Dl-arginine Acetate, Monohydrate
6. Hydrochloride, Arginine
7. L Arginine
8. L-arginine
9. L-isomer Arginine
10. Monohydrate Dl-arginine Acetate
1. L-arginine
2. 74-79-3
3. L-(+)-arginine
4. L(+)-arginine
5. L-arg
6. (s)-2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoic Acid
7. H-arg-oh
8. (l)-arginine
9. Arginina
10. Arginine, L-
11. Arginine (van)
12. L-arginin
13. Argininum [inn-latin]
14. Arginina [inn-spanish]
15. L-ornithine, N5-(aminoiminomethyl)-
16. Argamine
17. Argivene
18. Detoxargin
19. Levargin
20. L-alpha-amino-delta-guanidinovaleric Acid
21. Arg
22. Minophagen A
23. 1-amino-4-guanidovaleric Acid
24. Ccris 3609
25. (s)-(+)-arginine
26. Nsc 206269
27. Chebi:16467
28. Hsdb 1429
29. Ai3-24165
30. (s)-2-amino-5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)pentanoic Acid
31. (s)-2-amino-5-guanidinovaleric Acid
32. Brn 1725413
33. L-norvaline, 5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-
34. 2-amino-5-guanidinovaleric Acid
35. Chembl1485
36. (2s)-2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoic Acid
37. (s)-2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]pentanoic Acid
38. (2s)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic Acid
39. 94zla3w45f
40. Pentanoic Acid, 2-amino-5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-, (s)-
41. (2s)-2-amino-5-(carbamimidamido)pentanoic Acid
42. L-arginine, Monohydrochloride
43. Nsc-206269
44. Arginine (l-arginine)
45. R-gene
46. L-norvaline, 5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-
47. (2s)-2-amino-5-carbamimidamidopentanoic Acid
48. Dsstox_cid_21056
49. Dsstox_rid_79618
50. Dsstox_gsid_41056
51. Argininum
52. Pentanoic Acid, 2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-, (s)-
53. Arginine [usan:inn]
54. Cas-74-79-3
55. Arginine [usp:inn]
56. Einecs 200-811-1
57. Mfcd00002635
58. 2-amino-5-guanidino-pentanoic Acid
59. Unii-94zla3w45f
60. Nsc203450
61. 3h-l-arginine
62. L-arginine, Labeled With Tritium
63. 1laf
64. L-a-amino-d-guanidinovaleric Acid
65. Ncgc00015064-02
66. (s)-arginine
67. L(+) Arginine
68. L-aryginine,(s)
69. H-arg
70. L-(+) Arginine
71. L(+)-arginine;
72. L-arginine (9ci)
73. Arginine (usp/inn)
74. Tocris-0663
75. (2s)-2-amino-5-guanidino-pentanoic Acid
76. Arginine [hsdb]
77. Arginine [inci]
78. L-arginine (jp17)
79. Arginine [inn]
80. Arginine [ii]
81. Arginine [mi]
82. Arginine [vandf]
83. Gnd
84. Lopac-a-5006
85. Arginine, L- (8ci)
86. Arginine [mart.]
87. L-arginine [fcc]
88. L-arginine [jan]
89. Arginine [who-dd]
90. Bmse000029
91. Bmse000899
92. Bmse000919
93. Epitope Id:140084
94. L-arginine (h-arg-oh)
95. L-arginine [fhfi]
96. Ec 200-811-1
97. Schembl1791
98. 2-amino-5-guanidinovalerate
99. Lopac0_000077
100. Arginine Hydrochloride(usan)
101. Gtpl721
102. L-arginine [usp-rs]
103. 4-04-00-02648 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
104. L-a-amino-d-guanidinovalerate
105. L-amino-4-guanidovaleric Acid
106. Arginine [ep Impurity]
107. Us9138393, L-arginine
108. Us9144538, L-arginine
109. 1-amino-4-guanidovalerlic Acid
110. Arginine [ep Monograph]
111. Arginine [usp Monograph]
112. Dtxsid6041056
113. Bdbm21959
114. L-arginine, 99%, Fcc, Fg
115. Bdbm181132
116. Hms3260o15
117. N5-(aminoiminomethyl)-l-ornithine
118. Hy-n0455
119. Zinc1532525
120. L-arginine, Vetec(tm), 98.5%
121. Tox21_113046
122. Tox21_500077
123. Ac-083
124. L-2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoic Acid
125. L-alpha-amino-delta-guanidinovalerate
126. L-arginine, Reagent Grade, >=98%
127. S5634
128. Akos006239069
129. Akos015854096
130. Tox21_113046_1
131. Am81500
132. Ccg-204172
133. Db00125
134. Lp00077
135. Sdccgsbi-0050065.p002
136. L-arginine, 99%, Natural, Fcc, Fg
137. (s)-2-amino-5-guanidino-pentanoic Acid
138. 5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-l-norvaline
139. Ncgc00015064-01
140. Ncgc00024715-01
141. Ncgc00024715-02
142. Ncgc00024715-03
143. Ncgc00024715-04
144. Ncgc00024715-05
145. Ncgc00024715-10
146. Ncgc00260762-01
147. 4455-52-1
148. As-14190
149. L-arginine, Bioultra, >=99.5% (nt)
150. Sbi-0207062.p001
151. A0526
152. A7079
153. Eu-0100077
154. L-arginine, Saj Special Grade, >=98.0%
155. A 5006
156. C00062
157. D02982
158. L-arginine, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=98%
159. Lysine Acetate Impurity F [ep Impurity]
160. M02981
161. 2-azaniumyl-5-(diaminomethyleneammonio)pentanoate
162. Ab00374192_03
163. Norvaline, 5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-, (l)-
164. 002a635
165. A837397
166. A929348
167. Q173670
168. Sr-01000075479
169. Sr-01000597671
170. (s)-2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-pentanoate
171. (s)-2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]pentanoate
172. Sr-01000075479-1
173. Sr-01000597671-1
174. W-104410
175. (s)-2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-pentanoic Acid
176. Arginine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
177. (2s)-2-amino-5-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]pentanoic Acid
178. 7f15b0c7-356d-45d7-ac33-03aee4394a0e
179. S-(+)-2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]pentanoic Acid
180. (2s)-2-azanyl-5-[bis(azanyl)methylideneamino]pentanoic Acid
181. L-arginine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
182. L-arginine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
183. L-
184. L-arginine, From Non-animal Source, Meets Ep, Usp Testing Specifications, Suitable For Cell Culture, 98.5-101.0%
185. L-arginine, Pharmagrade, Ajinomoto, Ep, Usp, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture
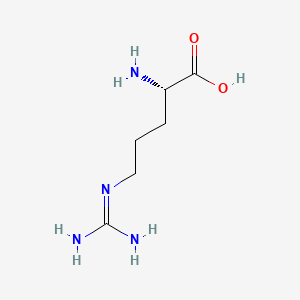
1. L-arginine
| Molecular Weight | 174.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 |
| XLogP3 | -4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 174.11167570 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 174.11167570 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 128 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 176 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | R-gene 10 |
| Active Ingredient | Arginine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | R-gene 10 |
| Active Ingredient | Arginine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
EXPTL USE: IN MICE, L-ARGININE-HCL HAD AN INHIBITORY EFFECT ON MURINE SARCOMA VIRUS-MOLONEY & C3H BREAST ADENOCARCINOMA TUMOR SYSTEMS.
CRITSELIS AN ET AL; L-ARGININE INCREASES RESISTANCE TO TUMORS; CURR CHEMOTHER PROC INT CONGR CHEMOTHER, 10TH, VOL 2, 1978, 1122-4
EXPTL USE: EXPTL DIETS GIVEN 10 DAYS AFTER WALKER 256 CARCINOSARCOMA CELLS INOCULATED INTO RATS, RESULTED IN LOWER TUMOR WEIGHTS.
TAKAMURA C; INHIBITORY EFFECT OF ARGININE-SUPPLEMENTED DIETS ON GROWTH OF WALKER 256 CARCINOSARCOMA; KANSAI IKA DAIGAKU ZASSHI 29(3) 519 (1977)
EXPTL USE: L-ARGININE-HCL INCR IN VITRO MOTILITY IN SPECIMENS OF HUMAN SEMEN EXHIBITING SUBNORMAL MOTILITY. EFFECT WAS DOSE DEPENDENT.
KELLER DW ET AL; L-ARGININE STIMULATION OF HUMAN SPERM MOTILITY IN VITRO; BIOL REPROD 13(2) 154 (1975)
EXPTL USE: ARGININE (1% IN DIET) GIVEN TO RATS INCR THYMIC SIZE & PREVENTED THYMIC INVOLUTION WHICH OCCURS WITH INJURY. ARGININE PROMOTED WOUND HEALING IN RATS.
BARBUL A ET AL; ARGININE: A THYMOTROPIC & WOUND-HEALING PROMOTING AGENT; SURG FORUM 28: 101 (1977)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for (L)-ARGININE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used for nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
Studies have shown that is has improved immune responses to bacteria, viruses and tumor cells; promotes wound healing and regeneration of the liver; causes the release of growth hormones; considered crucial for optimal muscle growth and tissue repair.
Absorption
Absorbed from the lumen of the small intestine into the enterocytes. Absorption is efficient and occurs by an active transport mechanism.
Some metabolism of L-arginine takes place in the enterocytes. L-arginine not metabolized in the enterocytes enters the portal circulation from whence it is transported to the liver, where again some portion of the amino acid is metabolized.
PRODUCT OF OXIDATIVE DEAMINATION OR TRANSAMINATION OF L-ARGININE IS ALPHA-KETO-GAMMA-GUANIDOVALERIC ACID; PRODUCT OF DECARBOXYLATION IS AGMATINE. PATHWAYS & PRODUCTS OF METABOLISM: ARGININE YIELDS ORNITHINE + UREA; ARGININE YIELDS CITRULLINE + NH3; ARGININE + GLYCINE YIELDS GUANIDOACETIC ACID + ORNITHINE /FROM TABLE/
Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients. Volume 2. Edited, translated, and revised by T.E. Furia and N. Bellanca. 2nd ed. Cleveland: The Chemical Rubber Co., 1975., p. 829
Many of supplemental L-arginine's activities, including its possible anti-atherogenic actions, may be accounted for by its role as the precursor to nitric oxide or NO. NO is produced by all tissues of the body and plays very important roles in the cardiovascular system, immune system and nervous system. NO is formed from L-arginine via the enzyme nitric oxide synthase or synthetase (NOS), and the effects of NO are mainly mediated by 3,'5' -cyclic guanylate or cyclic GMP. NO activates the enzyme guanylate cyclase, which catalyzes the synthesis of cyclic GMP from guanosine triphosphate or GTP. Cyclic GMP is converted to guanylic acid via the enzyme cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. NOS is a heme-containing enzyme with some sequences similar to cytochrome P-450 reductase. Several isoforms of NOS exist, two of which are constitutive and one of which is inducible by immunological stimuli. The constitutive NOS found in the vascular endothelium is designated eNOS and that present in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system is designated nNOS. The form of NOS induced by immunological or inflammatory stimuli is known as iNOS. iNOS may be expressed constitutively in select tissues such as lung epithelium. All the nitric oxide synthases use NADPH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) and oxygen (O2) as cosubstrates, as well as the cofactors FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), FMN (flavin mononucleotide), tetrahydrobiopterin and heme. Interestingly, ascorbic acid appears to enhance NOS activity by increasing intracellular tetrahydrobiopterin. eNOS and nNOS synthesize NO in response to an increased concentration of calcium ions or in some cases in response to calcium-independent stimuli, such as shear stress. In vitro studies of NOS indicate that the Km of the enzyme for L-arginine is in the micromolar range. The concentration of L-arginine in endothelial cells, as well as in other cells, and in plasma is in the millimolar range. What this means is that, under physiological conditions, NOS is saturated with its L-arginine substrate. In other words, L-arginine would not be expected to be rate-limiting for the enzyme, and it would not appear that supraphysiological levels of L-arginine which could occur with oral supplementation of the amino acid^would make any difference with regard to NO production. The reaction would appear to have reached its maximum level. However, in vivo studies have demonstrated that, under certain conditions, e.g. hypercholesterolemia, supplemental L-arginine could enhance endothelial-dependent vasodilation and NO production.
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
A L-Arginine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of L-Arginine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates L-Arginine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. L-Arginine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A L-Arginine supplier is an individual or a company that provides L-Arginine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or L-Arginine finished formulations upon request. The L-Arginine suppliers may include L-Arginine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A L-Arginine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of L-Arginine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of L-Arginine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as L-Arginine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A L-Arginine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. L-Arginine USDMF includes data on L-Arginine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The L-Arginine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The L-Arginine Drug Master File in Japan (L-Arginine JDMF) empowers L-Arginine API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the L-Arginine JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of L-Arginine JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A L-Arginine CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a L-Arginine Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a L-Arginine CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of L-Arginine EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of L-Arginine to their clients by showing that a L-Arginine CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a L-Arginine CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a L-Arginine CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the L-Arginine CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the L-Arginine DMF.
A L-Arginine CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. L-Arginine CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing L-Arginine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for L-Arginine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture L-Arginine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain L-Arginine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a L-Arginine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of L-Arginine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
L-Arginine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of L-Arginine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right L-Arginine GMP manufacturer or L-Arginine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A L-Arginine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to L-Arginine's compliance with L-Arginine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
L-Arginine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each L-Arginine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
L-Arginine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (L-Arginine EP), L-Arginine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (L-Arginine USP).


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?