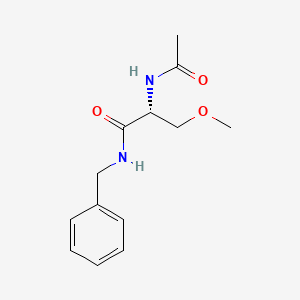

1. 2-(acetylamino)-3-methoxy-n-(phenylmethyl)-, (2r)-
2. Add-234037
3. Ertosamide
4. Harkoseride
5. Spm-927
1. 175481-36-4
2. Erlosamide
3. Vimpat
4. (r)-2-acetamido-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
5. Harkoseride
6. Spm 927
7. Spm-927
8. (2r)-2-acetamido-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
9. (r)-lacosamide 1
10. Propanamide, 2-(acetylamino)-3-methoxy-n-(phenylmethyl)-, (2r)-
11. Add 243037
12. Add-234037
13. Chembl58323
14. 563ks2pqy5
15. Add-243037
16. Erlosamide [inn]
17. Ncgc00253740-01
18. (r)-2-acetamido-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropionamide.
19. (r)-2-acetylamino-n-benzyl-3-methoxy-propionamide
20. Lacosamide [usan]
21. (+)-(2r)-2-(acetylamino)-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
22. Ertosamide
23. Add 234037
24. Harkeroside
25. Unii-563ks2pqy5
26. Lacosamide [usan:inn:ban]
27. Lacosamide Cv
28. Spm-929
29. Lacosamide Racemate
30. Lacosamide- Bio-x
31. (2r)-2-(acetylamino)-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
32. Vimpat (tn)
33. Lacosamide [mi]
34. Lacosamide [inn]
35. Lacosamide [jan]
36. Lacosamide [vandf]
37. Lacosamide [mart.]
38. (r)-n-benzyl-2-acetamido-3-methoxypropionamide
39. Dsstox_cid_31455
40. Dsstox_rid_97341
41. Lacosamide [who-dd]
42. Dsstox_gsid_57666
43. Schembl35330
44. Lacosamide (jan/usan/inn)
45. Lacosamide [ema Epar]
46. Gtpl7472
47. Zinc7673
48. Dea No. 2746
49. Lacosamide Cv [usp-rs]
50. Dtxsid1057666
51. Lacosamide [orange Book]
52. Lacosamide [ep Monograph]
53. Chebi:135939
54. Lacosamide [usp Monograph]
55. Bcp02197
56. Tox21_113857
57. Bdbm50300204
58. Mfcd08272557
59. Akos005146274
60. Lacosamide 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
61. Cs-0529
62. Db06218
63. Ks-1227
64. Ac-22750
65. Am808141
66. Bl164605
67. Hy-13015
68. A3897
69. Bb 0260890
70. Cas-175481-36-4
71. (r)-n-benzyl-2-acetamido-3-methoxypropanamide
72. D07299
73. (2r)-n-benzyl-2-acetamido-3-methoxypropanamide
74. (r)-2-acetamido-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropionamide
75. (r)-n-benzyl 2-acetamido-3-methoxypropionamide
76. (r)-n-benzyl 2-acetamido-3-methoxypropionamide,
77. Ab01559947-01
78. (2r)-2-acetylamino-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
79. (r)-2-acetylamino-n-benzyl-3-methoxypropionamide
80. 481l364
81. Ar-270/11402703
82. Q420077
83. Sr-01000942286
84. Sr-01000942286-1
85. (2r)-2-acetamido-3-methoxy-n-(phenylmethyl)propanamide
86. 2-(acetylamino)-3-methoxy-n-(phenylmethyl)-, (2r)-
87. Z1550648754
88. Lacosamide Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 250.29 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H18N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 250.13174244 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 250.13174244 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 67.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 275 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 1 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | VIMPAT |
| Active Ingredient | LACOSAMIDE |
| Company | UCB INC (Application Number: N022253. Patent: RE38551); UCB INC (Application Number: N022254. Patent: RE38551); UCB INC (Application Number: N022255. Patent: RE38551) |
Lacosamide is indicated for adjunctive therapy for partial onset seizures in patients with epilepsy over 17 years old. Injection is indicated for short term use when oral therapy is not feasible.
FDA Label
Vimpat is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with epilepsy.
Lacosamide Accord is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with epilepsy.
Lacosamide Accord is indicated as adjunctive therapy
in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with epilepsy.
in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Lacosamide UCB is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with epilepsy.
Treatment of epilepsy with partial-onset seizures
Treatment of generalised epilepsy and epileptic syndromes
Lacosamide therapy is correlated with a decrease in seizure frequency. It should be noted that in group analyses, dosages above 400 mg/day do not appear to result in additional benefit.
N03AX18
N03AX18
N03AX18
N03AX18
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AX - Other antiepileptics
N03AX18 - Lacosamide
Absorption
Lacosamide has a negligible first pass effect with bioavailability of about 100%. The maximum Lacosamide plasma concentrations occur about 1-4 hours after oral administration, and the pharmacokinetics of Lacosamide are dose proportional. Food does not affect absorption.
Route of Elimination
Lacosamide is eliminated primarily from the systemic circulation by biotransformation and renal excretion.
Volume of Distribution
approximately 0.6 L/kg; thus close to the volume of total body water.
Clearance
95% recovered in the urine 0.5% in the feces
Lacosamide is a CYP2C19 substrate. The relative contribution of other CYP isoforms or non-CYP enzymes in the metabolism of lacosamide is not known. Primary compounds excreted were unchanged lacosamide (approximately 40% of the dose), its O-desmethyl metabolite (approximately 30%), and a structurally unknown polar fraction (~20%). The plasma exposure of the major human metabolite, O-desmethyl-lacosamide, is approximately 10% of that of lacosamide. This metabolite has no known pharmacological activity.
13 Hours
It is proposed that lacosamide's inhibition of sodium channels is responsible for analgesia. Lacosamide may be selective for inhibiting depolarized neurons rather than neurons with normal resting potentials. Pain and nociceptor hyperexcitability are associated with neural membrane depolarization. Lacosamide binds to collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP-2), a phosphoprotein which is expressed primarily in the nervous system and is involved in neuronal differentiation and control of axonal outgrowth. The role CRMP-2 of binding in seizure control is hasn't been elucidated.
