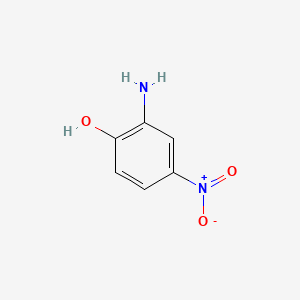

1. 2-amino-p-nitrophenol
1. 99-57-0
2. 2-hydroxy-5-nitroaniline
3. Phenol, 2-amino-4-nitro-
4. 4-nitro-2-aminophenol
5. P-nitro-o-aminophenol
6. Rodol 42
7. 4-nitro-2-aminofenol
8. P-nitroaminofenol
9. 3-amino-4-hydroxynitrobenzene
10. 1-amino-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzene
11. 1-hydroxy-2-amino-4-nitrobenzene
12. 1-nitro-3-amino-4-hydroxybenzene
13. Nci-c55958
14. C.i. 76530
15. 2-amino-4-nitrofenol
16. 2-amino-4-nitro-phenol
17. Nsc 4664
18. Mfcd00007695
19. 2-amino-4-nitro Phenol
20. 5-nitro-2-hydroxyaniline
21. G501uci6t9
22. Chebi:82383
23. 4-nitro-2-amino-1-hydroxybenzene
24. Nsc-4664
25. Dsstox_cid_62
26. Dsstox_rid_75341
27. Dsstox_gsid_20062
28. P-nitroaminofenol [polish]
29. Cas-99-57-0
30. Smr000221023
31. Ccris 890
32. 2-amino-4-nitrofenol [czech]
33. 4-nitro-2-aminofenol [czech]
34. Ci 76530
35. Hsdb 4165
36. Einecs 202-767-9
37. Brn 0776533
38. Unii-g501uci6t9
39. Ai3-08864
40. 4nitro-o-aminophenol
41. 2-amino4-nitrophenol
42. 4-nitro-o-aminophenol
43. Wln: Zr Bq Enw
44. 2-amino-4-nitro-phenolate
45. 5-nitro 2-hydroxy Aniline
46. Ec 202-767-9
47. Schembl22943
48. Mls000331524
49. Mls002152867
50. Chembl316992
51. 2-amino-4-nitrophenol, 96%
52. Dtxsid6020062
53. Schembl10232244
54. Nsc4664
55. 1-hydroxy-2 Amino-4-nitrobenzene
56. Amino-4-nitrophenol, 2-
57. Hms2549h14
58. Act07277
59. Tox21_201351
60. Tox21_302788
61. Bbl011594
62. Stk802465
63. Zinc35051195
64. Akos000121534
65. 2-amino-4-nitrophenol [hsdb]
66. 2-amino-4-nitrophenol [iarc]
67. 2-amino-4-nitrophenol [inci]
68. Am10716
69. Ps-4603
70. Ncgc00091626-01
71. Ncgc00091626-02
72. Ncgc00091626-03
73. Ncgc00256395-01
74. Ncgc00258903-01
75. Ac-11277
76. 2-amino-4-nitrophenol, >=99.0% (nt)
77. Db-020444
78. A0378
79. Ft-0619188
80. C19321
81. W-100031
82. Q27155912
83. F0001-2336
| Molecular Weight | 154.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H6N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 154.03784206 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 154.03784206 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 92.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 156 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Percutaneous absorption through the skin of Sprague-Dawley rats of each sex was examined following application of two hair dye formulations: formulation 1 contained 1.54% 14C-2-amino-4-nitrophenol; formulation 2 contained 0.77% 14C-2-amino-4-nitrophenol, 1,4-diaminobenzene (1,4-phenylenediamine), 2,4-diaminoanisole, oleic acid and isopropanol and was mixed with equal amt of a 6% hydrogen peroxide soln. After 1 and 5 days, 0.21 and 0.36% of the radiolabel administered in formulation 1 and 1.12 and 1.67% of that administered in formulation 2 had been absorbed (calculated as combined radiolabel in urine, feces, expired air and carcass, without treated skin area). Absorbed material was excreted predominantly in the urine within 24 hr after the initial application ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V57 170 (1993)
Five days after oral administration by gavage of 2 mL (14)C-2-amino-4-nitrophenol (0.2% in saline), 68.3% + 9.4 (SD) of the radiolabel had been excreted in the urine and 25.4% + 6.9% in the feces. Within 3 hr, about 4% of the radiolabel was eliminated in the bile. Following subcutaneous injection of the same dose, 89% of the dose was eliminated after 1 day, predominantly in the urine ... (/It was/ noted that metabolites were not identified in the urine, bile or feces in either study.)
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V57 170 (1993)
Percutaneous absorption of (14)C-2-amino-4-nitrophenol (specific radioactivity 10 mCi/mmol (65 uCi/mg); purity, 98%) was studied in vitro by partitioning between excised human abdominal skin preparations and water. 2-Amino-4-nitrophenol appeared to bind to skin components ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V57 170 (1993)
A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) analysis of biological fluids (blood, urine, gastric content, and bile) collected at autopsy in a case of suspected 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) fatal poisoning allowed the determination of DNP and its known metabolites (2-amino-4-nitrophenol and nitro-4-aminophenol). The tentative identification of three conjugated metabolites (DNP glucuronide, DNP sulfate, and 2-amino-4-nitrophenol glucuronide) could be made on the basis of their pseudomolecular ion, isotopic and fragmentation patterns, and retention characteristics. Another DNP metabolite reported in the literature, 2,4-diaminophenol, was not detected in the samples. Postmortem blood concentrations were 48.4 mg/L for DNP and 1.2 mg/L for 2-amino-4-nitrophenol. ...
PMID:17389084 Politi L et al; J Anal Toxicol 31 (1): 55-61 (2007)
YIELDS 2,4-DIAMINOPHENOL PROBABLY IN RATS. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. A-46
2-Amino-4-nitrophenol was the predominant metabolite formed enzymatically by nitroreduction following oral administration of 2,4-dinitrophenol (22.5 mg/kg bw) to ICR mice.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V57 170 (1993)
It had an elimination half-time from the plasma /of ICR mice/ of 46 hr ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V57 170 (1993)
Two hair dye components, carcinogenic 4-nitro-2-aminophenol and 5-nitro-2-aminophenol, induced Cu(II)-dependent DNA cleavage frequently at thymine and guanine residues in DNA fragments obtained from the c-Ha-ras-1 protooncogene. When the p53 tumor suppressor gene was used, 4-nitro-2-aminophenol caused Cu(II)-dependent piperidine-labile sites at poly G sequences. In the presence of Cu(II), both components increased 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine formation in DNA. The inhibitory effects of catalase and bathocuproine on DNA damage suggest the involvement of H2O2 and Cu(I). It is speculated that nitro-2-aminophenols undergo Cu(II)-mediated autoxidation to generate active oxygen species causing DNA damage which leads to their carcinogenesis.
PMID:9563650 Chen F et al; Cancer Lett 126 (1): 67-74 (1998)
