
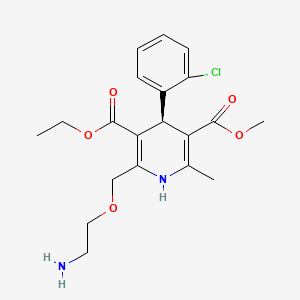

1. 2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxy-carbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine
1. (s)-amlodipine
2. 103129-82-4
3. S-amlodipine
4. Levoamlodipine
5. Levamlodipine [inn]
6. L-amlodipine
7. Amlodipine, (s)-
8. Unii-0p6nlp6806
9. Chebi:53796
10. 0p6nlp6806
11. (4s)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-ethyl 5-methyl Ester
12. 3-ethyl 5-methyl (s)-2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
13. Levoamlodipine Besylate
14. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-, 3-ethyl 5-methyl Ester, (4s)-
15. 3-ethyl 5-methyl (4s)-2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
16. 3-ethyl 5-methyl (4s)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
17. (-)-amlodipine
18. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-, 3-ethyl 5-methyl Ester, (4s)-
19. S-amlodipine Besylate
20. S-amlodipine Gentisate
21. D0i2wv
22. Levamlodipine (hypertension)
23. Schembl41283
24. Levamlodipine [who-dd]
25. Chembl2111097
26. Dtxsid50904504
27. Htiqeaqvcytubx-krwdzbqosa-n
28. Hms3885m19
29. Bcp22052
30. Mfcd09832686
31. S3674
32. Akos015896087
33. Am90308
34. Bcp9000849
35. Ccg-268748
36. Db09237
37. Agsav301 Component Levamlodipine
38. Bs-42190
39. Hy-14744
40. Levamlodipine (hypertension), Sk Chemicals
41. S-amlodipine (hypertension), Sk Chemicals
42. Ls-194044
43. Cs-0003533
44. A14935
45. D97381
46. A800681
47. En300-19633977
48. Q-101935
49. Q6534831
50. 2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxy-carbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine
51. 3-o-ethyl 5-o-methyl (4s)-2-(2-aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 408.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 |
| XLogP3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 99.9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 647 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Levamlodipine is indicated alone or in combination to treat hypertension in adults and children.
FDA Label
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA17 - Levamlodipine
Absorption
Oral levamlodipine has a Tmax of 6-12h and a bioavailability of 64-90%. Absorption of levamlodipine is not significantly affected by food. 20mg or oral s-amlodipine besylate reaches a Cmax of 6.131.29ng/mL with a Tmax of 8.43.6h and an AUC of 35172h\*ng/mL. 20mg or oral s-amlodipine maleate reaches a Cmax of 5.071.09ng/mL with a Tmax of 10.73.4h and an AUC of 33088h\*ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
Levamlodipine is 60% eliminated in urine with 10% eliminated as the unmetabolized drug.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of levamlodipine is similar to amlodipine. The volume of distribution of amlodipine is 21L/kg.
Clearance
The oral clearance of S-amlodipine besylate is 6.91.6mL/min/kg and the oral clearance of S-amlodipine maleate is 7.32.1mL/min/kg.
Levamlodipine is 90% metabolized to inactive metabolites. Incubation with liver microsomes has shown that this metabolism is primarily mediated by CYP3A4. Levamlodipine's dehydrogenation to a pyridine metabolite (M9) is the most important metabolic pathway in human liver microsomes. This derivative can be further oxidatively deaminated or O-dealkylated, but does not appear to undergo O-demethylation like racemic amlodipine.
Levamlodipine has a half life of 30-50h.
Levamlodipine blocks the transmembrane influx of calcium through L-type calcium channels into the vascular and cardiac smooth muscles resulting in vasodilation and a subsequent decrease in blood pressure. Levamlodipine inhibits calcium influx in vascular smooth muscle to a greater degree than in cardiac muscle, leading to decreased peripheral vascular resistance and lowered blood pressure. In vitro studies have shown a negative inotropic effect but this is unlikely to be clinically relevant.
BUILDING BLOCK

