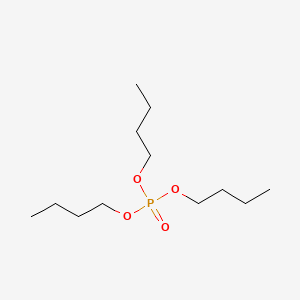

1. Tbp
2. Tri-(n-butyl )-phosphate
3. Tri-n-butyl Phosphate
4. Tri-n-butylphosphate
5. Tributylphosphate
1. 126-73-8
2. Tri-n-butyl Phosphate
3. Tributylphosphate
4. Phosphoric Acid Tributyl Ester
5. Butyl Phosphate
6. Tributylphosphat
7. Celluphos 4
8. Phosphoric Acid, Tributyl Ester
9. Disflamoll Tb
10. Tbpa
11. Tributilfosfato
12. Tributylfosfaat
13. Tbp
14. Tributyle (phosphate De)
15. Butyl Phosphate, Tri-
16. Tributoxyphosphine Oxide
17. Tributylfosfat
18. Butyl Phosphate, ((buo)3po)
19. Phosphoric Acid Tri-n-butyl Ester
20. Nsc 8484
21. N-butyl Phosphate
22. 95uas8yaf5
23. Dtxsid3021986
24. Chebi:35019
25. Nsc-8484
26. Tri-n-butylphosphate
27. Dsstox_cid_1986
28. Dsstox_rid_76443
29. Dsstox_gsid_21986
30. Tributylfosfat [czech]
31. Tributylfosfaat [dutch]
32. Tributilfosfato [italian]
33. Tributylphosphat [german]
34. Cas-126-73-8
35. Ccris 6106
36. Hsdb 1678
37. Tributyle (phosphate De) [french]
38. Mcs 2495
39. Einecs 204-800-2
40. Unii-95uas8yaf5
41. Brn 1710584
42. Ai3-00399
43. Tributylphsophate
44. Kronitex Tbp
45. Tributyl Ester Of Phosphoric Acid
46. Tributyle(phosphate De)
47. Phosphoric Acid Tributyl
48. Tris(1-butyl) Phosphate
49. Tributyl Phosphate, 97%
50. Tributyl Phosphate, 99%
51. Bmse000777
52. Ec 204-800-2
53. Syn-o-ad 8412
54. Schembl18570
55. Tributyl Phosphate, >=99%
56. 4-01-00-01531 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
57. Bidd:er0345
58. Tributyl Phosphate [mi]
59. Chembl1371096
60. Nsc8484
61. Tributyl Phosphate [hsdb]
62. Phosphoric Acid, Tri-n-butyl Ester
63. Zinc1586777
64. Tox21_201872
65. Tox21_300107
66. Mfcd00009436
67. Wln: 4opo & O4 & O4
68. Akos015995460
69. Tri-n-butyl Phosphate [mart.]
70. Tributyl Phosphate, Analytical Standard
71. Ncgc00091588-01
72. Ncgc00091588-02
73. Ncgc00091588-03
74. Ncgc00091588-04
75. Ncgc00254202-01
76. Ncgc00259421-01
77. Ft-0657452
78. P0266
79. Tri-n-butyl Phosphate [ep Monograph]
80. Tributyl Phosphate 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
81. Tributyl Phosphate 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
82. Tributyl Phosphate 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
83. Tributyl Phosphate, Puriss., >=99.0% (gc)
84. Tributyl Phosphate, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
85. Tributyl Phosphate, Selectophore(tm), >=98.0%
86. A805594
87. Q613394
88. J-005429
89. F1905-7225
90. Tributyl Phosphate, 10 Mug/ml In Hexane, Analytical Standard
91. Tributyl Phosphate, For Extraction Analysis, >=99.0% (gc)
92. Tri-n-butyl Phosphate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
93. Tributyl Phosphate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 266.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H27O4P |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 266.16469634 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 266.16469634 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 44.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 175 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
3= Moderately toxic: probable oral lethal dose (human) 0.5-5 g/kg, between 1 oz & 1 pint (or 1 lb) for 70 kg person (150 lb).
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-302
Radiation-Protective Agents
Drugs used to protect against ionizing radiation. They are usually of interest for use in radiation therapy but have been considered for other purposes, e.g. military. (See all compounds classified as Radiation-Protective Agents.)
Dermal absorption of tributyl phosphate has been demonstrated in pigs, and there was little difference in the rate of skin penetration between regions with or without hair follicles.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Rats given a single oral dose of (14)C labeled tributyl phosphate at 14 mg/kg excreted 50, 10, and 6% of the administered dose in the urine, exhaled air, and feces, respectively, within 24 hr. A single intraperitoneal dose at the same rate resulted in 70, 7, and 4% of the administered dose in the urine, exhaled air, and feces within the first 24 hr.
Snyder, R. (ed.). Ethel Browning's Toxicity and Metabolism of Industrial Solvents. 2nd ed. Volume II: Nitrogen and Phosphorus Solvents. Amsterdam-New York-Oxford: Elsevier, 1990., p. 456
In vitro investigations on isolated human skin showed that tributyl phosphate has a high penetrating capacity. The average maximum steady-state rate of penetration through isolated human skin is 6.7X10-4 umol/cm sq/min.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Substantial absorption from the gastrointestinal tract occurred in rats given a single oral dose of tributyl phosphate (TBP) ... more than 50% of an orally administered dose of TBP was absorbed within 24 hr.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Following single or repeated oral dosing in rats, tributyl phosphate was detected in the gastrointestinal tract, blood, and liver.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Tributyl phosphate (TBP) is a toxic organophosphorous compound widely used in many industrial applications, including significant usage in nuclear processing. The industrial application of this chemical is responsible for occupational exposure and environmental pollution. In this study, (1)H NMR-based metabonomics has been applied to investigate the metabolic response to TBP exposure. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were given a TBP-dose of 15 mg/kg body weight, followed by 24hr urine collection, as was previously demonstrated for finding most of the intermediates of TBP. High-resolution (1)H NMR spectroscopy of urine samples in conjunction with statistical pattern recognition and compound identification allowed for the metabolic changes associated with TBP treatment to be identified. Discerning NMR spectral regions corresponding to three TBP metabolites, dibutyl phosphate (DBP), N-acetyl-(S-3-hydroxybutyl)-L-cysteine and N-acetyl-(S-3-oxobutyl)-L-cysteine, were identified in TBP-treated rats. In addition, the (1)H NMR spectra revealed TBP-induced variations of endogenous urinary metabolites including benzoate, urea, and trigonelline along with metabolites involved in the Krebs cycle including citrate, cis-aconitate, trans-aconitate, 2-oxoglutarate, succinate, and fumarate. These findings indicate that TBP induces a disturbance to the Krebs cycle energy metabolism and provides a biomarker signature of TBP exposure. ... /The/ three metabolites of TBP, dibutylphosphate, N-acetyl-(S-3-hydroxybutyl)-L-cysteine and N-acetyl-(S-3-oxobutyl)-L-cysteine, which are not present in the control groups, are the most important factors in separating the TBP and control groups (p<0.0023), while the endogenous compounds 2-oxoglutarate, benzoate, fumarate, trigonelline, and cis-aconetate were also important (p<0.01).
PMID:20688139 Neerathilingam M et al; Toxicol Lett 199 (1): 10-6 (2010)
The metabolic transformation of tributyl phosphate has been studied in male rats following oral or intraperitoneal administration of (14)C-labelled tributyl phosphate. The first stage in the metabolic process appeared to be oxidation, catalysed by cytochrome P-450-dependent mono-oxygenase, at the omega or omega-1 position on the butyl chains. The hydroxy groups generated at the w and w-1 positions were further oxidized to produce carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. Following these oxidations, the oxidized alkyl moieties were removed as glutathione conjugates, which were then excreted as N-acetyl cysteine derivatives. ... In the urine, the major phosphorus-containing metabolites are dibutyl hydrogen phosphate, butyl dihydrogen phosphate, and butyl bis(3-hydroxybutyl) phosphate as well as small amounts of the following phosphates: dibutyl 3-hydroxy-butyl, butyl 2-hydroxybutyl hydrogen, butyl 3-hydroxybutyl hydrogen, butyl 3-carboxypropyl hydrogen, 3-carboxypropyl dibutyl, butyl 3-carboxypropyl 3-hydroxybutyl, butyl bis (3-carboxypropyl), and 3-hydroxybutyl dihydrogen.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
A single ip dose of tributyl phosphate at 250 mg/kg to rats resulted in 11 phosphorus containing metabolites in the urine within 24 hr. The principal metabolic pathway resulted in stepwise debutylation, through hydroxylated intermediates, to give dibutyl hydrogen phosphate and butyl dihydrogen phosphate . Rat liver microsomal preparations also metabolized tributyl phosphate to mono- and dihydroxylated intermediates, giving dibutyl hydrogen phosphate as the terminal metabolite. Microsomal preparations from goldfish liver and killfish also resulted in dibutyl 3-hydroxybutyl phospate and dibutyl hydrogen phosphate.
Snyder, R. (ed.). Ethel Browning's Toxicity and Metabolism of Industrial Solvents. 2nd ed. Volume II: Nitrogen and Phosphorus Solvents. Amsterdam-New York-Oxford: Elsevier, 1990., p. 456
The rate of metabolism of tributyl phosphate and the nature of the metabolites produced were determined in in vitro tests on rat liver homogenate. It was found that rat liver microsomal enzymes rapidly metabolized tributyl phosphate in the presence of NADPH (within 30 min), but only slight metabolic breakdown (11%) occurred in the absence of added NADPH. Dibutyl(3-hydroxybutyl) phosphate was obtained as a metabolite in the first stage of the test. The extended incubation time in the second stage of the test yielded two further metabolites, butyl di(3-hydroxybutyl) phosphate and dibutyl hydrogen phosphate, which were produced from the primary metabolite dibutyl(3-hydroxybutyl) phosphate.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 112: Tri-n-butyl phosphate (1991). Available from, as of September 4, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
