
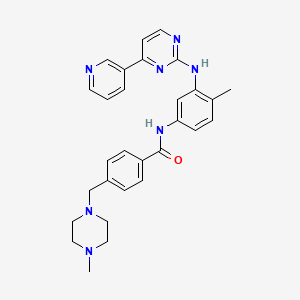

1. Alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-tolu-p-toluidide
2. Cgp 57148
3. Cgp-57148
4. Cgp57148
5. Cgp57148b
6. Gleevec
7. Glivec
8. Imatinib Mesylate
9. Imatinib Methanesulfonate
10. Mesylate, Imatinib
11. Methanesulfonate, Imatinib
12. St 1571
13. St1571
14. Sti 571
15. Sti-571
16. Sti571
1. 152459-95-5
2. Sti571
3. Imatinib (sti571)
4. Imatinib Free Base
5. N-(4-methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
6. Cgp 57148
7. Glamox
8. Sti 571
9. Imatinib (inn)
10. Imatinib Methansulfonate
11. 4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-n-[4-methyl-3-(4-pyridin-3-yl-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-phenyl]-benzamide
12. 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
13. Cgp-57148
14. 152459-95-5 (free Base)
15. Bkj8m8g5hi
16. Chembl941
17. Nsc-743414
18. Nsc-759854
19. Chebi:45783
20. Mfcd05662257
21. Nsc743414
22. 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-{4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl}benzamide
23. N-(4-methyl-3-{[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)-4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]benzamide
24. Imatinib [inn]
25. Imatinib [inn:ban]
26. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide
27. Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl)-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-
28. Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-
29. Sti
30. Alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-toluidide
31. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
32. Glamox (tn)
33. Ccris 9076
34. Sr-01000763561
35. Ncgc00159456-02
36. Unii-bkj8m8g5hi
37. St1571
38. St 1571
39. Imatinib-cd3
40. 1iep
41. 1xbb
42. Gleevec(tm)
43. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-methyl]-n-{4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-amino]-phenyl)-benzamide
44. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-methyl]-n-{4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-amino]-phenyl}-benzamide
45. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[(4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide
46. Imatinib (gleevec)
47. Imatinib - Gleevec
48. Imatinib, 21
49. Imatinib, Free Base
50. Alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-tolu-p-toluidide
51. Kinome_3724
52. 112gi019
53. Imatinib [mi]
54. Imatinib [vandf]
55. Imatinib [who-dd]
56. Gleevec (tn) (novartis)
57. Cid_5291
58. Schembl3827
59. Imatinib-d3(n-methyl-d3)
60. Imatinib [ema Epar]
61. Sti-571; Imatinib
62. 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-(4-methyl-3-{[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)benzamide
63. Bidd:gt0047
64. Gtpl5687
65. Dtxsid3037125
66. Bdbm13530
67. Ex-a063
68. Bcpp000205
69. Cgp057148b
70. Hms2089d03
71. Hms3244p06
72. Hms3244p10
73. Hms3244p14
74. Hms3656k04
75. Hms3715p03
76. Pharmakon1600-01502276
77. Bcp01542
78. Ac-524
79. Nsc759854
80. Nsc800772
81. Stk617705
82. Vcc905240
83. Zinc19632618
84. Akos000280662
85. Bcp9000775
86. Ccg-101289
87. Cs-0964
88. Db00619
89. Es-0058
90. Nsc 743414
91. Nsc 759854
92. Nsc-800772
93. Sb17306
94. St-1571
95. Mrf-0000449
96. Ncgc00159456-01
97. Ncgc00159456-03
98. Ncgc00159456-04
99. Ncgc00159456-05
100. Ncgc00159456-06
101. Ncgc00159456-07
102. Ncgc00159456-09
103. Ncgc00159456-16
104. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide Methanesulfonate
105. Bi164570
106. Hy-15463
107. N-(3-(4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-4-methylphenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
108. N-(4-methyl-3-(4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
109. N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidyl]amino]phenyl]-4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]benzamide
110. Sy028029
111. Am20090646
112. Ft-0651483
113. I0906
114. S2475
115. Sw197805-5
116. D08066
117. Ab00698388-07
118. Ab00698388-10
119. Ab00698388-11
120. Ab00698388-12
121. Ab00698388-13
122. Ab00698388_15
123. Ab00698388_16
124. 459i955
125. A809313
126. Q177094
127. Q-201231
128. Sr-01000763561-4
129. Sr-01000763561-6
130. Brd-k92723993-066-02-9
131. Brd-k92723993-066-04-5
132. Z1551429727
133. 1080014-82-9
134. 4-(4-me-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-n-[4-me-3-(4-pyridin-3-yl-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-phenyl]-benzamide
135. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
136. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3- Pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
137. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
138. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
139. Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)aminophenyl)-
140. Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]- (9ci)
141. Methanesulfonic Acid; 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 493.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H31N7O |
| XLogP3 | 3.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 493.25900864 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 493.25900864 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 706 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML), Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases, aggressive systemic mastocytosis, hypereosinophilic syndrome and/or chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL), dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST).
FDA Label
Glivec is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia-chromosome (bcr-abl)-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone-marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment;
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis;
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia-chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy;
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy;
- adult patients with myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases (MDS / MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements;
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and / or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFRa rearrangement.
The effect of Glivec on the outcome of bone-marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Glivec is indicated for:
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117)-positive unresectable and / or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST);
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment;
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and / or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of Glivec is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS / MPD, on haematological response rates in HES / CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and / or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with Glivec in patients with MDS / MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib medac is indicated for the treatment of:
- paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment;
- paediatric patients with Ph+CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase;
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+CML in blast crisis;
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ALL) integrated with chemotherapy;
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ALL as monotherapy;
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements;
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement;
- adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic DFSP.
The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited. Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Accord is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
- adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic DFSP. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Actavis is indicated for the treatment of:
- paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment;
- paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis;
- adult patients with Ph+ CML in blast crisis;
- adult patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy;
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy;
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements;
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement;
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Actavis is indicated for:
- In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic DFSP. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Teva is indicated for the treatment of
- Adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcrabl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- Adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferonalpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- Adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- Adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- Adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Teva is indicated for
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST). the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- The treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Teva B. V. is indicated for the treatment of:
- Paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- Paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- Adult patients with Ph+ CML in blast crisis.
- Adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- Adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- Adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Teva B. V. is indicated for:
- The treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- The adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- The treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, Treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia
Imatinib Koanaa is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
The effect of Imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Koanaa is indicated for
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of Imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with Imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib is an antineoplastic agent and a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative that is used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia. It works as a specific inhibitor of a number of tyrosine kinase enzymes. Chronic myelogenous leukemia is associated with the Philadelphia chromosome promoting the generation of BCR-ABL mutation, which results from the combination of two genes, known as BCR and ABL. BCR-ABL generates a fusion protein that acts as a constitutively active tyrosine kinase and imatinib works to inhibit this constitutive enzymatic activity.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EA01
L01XE01
L01EA01
L01EA01
L01EA01
L01XE01
L01EA01
L01XE01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EA - Bcr-abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EA01 - Imatinib
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics in CML and GIST patients are similar. Imatinib is well absorbed with mean absolute bioavailability is 98% and maximum plasma levels achieved within 2-4 hours of dosing
Route of Elimination
Imatinib elimination is predominately in the feces, mostly as metabolites. 81% of the dose is eliminated within 7 days, in feces (68% of the dose) and urine (13% of the dose). Unchanged imatinib accounted for 25% of the dose (5% urine, 20% faces), the remainder being metabolites.
Clearance
8 L/h [50-year-old CML and GIST patient weighing 50 kg]
14 L/h [50-year-old CML and GIST patient weighing 100 kg]
Primarily hepatic via CYP3A4. Other cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, play a minor role in its metabolism. The main circulating active metabolite in humans is the N-demethylated piperazine derivative, formed predominantly by CYP3A4. This metabolite is similar in potency to the parent compound.
Imatinib has known human metabolites that include N-desmethylimatinib.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Following oral administration in healthy volunteers, the elimination half-lives of imatinib and its major active metabolite, the N-demethyl derivative (CGP74588) are approximately 18 and 40 hours, respectively.
Imatinib mesylate is a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase, the constitutive abnormal tyrosine kinase created by the Philadelphia chromosome abnormality in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in Bcr-Abl positive cell lines as well as fresh leukemic cells from Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Imatinib also inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinases for platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) and stem cell factor (SCF) - called c-kit. Imatinib was identified in the late 1990s by Dr Brian J. Druker. Its development is an excellent example of rational drug design. Soon after identification of the bcr-abl target, the search for an inhibitor began. Chemists used a high-throughput screen of chemical libraries to identify the molecule 2-phenylaminopyrimidine. This lead compound was then tested and modified by the introduction of methyl and benzamide groups to give it enhanced binding properties, resulting in imatinib.
BUILDING BLOCK



LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?