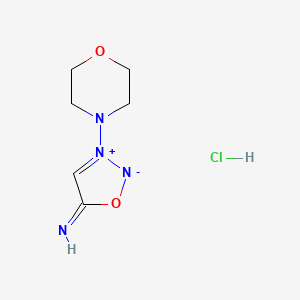

1. 3-morpholino-sydnonimine
2. 3-morpholino-sydnonimine Monohydrochloride
3. 3-morpholinosydnonimine N-ethylcarbamide
4. 3-morpholinosydonimine
5. 5-amino-3-(4-morpholinyl)-1,2,3-oxadiazolium
6. Corvasal
7. Cv 664
8. Cv-664
9. Linsidomine
10. N-morpholino Sydnonimine
11. Sin-1 Morpholine
1. Sin-1
2. Mls000028691
3. (3-morpholino-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-5-yl)amide Hydrochloride
4. Smr000058925
5. 5-amino-3-(4-morpholinyl)-1,2,3-oxadiazolium Chloride
6. 3-morpholin-4-yl-1-oxa-3-azonia-2-azanidacyclopent-3-en-5-imine;hydrochloride
7. 3-morpholino-sydnonimine Hydrochloride
8. Molsidomine Impurity A
9. Opera_id_1704
10. 3-morpholinosydnonimine Hcl
11. Mls000860006
12. Schembl960238
13. Chembl538104
14. 3-(4-morpholinyl)sydnonimine Hcl
15. 3-morpholinosydnoimine Hydrochloride
16. 3-morpholino-sydnoniminehydrochloride
17. Tox21_500247
18. Tox21_500854
19. 3-morpholinosydnonimine Hydro-chloride
20. Akos022181148
21. Akos025213271
22. Ccg-221551
23. Ccg-222158
24. Lp00247
25. Lp00854
26. Ncgc00094181-01
27. Ncgc00260932-01
28. Ncgc00261539-01
29. Smr000326865
30. Mls-0003225.p022
31. Eu-0100854
32. Ft-0616203
33. M-184
34. J-009828
35. J-019356
36. (3-morpholino-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-5-yl)amidehydrochloride
37. 5-imino-3-morpholino-5h-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-2-ide Hydrochloride
38. 3-(morpholin-4-yl)sydnonimine Hydrochloride (linsidomine Hydrochloride)
39. 3-morpholinosydnonimine Hydrochloride, (consistent With Structure, Nmr)
40. 1,2,3-oxadiazolium, 5-amino-3-(4-morpholinyl)-, Inner Salt, Hydrochloride (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 206.63 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H11ClN4O2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 206.0570533 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 206.0570533 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 222 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Nitric Oxide Donors
A diverse group of agents, with unique chemical structures and biochemical requirements, which generate NITRIC OXIDE. These compounds have been used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and the management of acute myocardial infarction, acute and chronic congestive heart failure, and surgical control of blood pressure. (Adv Pharmacol 1995;34:361-81) (See all compounds classified as Nitric Oxide Donors.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
