
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
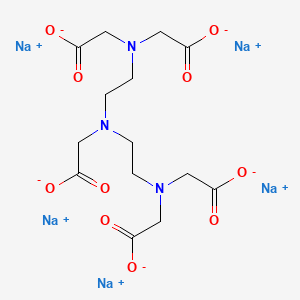

1. 140-01-2
2. Pentasodium Dtpa
3. Pentasodium Pentetate
4. Tetralon B
5. Trilon C
6. Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid Pentasodium Salt
7. Versenex 80
8. Hamp-ex 80
9. Plexene D
10. Syntron C
11. Perma Kleer 140
12. Chel 330
13. 961toz5l7t
14. Detarex Py
15. Glycine, N,n-bis(2-(bis(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl)-, Pentasodium Salt
16. Kiresuto P
17. Pentasodium;2-[bis[2-[bis(carboxylatomethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]acetate
18. Chelest P
19. Diethylenetriaminepentaaceticacidpentasodiumsalt
20. Dtpa Pentasodium Salt
21. Clewat Dp 80
22. Caswell No. 642b
23. Glycine, N,n-bis[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]-, Pentasodium Salt
24. Glycine, N,n-bis(2-(bis(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:5)
25. Hsdb 5629
26. Sodium Diethylenetriaminepentaacetate
27. Einecs 205-391-3
28. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 039120
29. Unii-961toz5l7t
30. Pentasodium (carboxylatomethyl)iminobis(ethylenenitrilo)tetraacetate
31. Dtpa Na5
32. Dissolvine D 50
33. N,n-bis(2-(bis(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl)glycine, Pentasodium Salt
34. Dissolvine D 40k
35. (((carboxymethyl)imino)bis(ethylenenitrilo))tetraacetic Acid, Pentasodium Salt
36. Acetic Acid, ((carboxymethylimino)bis(ethylenenitrilo))tetra-, Pentasodium Salt
37. Ec 205-391-3
38. Pentetate Pentasodium
39. Dtxsid9027077
40. Pentasodium Pentetate [ii]
41. Pentasodium Pentetate [hsdb]
42. Pentasodium Pentetate [inci]
43. Mfcd00051016
44. Pentetate Pentasodium [vandf]
45. Akos015914109
46. Pentasodiumdiethylenetriaminepentaacetate
47. Pentasodium Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetate
48. Db-042500
49. Divinyl Three Amine Five Acetic Five Sodium
50. D1870
51. Ft-0624890
52. Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid, Pentasodium Salt
53. Q27271841
54. Pentasodium 2,2',2'',2''',2''''-(ethane-1,2-diylnitrilo)pentaacetate
55. Diethylenetriamine-pentaacetic Acid Pentasodium Salt Solution, Purum, ~40% In H2o
56. Pentasodium Diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (ca. 40% In Water, Ca. 1.0mol/l)
57. Sodium 2,2',2'',2'''-(2,2'-(carboxylatomethylazanediyl)bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)bis(azanetriyl))tetraacetate
| Molecular Weight | 503.26 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N3Na5O10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 503.0480652 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 503.0480652 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 210 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 454 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 6 |
Antidotes; Chelating Agents; Iron Chelating Agents /Ca-DTPA/
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Pentetic Acid (140-01-2), MESH Heading. Available from, as of March 15, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Ca-DTPA is indicated for treatment of individuals with known or suspected internal contamination with plutonium, americium, or curium to increase the rates of elimination. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Chelation treatment is most effective if administered within the first 24 hours after internal contamination and should be started as soon as possible after suspected or known internal contamination. However, even when treatment cannot be started right away, individuals should be given chelation treatment as soon as it becomes available. Chelation treatment is still effective even after time has elapsed following internal contamination however, the chelating effects of Ca-DTPA are greatest when radiocontaminants are still circulating or are in interstitial fluids. The effectiveness of chelation decreases with time following internal contamination as the radiocontaminants become sequestered in liver and bone. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
When an individual is contaminated with multiple radiocontaminants, or when the radiocontaminants are unknown, additional therapies may be needed (e.g., Prussian blue, potassium iodide). /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PENTASODIUM PENTETATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Studies in animals and humans showed that Ca-DTPA binds endogenous metals of the body (i.e., zinc (Zn), magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn)). In an animal study, high doses of Ca-DTPA led to the loss of zinc and manganese mainly from the small intestine, skeleton, pancreas, and testes. Dosing over several days resulted in mobilization or binding of endogenous metals in exchange for calcium and a consequent impairment of metalcontrolled or activated systems. The rate and amount of endogenous metal depletion increased with split daily dosing and with the length of treatment. Depletion of these endogenous metals can interfere with necessary mitotic cellular processes. Over longer time periods, depletion of zinc due to Ca-DTPA therapy may result in transient inhibition of a metalloenzyme-daminolevulinic acid dehydrase (ALAD) in the blood and suppressed hematopoiesis. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
In the event of injury accompanied by radioactive contamination of the wound...it is better to refrain from washing the wound with complexing (chelating) solutions.../such as/ DTPA, for they intensify absorption of radioactive substances into the blood.
International Labour Office. Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety. Volumes I and II. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1971., p. 1159
Serum electrolytes and essential metals should be closely monitored during Ca-DTPA treatment. Mineral or vitamin plus mineral supplements that contain zinc should be given as appropriate. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Multiple doses of Ca-DTPA could result in an increased risk for adverse reproductive outcomes and thus are not recommended during pregnancy. Therefore, treatment of pregnant women should begin and continue with Zn-DTPA, if available, except in cases of high internal radioactive contamination. In these cases, the risk of immediate and delayed radiation-induced toxicity to both the mother and the fetus should be considered in comparison to the risk of Ca-DTPA toxicity. Also, because Ca-DTPA is more effective than Zn-DTPA in the first 24 hours after internal contamination, it may be appropriate to use a single dose of Ca-DTPA with vitamin or mineral supplements that contain zinc as the initial treatment. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PENTASODIUM PENTETATE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ca-DTPA is poorly absorbed in the GI tract. In animal studies, after oral administration, absorption was approximately 5%. In a U.S. Registry of 18 patients who received a single inhaled or intravenous dose of 1 gram, urine data indicate that the inhaled product was absorbed and resulted in a comparable elimination of the radiocontaminant. One study of 2 human subjects that received Ca-DTPA with (14)C-DTPA by inhalation revealed approximately 20% absorption from the lungs. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Following intravenous administration, Ca-DTPA is rapidly distributed throughout the extracellular fluid space. No significant amount of Ca-DTPA penetrates into erythrocytes or other cells. No accumulation of Ca-DTPA in specific organs has been observed. There is little or no binding of the chelating agent by the renal parenchyma. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Ca-DTPA is cleared from the plasma in the first few hours after dosing through urinary excretion by glomerular filtration. Renal tubular excretion has not been documented. In stool samples tested, only a very small amount of radioactivity (<3%) was detected.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Plasma retention and urinary excretion data were obtained in 2 subjects that received 750 kBq of (14)C-DTPA. The radiolabeled DTPA was rapidly distributed throughout the extracellular fluid space and was cleared by glomerular filtration. The plasma retention up to 7 hours post dosing was expressed by the sum of three exponential components with average half lives of 1.4 min, 14.5 min, and 94.4 min. The level of activity in the plasma was below the limit of detection 24 hours after injection. During the study, no detectable activity was exhaled or excreted in the feces. By 24 hours, cumulative urinary excretion was more than 99% of the injected dose. /DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=6052c707-a8a3-43a7-80c2-7ad1ad9391a4
Ca-DTPA undergoes a minimal amount of metabolic change in the body. /Ca-DTPA/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Pentetate Calcium Trisodium, injection, solution, concentrate (December 2006). Available from, as of November 22, 2011: https://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/label/2004/021749lbl.pdf
ABOUT THIS PAGE
76
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pentasodium Dtpa API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pentasodium Dtpa manufacturer or Pentasodium Dtpa supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Pentasodium Dtpa manufacturer or Pentasodium Dtpa supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Pentasodium Dtpa API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Pentasodium Dtpa API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Pentasodium Dtpa Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Pentasodium Dtpa Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Pentasodium Dtpa manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Pentasodium Dtpa, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Pentasodium Dtpa manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Pentasodium Dtpa API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Pentasodium Dtpa supplier is an individual or a company that provides Pentasodium Dtpa active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Pentasodium Dtpa finished formulations upon request. The Pentasodium Dtpa suppliers may include Pentasodium Dtpa API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Pentasodium Dtpa Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pentasodium Dtpa GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pentasodium Dtpa GMP manufacturer or Pentasodium Dtpa GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Pentasodium Dtpa CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Pentasodium Dtpa's compliance with Pentasodium Dtpa specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Pentasodium Dtpa CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Pentasodium Dtpa CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Pentasodium Dtpa may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Pentasodium Dtpa EP), Pentasodium Dtpa JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Pentasodium Dtpa USP).
