
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
API
0
FDF
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
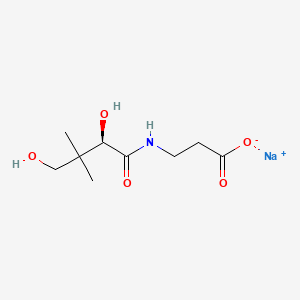

1. 867-81-2
2. Sodium D-pantothenate
3. Sodium (r)-3-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido)propanoate
4. D-pantothenic Acid Sodium
5. D-pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt
6. Pantothenate Sodium
7. Sodium Pantothenic Acid
8. D-pantothenic Acid (sodium)
9. Pantothenic Acid, Monosodium Salt, D-
10. Oes0r93f0c
11. Sodium;3-[[(2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoate
12. D-pantothenate Sodium
13. Mfcd00002767
14. Unii-oes0r93f0c
15. Pantothenic Acid, Sodium Salt
16. Ccris 1905
17. Hsdb 760
18. Vitamin B5 Sodium
19. Einecs 212-768-6
20. Sodium Pantothenate,(s)
21. Pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt
22. Dsstox_cid_27173
23. Dsstox_rid_82171
24. Dsstox_gsid_47173
25. Panthothenic Acid Sodium Salt
26. Schembl124920
27. Dtxsid4047173
28. Hy-b0430a
29. Hms2093p20
30. Sodium Pantothenate [hsdb]
31. Sodium Pantothenate [inci]
32. Tox21_302487
33. Pantothenate Sodium [who-dd]
34. Sodium N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-beta-alanine, (r)-
35. Ccg-213530
36. Cs-5150
37. Beta-alanine, N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Monosodium Salt, (r)-
38. Ncgc00256852-01
39. Cas-867-81-2
40. Pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt [mi]
41. P0013
42. D11519
43. O12072
44. Q-201535
45. Q27285618
46. Beta-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Monosodium Salt
47. Beta-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:1)
48. .beta.-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 241.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H16NNaO5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 241.09261689 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 241.09261689 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 244 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Topical application of pantothenate is widely used in clinical practice for wound healing.
Wiederholt T et al; Exper Dermatol 18 (11): 969-78 (2009). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19397697
Distribution of pantothenate from plasma into liver was very rapid; during 10 min after iv admin about 80% of dose was cleared from plasma.
PMID:1265350 Taylor T et al; Res Vet Sci 20 (2): 151-4 (1976).
Total blood pantothenic acid levels were higher after oral admin of 21.6 uM/kg pantethine than after calcium pantothenate in rats but no difference in amount of bound pantothenic acid. Max concentrations were observed at 2-4.5 hr after ingestion of both groups.
Ono S et al; J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 20(3) 203 (1974)
Total pantothenic acid excretions after 24 hr oral admin to rats were 29% and 18% after administration of pantethine and calcium pantothenate, respectively. Pantethine was more readily absorbed from GI tract than calcium pantothenate.
Ono S et al; J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 20(3) 203 (1974)
... To test the functional effect of pantothenate on dermal fibroblasts, cells were cultured and in vitro proliferation tests were performed using a standardized scratch test procedure. For all three donors analyzed, a strong stimulatory effect of pantothenate at a concentration of 20 ug/mL on the proliferation of cultivated dermal fibroblasts was observed. To study the molecular mechanisms resulting in the proliferative effect of pantothenate, gene expression was analyzed in dermal fibroblasts cultivated with 20 ug/mL of pantothenate compared with untreated cells using the GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Array. A number of significantly regulated genes were identified including genes coding for interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, Id1, HMOX-1, HspB7, CYP1B1 and MARCH-II. Regulation of these genes was subsequently verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Induction of HMOX-1 expression by pantothenol and pantothenic acid in dermal cells was confirmed on the protein level using immunoblots. Functional studies revealed the enhanced suppression of free radical formation in skin fibroblasts cultured with panthenol. In conclusion, these studies provided new insight in the molecular mechanisms linked to the stimulatory effect of pantothenate and panthenol on the proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. /Calcium pantotenate/
Wiederholt T et al; Exper Dermatol 18 (11): 969-78 (2009). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19397697
ABOUT THIS PAGE
94
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sodium Pantothenate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sodium Pantothenate manufacturer or Sodium Pantothenate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Sodium Pantothenate manufacturer or Sodium Pantothenate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Sodium Pantothenate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Sodium Pantothenate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Sodium Pantothenate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Sodium Pantothenate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Sodium Pantothenate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Sodium Pantothenate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Sodium Pantothenate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Sodium Pantothenate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Sodium Pantothenate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Sodium Pantothenate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Sodium Pantothenate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Sodium Pantothenate finished formulations upon request. The Sodium Pantothenate suppliers may include Sodium Pantothenate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Sodium Pantothenate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Sodium Pantothenate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sodium Pantothenate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sodium Pantothenate GMP manufacturer or Sodium Pantothenate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Sodium Pantothenate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Sodium Pantothenate's compliance with Sodium Pantothenate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Sodium Pantothenate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Sodium Pantothenate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Sodium Pantothenate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Sodium Pantothenate EP), Sodium Pantothenate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Sodium Pantothenate USP).
