By PharmaCompass
2023-08-31
Impressions: 4098
After a year when drug approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) slipped to the lowest since 2016, the first half of 2023 (H1 2023) saw a 62.5 percent growth in drug approvals by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) as compared with the same period last year. FDA’s CDER approved 26 new drugs in 2023, up from 16 in H1 2022. Approvals of biologics by the FDA surpassed full-year totals for many of the past 20 years. Nine new biologics were approved by FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) in H1 2023, as against just eight for 2022.
While FDA approved more drugs, authorizations by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) also increased but drug approvals by Health Canada dipped by approximately 50 percent. In the first half of 2023, EMA authorized 14 drugs, as opposed to 10 in H1 2022. Similarly, Health Canada approved 13 drugs against 25 in H1 2022.
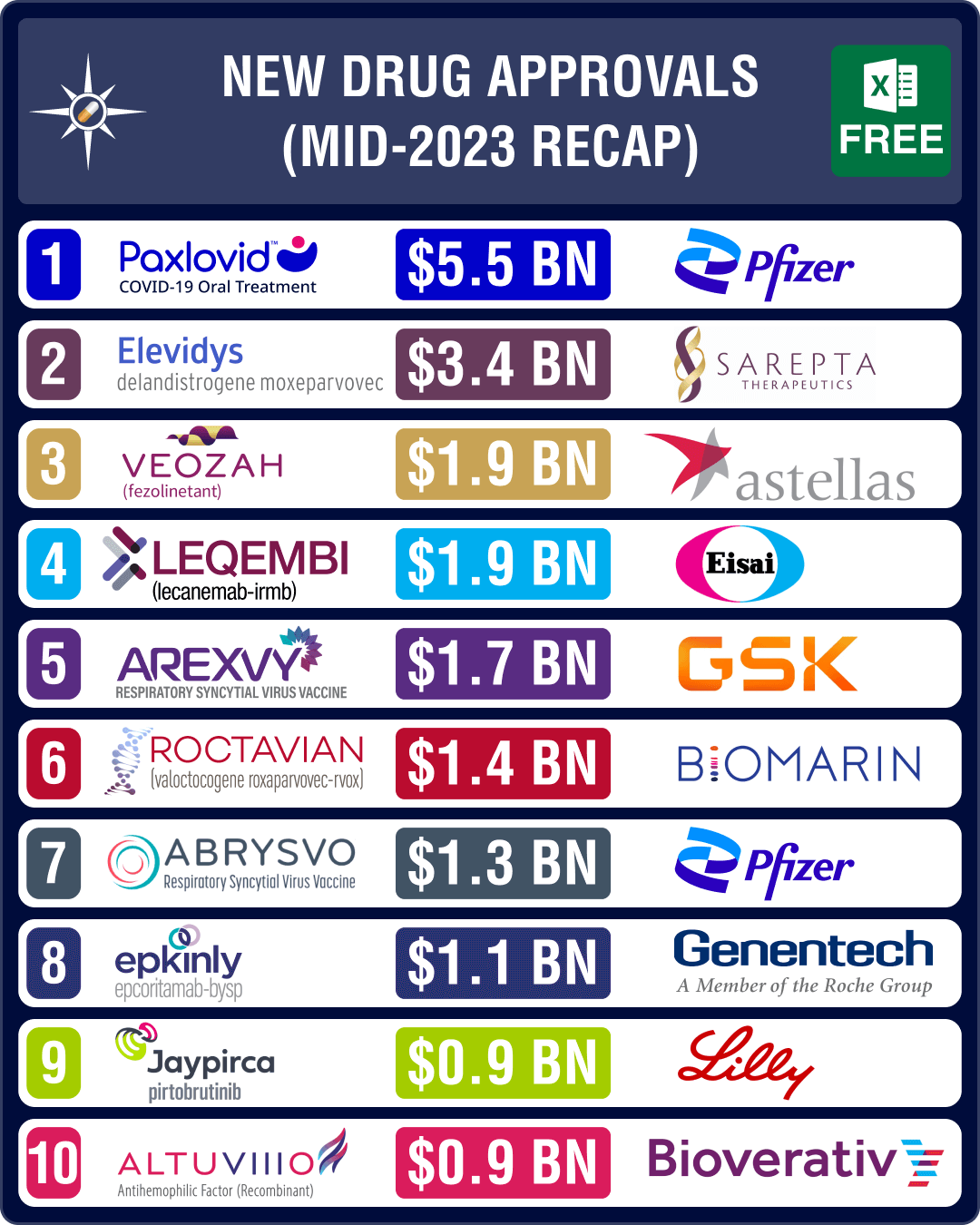
Among the promising drugs approved in H1 2023 are Biogen and Eisai’s Alzheimer’s drug Leqembi (lecanemab), Astellas Pharma’s drug for hot flashes (associated with menopause) Veozah, AbbVie and Genmab’s blood cancer drug Epkinly and, GSK and Pfizer’s RSV vaccines Arexvy and Abrysvo, respectively.
View New Drug Approvals in first half of 2023 with Estimated Sales (Free Excel Available)
GSK, Pfizer’s RSV vaccines to generate over US$ 1 billion by 2028
The highlight of H1 2023 has been the approval of vaccines for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), a contagious virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract, and can cause severe illness in older adults and infants.
In May 2023, FDA approved GSK’s Arexvy, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine for people aged 60 and older, making it the first vaccine approved in the US that protects against the disease. The drug is expected to generate US$ 1.73 billion in peak sales by 2028.
Weeks later, the agency approved Pfizer’s Abrysvo, another RSV vaccine for older adults. The vaccine is expected to be available in the third quarter of 2023. In late August, Pfizer also bagged an FDA nod for use of Abrysvo to prevent RSV in infants by vaccinating pregnant women. The drug is expected to generate US$ 1.31 billion in peak sales by 2028.
View New Drug Approvals in first half of 2023 with Estimated Sales (Free Excel Available)
Leqembi, Veozah, Epkinly likely to join ‘over US$ 1 billion club’ by 2028
In March, the US health regulator suggested stricter trials for accelerated approval of cancer drugs. The proposed recommendation followed criticism over the approval of Biogen and Eisai’s Alzheimer’s treatment Aduhelm through this pathway in June 2021.
Contrary to this stand though, FDA had approved another Alzheimer’s drug from Biogen and Eisai — Leqembi (lecanemab) — through the same pathway in January 2023. Leqembi is an amyloid beta-directed antibody indicated for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The drug is expected to generate US$ 1.9 billion in peak sales by 2028. Later in July, FDA expanded the accelerated approval of lecanemab to a traditional approval for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
The US regulator approved several potential blockbuster drugs during the month of May. It granted full approval to Pfizer’s Covid-19 oral antiviral pill Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) during the month, which had been granted an emergency use authorization during the heydays of the pandemic. Paxlovid is the first oral antiviral pill for Covid-19. With the pandemic behind us, Paxlovid’s sales have been waning, though it is still projected to yield approximately US$ 5.5 billion in sales by 2028.
The other important drug approved in May is Japanese drugmaker Astellas Pharma’s oral drug Veozah (fezolinetant) for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS), or hot flashes associated with menopause. The drug will cost US$ 550 for a month’s supply. Veozah is expected to generate US$ 1.9 billion in sales by 2028.
FDA also granted accelerated approval to AbbVie and Genmab’s blood cancer therapy Epkinly (Epcoritamab-Bysp) in May. It has bagged approval to treat patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and is likely to emerge as a US$ 1.1 billion product.
View New Drug Approvals in first half of 2023 with Estimated Sales (Free Excel Available)
Sarepta, Biomarin’s gene therapies bag FDA nod; Lilly’s Jaypirca okayed for lymphoma
In June, FDA approved Sarepta’s Elevidys and Biomarin’s Roctavian. Elevidys bagged accelerated approval in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients aged four to five years. This is the first gene therapy approved by the FDA for the treatment of certain patients with DMD. Elevidys is expected to generate US$ 3.36 billion in peak sales by 2028.
BioMarin’s one-time gene therapy – Roctavian – has been approved by the FDA to treat severe hemophilia A, a rare bleeding disorder. Priced at US$ 2.9 million, Roctavian is the first gene replacement therapy to be approved for the condition. Roctavian is expected to generate US$ 1.43 billion in peak sales by 2028. This approval follows another approval granted in November 2022 for the first gene therapy to treat adults with hemophilia B — CSL Behring and uniQure’s Hemgenix.
In January, Lilly’s Jaypirca (pirtobrutinib) bagged FDA nod, thereby becoming the first and only non-covalent, BTK Inhibitor for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma which did not respond to other BTK Inhibitors. Jaypirca is expected to generate US$ 0.91 billion in peak sales by 2028.
In March, FDA approved Pfizer’s Zavzpret (zavegepant) as the first and only calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist nasal spray for the acute treatment of migraine. Zavzpret is expected to generate US$ 0.649 billion in peak sales by 2028.
Another important FDA approval was granted to GSK’s drug Jesduvroq — it is now the first oral treatment for anemia caused by chronic kidney disease in adults who have been on dialysis for at least four months.
View New Drug Approvals in first half of 2023 with Estimated Sales (Free Excel Available)
FDA rejects Lilly’s donanemab, Alvotech/Teva’s Humira biosimilar
In January, when the FDA had approved Leqembi, the agency had rejected Eli Lilly’s bid for an accelerated approval pathway for its experimental Alzheimer’s disease drug donanemab. The agency had cited a lack of participants who received continuous treatment with donanemab for at least 12 months as the reason for its decision.
However, Lilly announced positive late-stage trial results on donanemab in July — it slowed cognitive decline by 35 percent compared to a placebo in a late-stage trial. An FDA decision on the drug is likely around 2023-end or in early 2024.
Similarly, FDA turned down Lilly’s mirikizumab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. The agency also rejected a BLA for Eli Lilly’s ulcerative colitis drug mirikizumab over manufacturing concerns. Besides these, FDA also rejected Alvotech/Teva’s Humira biosimilar — AVT02 — for a second time this year.
View New Drug Approvals in first half of 2023 with Estimated Sales (Free Excel Available)
Our view
After the pandemic, business is back to normal at the FDA. The number of CDER approvals in the first half of this year are approximately 70 percent of the approvals in 2022. We anticipate more approvals in the upcoming months. If the FDA sustains this pace, approvals this year could potentially double those of the previous years.
The PharmaCompass Newsletter – Sign Up, Stay Ahead
Feedback, help us to improve. Click here
Image Credit : New Drug Approvals by FDA, EMA & Health Canada: Mid-2023 Recap by PharmaCompass license under CC BY 2.0
“ The article is based on the information available in public and which the author believes to be true. The author is not disseminating any information, which the author believes or knows, is confidential or in conflict with the privacy of any person. The views expressed or information supplied through this article is mere opinion and observation of the author. The author does not intend to defame, insult or, cause loss or damage to anyone, in any manner, through this article.”







