J&J’s Intra‑Cellular buyout, BMS’ oncology gambit, Sanofi’s Blueprint acquisition drive mega deals in H1 2025
The pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a wave of mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnership
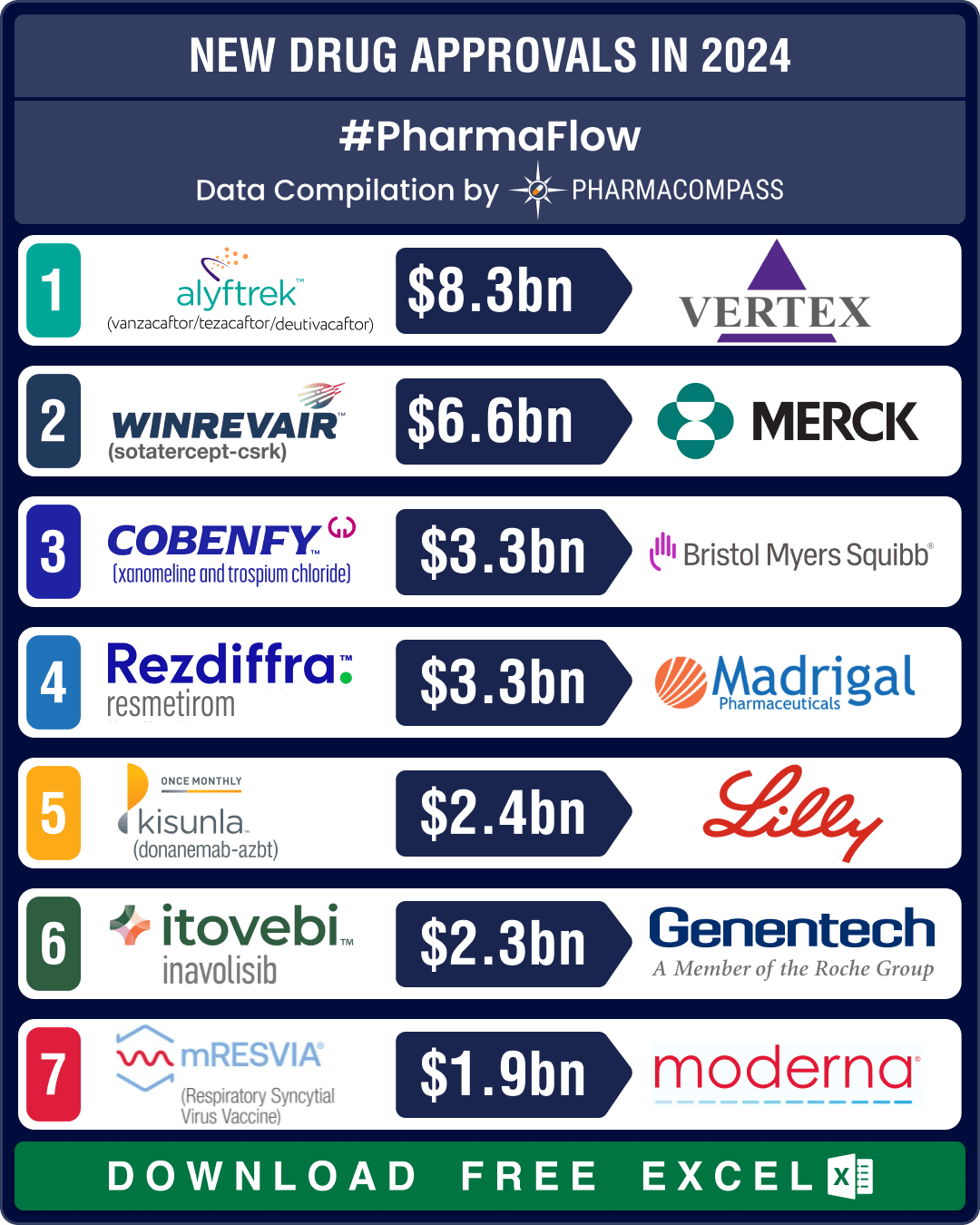
FDA okays 50 new drugs in 2024; BMS’ Cobenfy, Lilly’s Kisunla lead pack of breakthrough therapies
In 2024, the biopharma industry continued to advance on its robust trajectory of innovation. Though
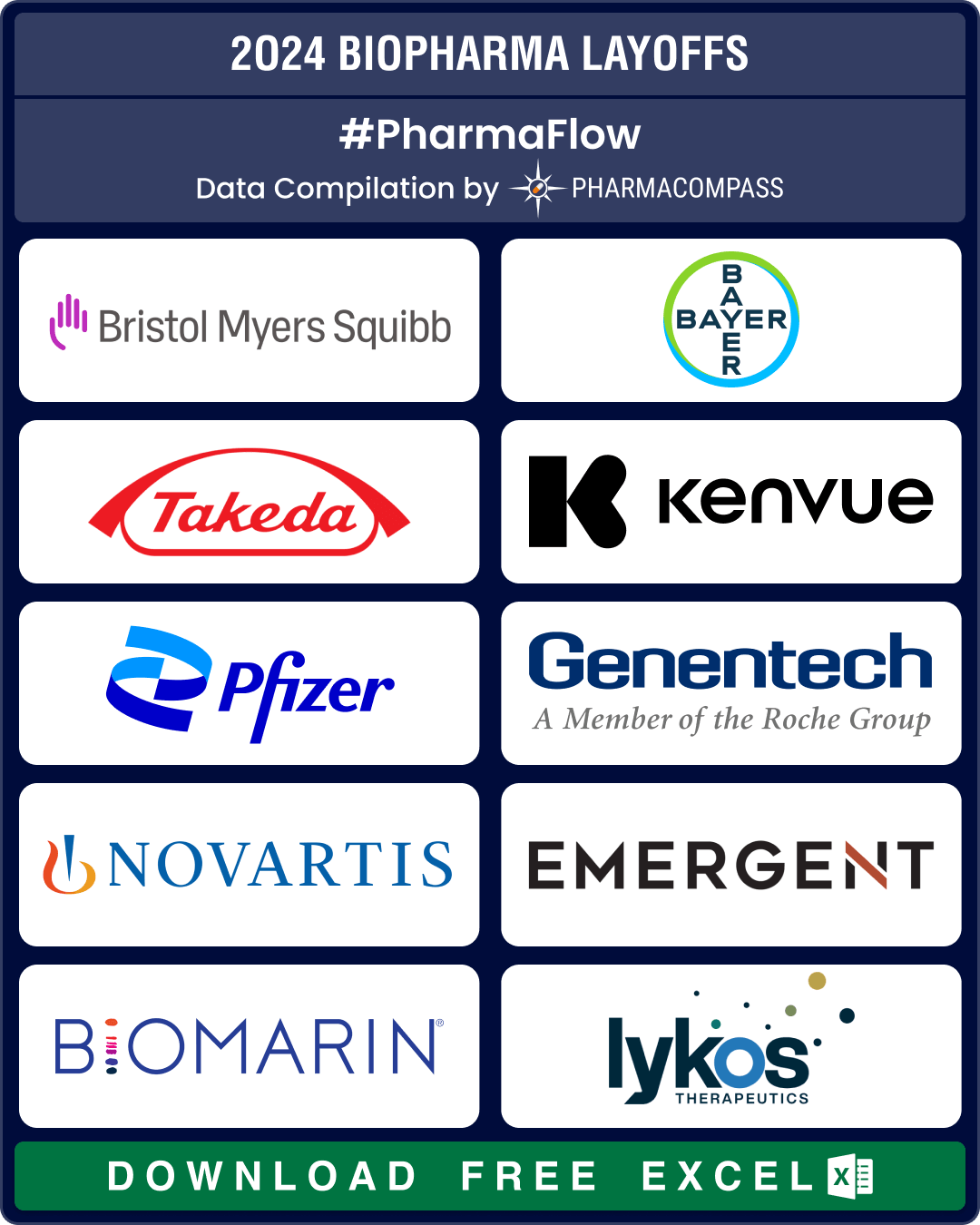
BMS, J&J, Bayer lead 25,000+ pharma layoffs in 2024; Amylyx, FibroGen, Kronos Bio hit by trial failures, cash crunch
Since 2022, there has been a significant surge in layoffs by pharmaceutical and biotech companies. W
BMS, Bayer, Takeda, Pfizer downsize to combat cost pressures, meet restructuring plans
Over
the last two years, there has been a significant surge in layoffs by
pharmaceutical and biote
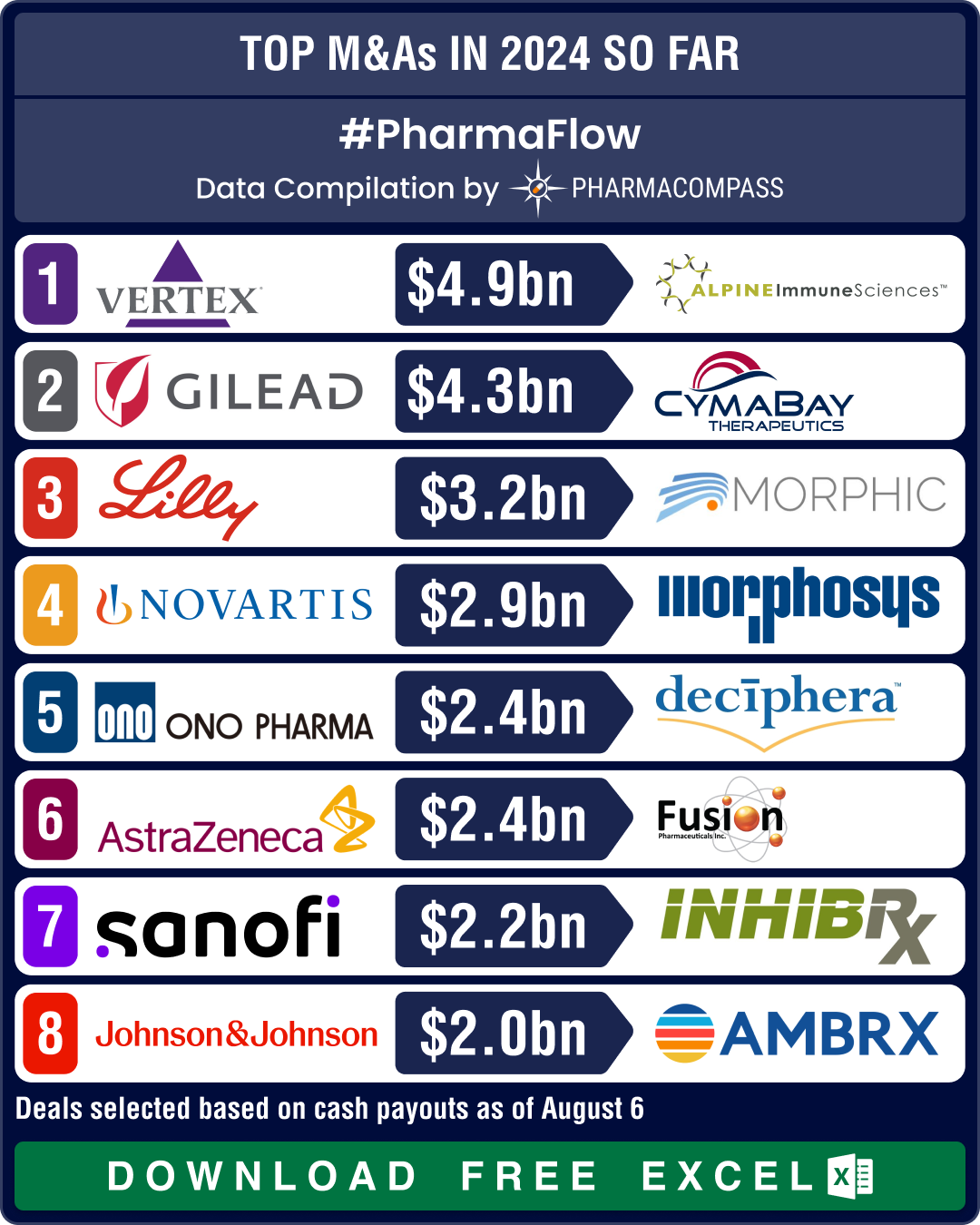
Novartis, GSK, Sanofi, BMS shell out over US$ 10 bn in dealmaking, as mid-size deals take centerstage in 2024
The world of pharmaceuticals and biotechnology continued to evolve
this year with strategic allianc
CDMO Activity Tracker: Novo’s parent buys Catalent for US$ 16.5 bn; Fujifilm, Merck KGaA, Axplora expand capabilities
During the first half (H1) of 2024, the global contract development and manufacturing organization (
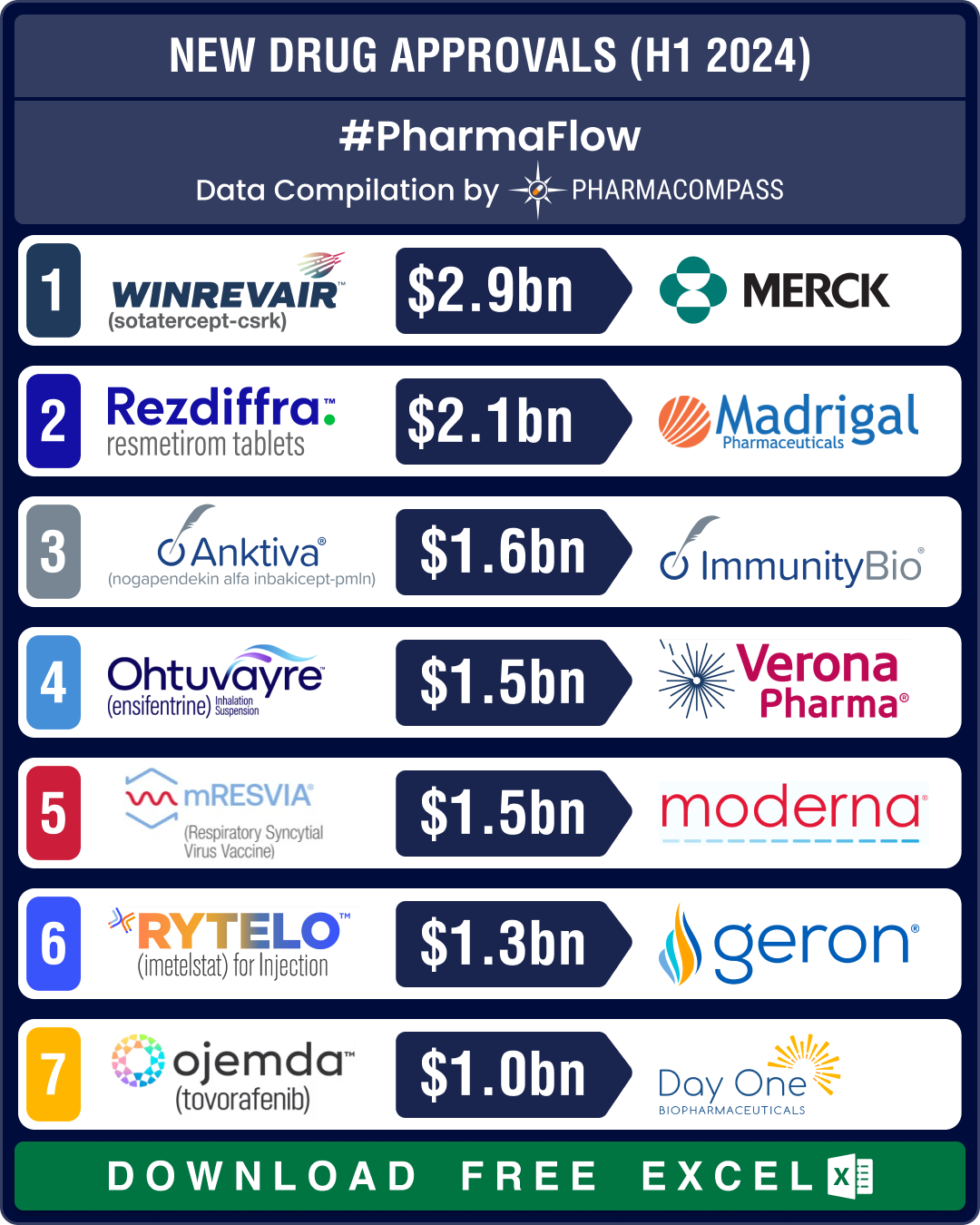
FDA approvals slump 19% in H1 2024; NASH, COPD, PAH get new treatment options
The first half of 2024 saw a significant slowdown in approvals of new drugs and biologics by the US


 Market Place
Market Place Sourcing Support
Sourcing Support