Top news of 2025: Drugmakers invest in US capacities, agree to lower Medicaid prices; Pfizer buys obesity-focused biotech Metsera
The year 2025 was an eventful one, marked by increased trade
tensions, tariff threats, accelerated
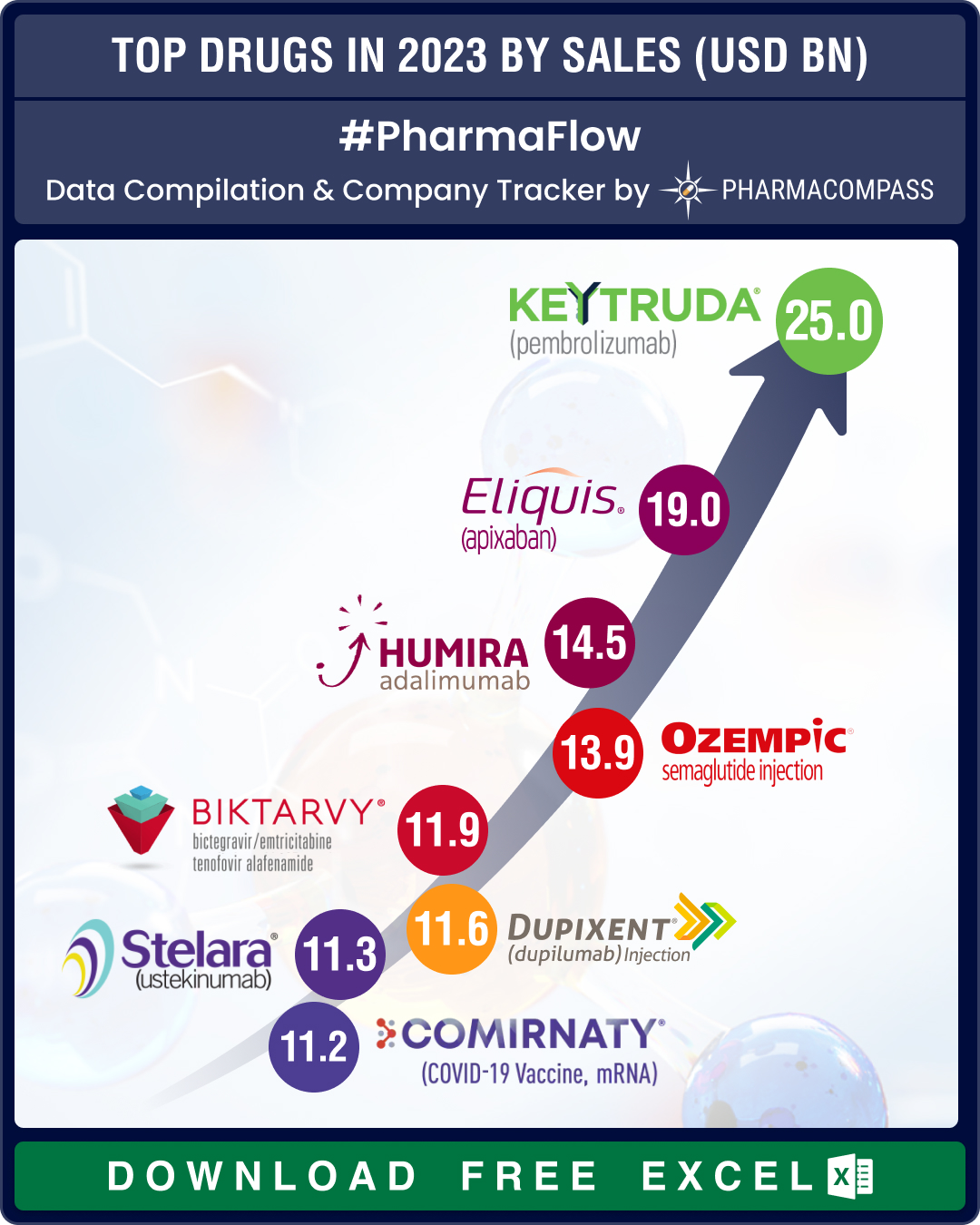
Top Pharma Companies & Drugs in 2024: Merck’s Keytruda maintains top spot as Novo’s semaglutide nips at its heels
In 2024, Big Pharma players consolidated
and maintained their dominance, even as innovation continu
Molecular glue degraders: Lilly, AbbVie sign billion-dollar deals; BMS leads with three late-stage drugs
This week, we delve into molecular glue degraders (MGDs), one of the most promising frontiers in dru
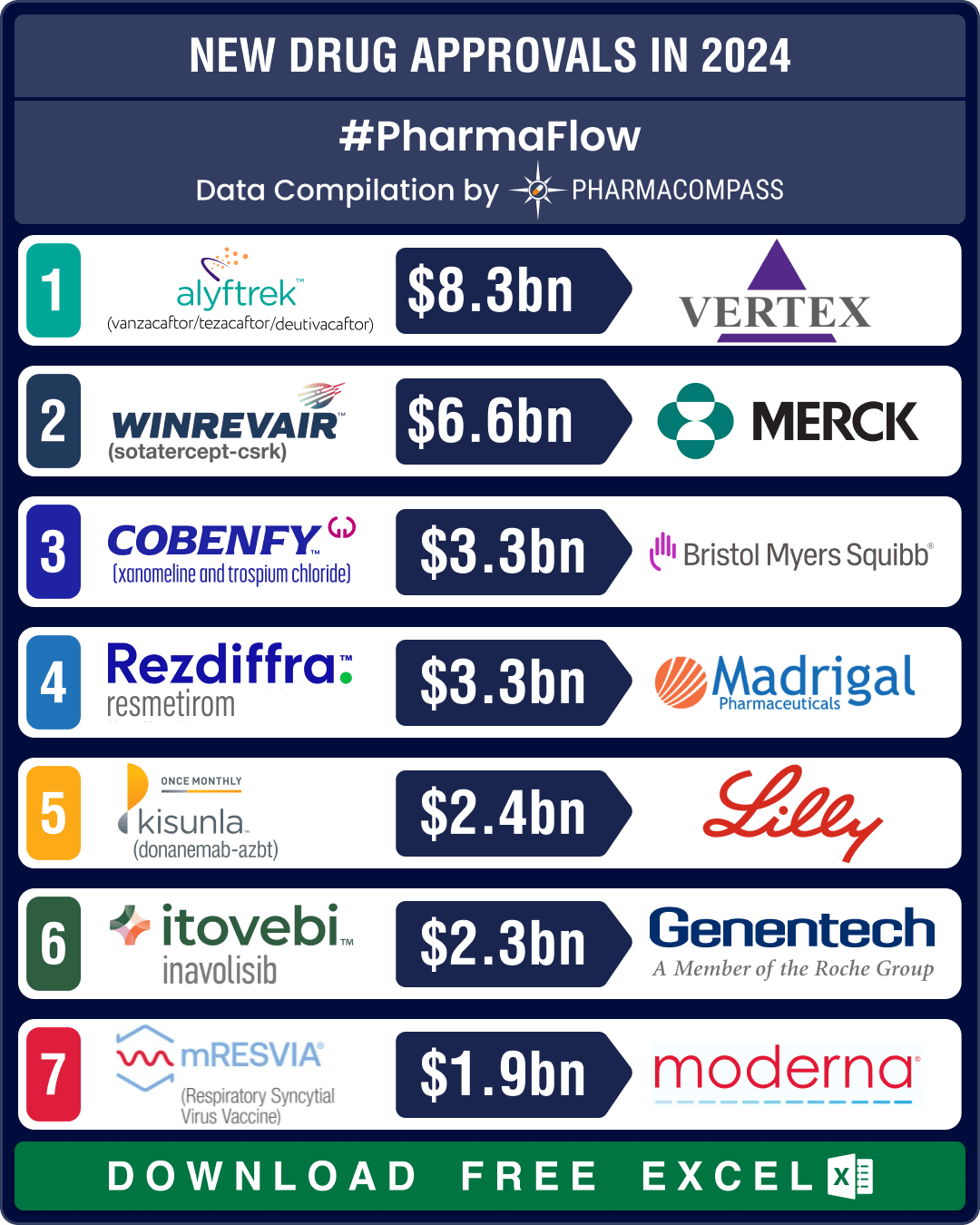
FDA okays 50 new drugs in 2024; BMS’ Cobenfy, Lilly’s Kisunla lead pack of breakthrough therapies
In 2024, the biopharma industry continued to advance on its robust trajectory of innovation. Though
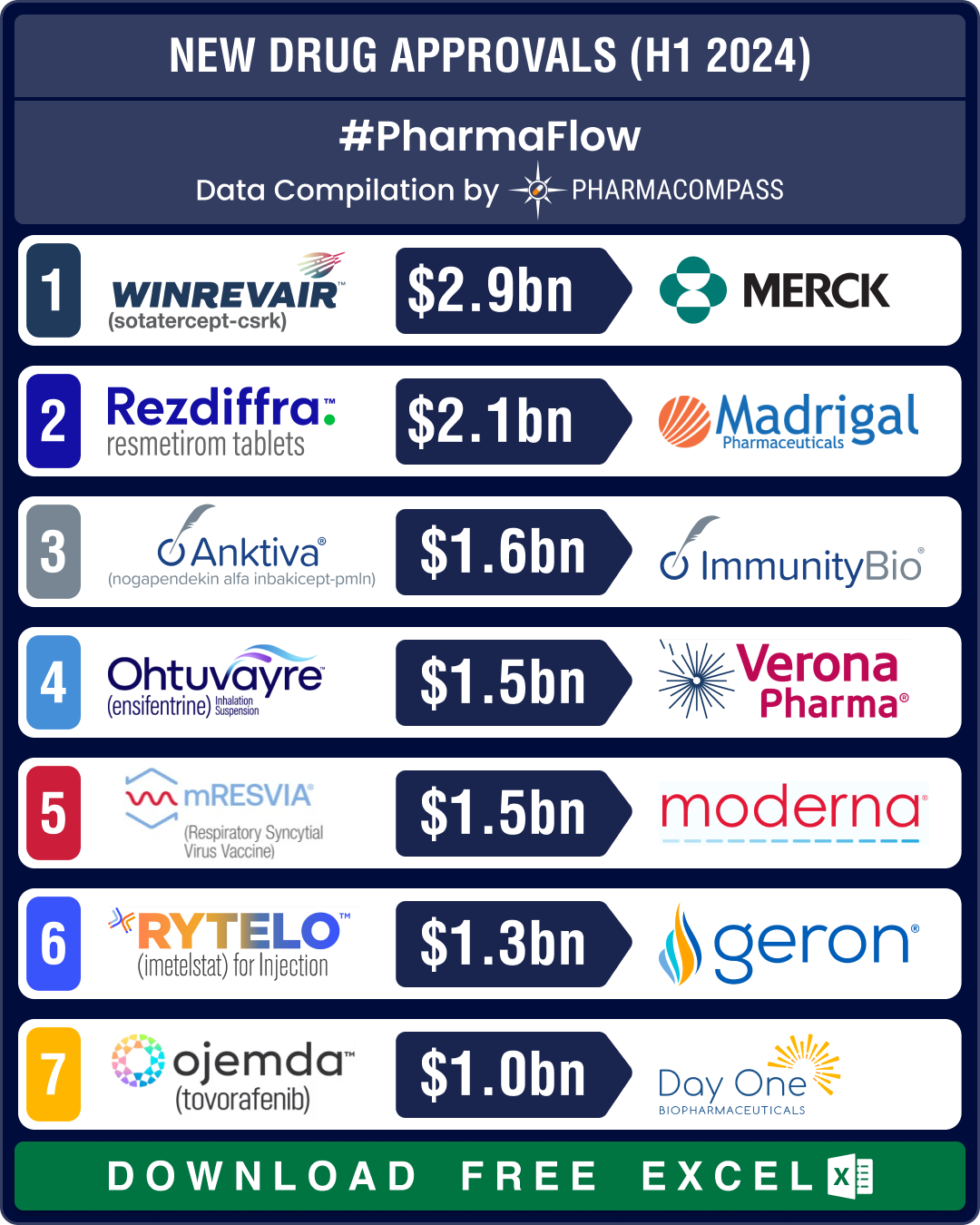
FDA approvals slump 19% in H1 2024; NASH, COPD, PAH get new treatment options
The first half of 2024 saw a significant slowdown in approvals of new drugs and biologics by the US
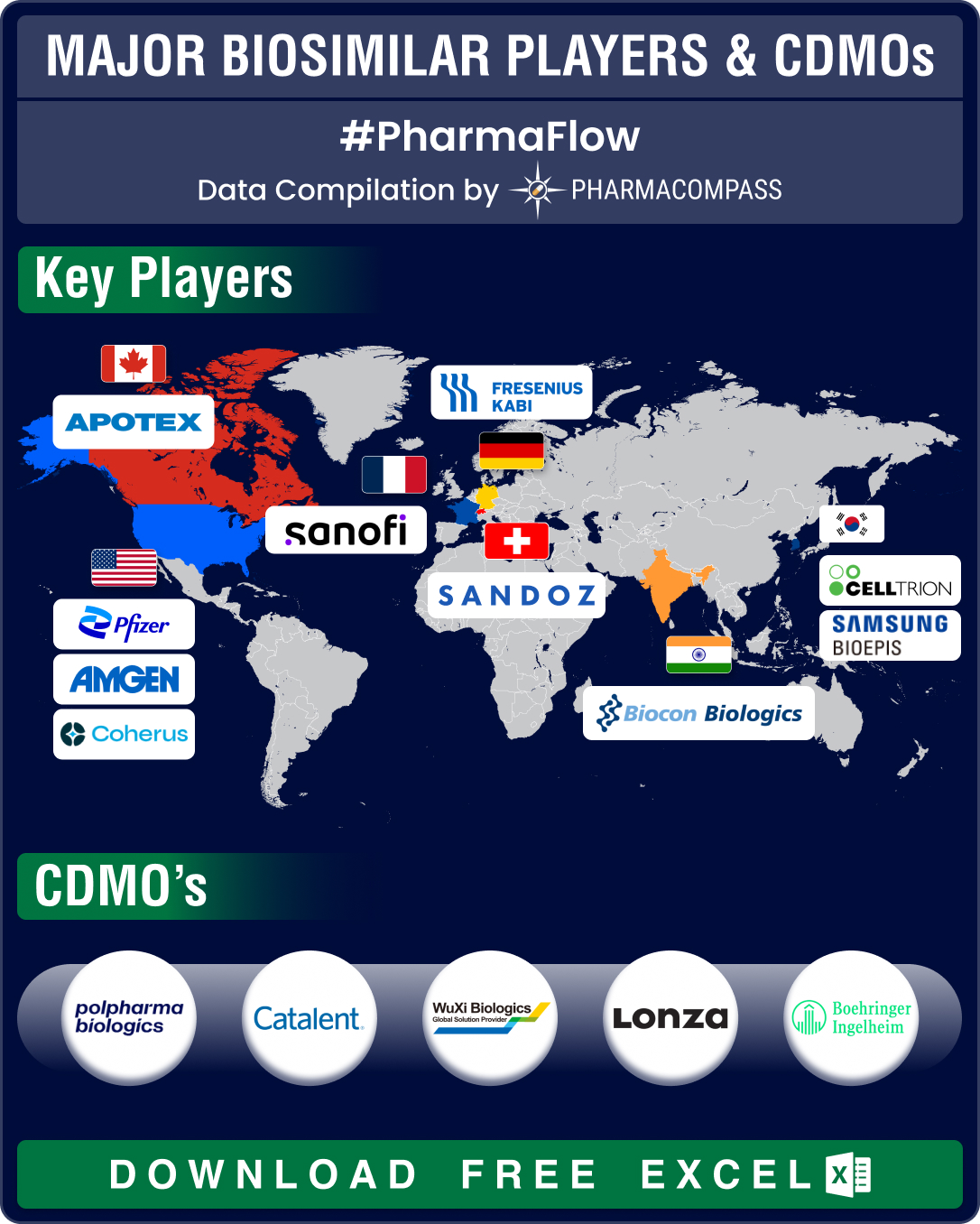
FDA approves record eight biosimilars in H1 2024; okays first interchangeable biosimilars for Eylea
Biologics, or complex drugs that are derived from living organisms, have revolutionized treatment of


 Market Place
Market Place Sourcing Support
Sourcing Support