
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
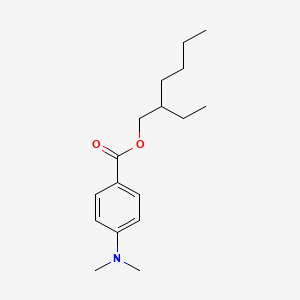

1. 2-ethylhexyl-p-dimethylaminobenzoate
2. 4-n,n'-dimethylamino-benzoic Acid, 2-ethylhexyl Ester
3. Arlatone 507
4. Climacel
5. Escalol 507
6. Padimate O
7. Padimate-o
1. 21245-02-3
2. Padimate O
3. 2-ethylhexyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate
4. Padimate-o
5. Escalol 507
6. Octyl Dimethyl Paba
7. Eusolex 6007
8. Arlatone Uvb
9. 2-ethylhexyl P-dimethylaminobenzoate
10. Benzoic Acid, 4-(dimethylamino)-, 2-ethylhexyl Ester
11. 2-ethylhexyl-p-dimethyl-aminobenzoate
12. Uvasorb Dmo
13. 2-ethylhexyl-4-dimethylaminobenzoate
14. 2-ethylhexyl P-(dimethylamino)benzoate
15. 4-(dimethylamino)benzoic Acid 2-ethylhexyl Ester
16. Ethylhexyl Dimethyl Paba
17. Z11006cmuz
18. Ncgc00090764-02
19. Dsstox_cid_9320
20. Dsstox_rid_78762
21. Dsstox_gsid_29320
22. Radiacare Lip Balm
23. Cas-21245-02-3
24. Octyl Dimethyl P-aminobenzoate
25. Caraloe Snow & Sun Lip Balm
26. Pamimate O
27. Hsdb 7169
28. Einecs 244-289-3
29. Mfcd00017526
30. Padimate O (usp)
31. Arlatone Uvb (tn)
32. Photoplex (salt/mix)
33. Padimate O [usan:usp]
34. Presun 23 (salt/mix)
35. Padimate O [hsdb]
36. Padimate O [usan]
37. Padimate O [vandf]
38. Padimate-o [vandf]
39. Pamimate O [vandf]
40. Unii-z11006cmuz
41. Padimate O [mart.]
42. Schembl15432
43. Padimate O [usp-rs]
44. Padimate O [who-dd]
45. 4-(dimethylamino)benzoic Acid, 2-ethylhexyl Ester
46. Mls001055379
47. (+/-)-padimate O
48. Benzoic Acid, P-(dimethylamino)-, 2-ethylhexyl Ester
49. Padimate O, Analytical Standard
50. Radiacare Lip Balm (salt/mix)
51. Chembl1323699
52. Dtxsid7029320
53. Chebi:135932
54. Padimate O, (+/-)-
55. Hms3039f10
56. Padimate O [usp Monograph]
57. Octyl Dimethyl Paba [vandf]
58. Tox21_111013
59. Tox21_202421
60. Tox21_303574
61. Akos015890282
62. Tox21_111013_1
63. 2-ethylhexyl-4'-dimethylamino-benzoate
64. Am84740
65. Db11570
66. Ethylhexyl Dimethyl Paba [inci]
67. Padimate O 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
68. Ncgc00090764-01
69. Ncgc00090764-03
70. Ncgc00090764-04
71. Ncgc00257250-01
72. Ncgc00259970-01
73. 2-ethylhexyl N,n-dimethyl-p-aminobenzoate
74. Ac-13165
75. As-75461
76. Smr000677935
77. Caraloe Snow & Sun Lip Balm (salt/mix)
78. Db-021046
79. 2-ethyl-hexyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate
80. D1871
81. Ft-0616757
82. 2-ethylhexyl 4-(dimethylamino)benzoate, 98%
83. 2-ethylhexyl 4-(dimetylamino)benzoate
84. P-dimethylaminobenzoic Acid 2-ethylhexyl Ester
85. D05335
86. F71555
87. A815219
88. Sr-01000864568
89. Q6628390
90. Sr-01000864568-2
91. 4-(dimethylamino)benzoic Acid 2-ethylhexyl Ester [mi]
92. Padimate O, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
93. Padimate O, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 277.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H27NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 277.204179104 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 277.204179104 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 270 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Daily use of a sunscreen with a high SPF (greater than 15) on usually exposed skin is recommended for residents of areas of high ... /solar radiation/ who work outdoors or ... /enjoy/ regular outdoor recreation. Daily use of a sunscreen can reduce the cumulative ... /solar/ exposure that causes actinic keratoses and squamous-cell carcinoma.
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Cancer-Preventive Agents (2001) Sunscreens (IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention, Vol. 5), Lyon, IARC; Unit of Chemoprevention: Cancer-Preventive Effects of Sunscreens.
PABA derivatives reportedly have weak sensitization potential, but the incidence of allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis associated with their use is increasing. Contamination of PABA derivatives with benzocaine which may cause allergic reactions has been reported. In patients allergic to compounds that are structurally similar to PABA (e.g., ester-type anesthetics, aniline dyes, thiazides, sulfonylurea and paraphenylenediamine drugs), cross-sensitivity to PABA derivatives has been reported occasionally; therefore, sunscreens containing PABA derivatives may be contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to these chemicals.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
The manufacturers of sunscreen preparations with propellants warn that concentrating and subsequently inhaling the fumes from these preparations may be harmful or fatal. /Propellants/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Because the absorptive characteristics of skin of children younger than 6 months of age may differ from those of adults and because the immaturity of metabolic and excretory pathways of these children may limit their ability to eliminate any percutaneously absorbed sunscreen agent, sunscreen products should be used in children younger than 6 months of age only as directed by a clinician. It is possible that the characteristics of geriatric skin also differ from those of skin in younger adults, but these characteristics and the need for special considerations regarding use of sunscreen preparations in this age group are poorly understood. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Little information is available regarding the safety of chronic sunscreen usage, but commercially available physical and chemical sunscreens appear to have a low incidence of adverse effects. Derivatives of PABA, benzophenone, cinnamic acid, and salicylate and 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid have caused skin irritation including burning, stinging, pruritus, and erythema on rare occasions. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PADIMATE O (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Indicated as an active UV-B filter to prevent photodamage.
Padimate O absorbs UV-B rays, which can in turn induce DNA damage in human keratinocytes. While treatment of padimate O suppresses the formation of UV-endonuclease-sensitive sites, there is also an increase in direct strand breaks of DNA in cells.
Sunscreening Agents
Chemical or physical agents that protect the skin from sunburn and erythema by absorbing or blocking ultraviolet radiation. (See all compounds classified as Sunscreening Agents.)
Absorption
Padimate O is capable of human skin penetration.
Route of Elimination
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Volume of Distribution
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Clearance
No pharmacokinetic data available.
... None of the subjects tested showed any sign of skin irritation at the application site. ... In four postmenopausal women (age 54-63 years, weight 67-93 kg) the mean estradiol level 24 hr postapplication over the 9 day study period was 53 pg/mL. This result was significantly greater (p < 0.001) than the baseline value of 13 pg/mL. The mean estradiol/estrone ratio also rose significantly (p < 0.04) from a baseline value of 0.2 up to 0.8.
PMID:9758681 Morgan TM et al; J Pharm Sci 87(10): 1226-8 (1998)
It appears that sunscreen agents are absorbed by the intact epidermis to varying degrees. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Sunscreen skin penetration and safety assessment should be considered together in order to ensure that in vitro cytotoxicity studies examine relevant doses of these organic chemical UV filters to which viable epidermal cells are realistically exposed. In this study, /investigators/ sought to determine whether sufficient topically applied sunscreens penetrated into human viable epidermis to put the local keratinocyte cell populations at risk of toxicity. The penetration and retention of five commonly used sunscreen agents (avobenzone, octinoxate, octocrylene, oxybenzone and padimate O) in human skin was evaluated after application in mineral oil to isolated human epidermal membranes. Sunscreen concentration-human keratinocyte culture response curves were then defined using changes in cell morphology and proliferation (DNA synthesis using radiolabelled thymidine uptake studies) as evidence of sunscreens causing toxicity. Following 24 hr of human epidermal exposure to sunscreens, detectable amounts of all sunscreens were present in the stratum corneum and viable epidermis, with epidermal penetration most evident with oxybenzone. The concentrations of each sunscreen found in human viable epidermis after topical application, adjusting for skin partitioning and binding effects, were at least 5-fold lower, based on levels detected in viable epidermal cells, than those appearing to cause toxicity in cultured human keratinocytes. It is concluded that the human viable epidermal levels of sunscreens are too low to cause any significant toxicity to the underlying human keratinocytes.
PMID:15908756 Hayden CG et al; Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 18 (4): 170-4 (2005)
Researchers in Europe analyzed samples of human milk for the presence of sunscreens and other chemicals with possible endocrine activity. Mothers were asked about their use of sunscreens and cosmetics that contained sunscreen ingredients (benzophenone 2, benzophenone 3, 3-benzylidene camphor, 4-MBC, OMC, homosalate, octocrylene, and octyl-dimethyl PABA). Responding to questionnaires, 78.8% of the women reported using products that contained sunscreens; 76.5% of human milk samples contained these chemicals. There was a high correlation reported between mothers' use of these chemicals and their concentrations in human milk. The authors concluded that except for lipsticks (the ingestion of which is probably important), their results agree with studies in animals and humans showing dermal absorption of sunscreens. Given that some of these chemicals have endocrine activity in animals, the authors suggested that exposure could be lessened if mothers abstained from using these products during their children's sensitive life stages.
Balk SJ et al; PEDIATRICS 127 (3): e791-e817 (2011)
Information on the cutaneous absorption, distribution, and elimination of most topically applied sunscreen agents is limited. Solvents used in sunscreen products affect the stability and binding of the drug to the skin; in general, alcoholic solvents allow for the most rapid and deepest epidermal penetration of sunscreens. It appears that sunscreen agents are absorbed by the intact epidermis to varying degrees. PABA reportedly diffuses into the stratum corneum, reaching maximum concentrations there 2 hours following application, but apparently does not penetrate deeper layers of the skin to a substantial extent. Homosalate's penetration also appears to be limited to the stratum corneum. One study in animals indicated that PABA may penetrate the skin to a greater extent than does padimate A. Although some studies have shown that substantive concentrations of PABA remain on the skin after washing, other studies have failed to confirm this. One study showed that PABA esters were removed from the skin less readily than was PABA or other chemical sunscreens. /PABA/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
No pharmacokinetic data available.
No pharmacokinetic data available.
It is proposed that simultaneous contact of padimate O with keratinocytes can stimulate the diffusion through human epidermis. Upon photoexcitation, padimate O generates singlet oxygen and forms carbon-centred free radicals. While padimate O attenuates simple and repairable, UV-induced cellular damage, it may also increase complex chemical damage that is more difficult to repair by normal cells.
Radiation is absorbed by chemical sunscreens when the electron energy level of the drug is raised from its ground state to a higher energy level or excited state. Chromophore groups (C=C, C=O, O-N=O) with loosely held electrons are easily excited by radiation. Compounds which have several chromophore groups in optimal positions have high absorbance over a broad range of wavelengths. Chemical sunscreens are usually agents that absorb not less than 85% of UVB radiation (thus preventing burning) but may permit transmission of UVA radiation (thus allowing tanning). Some sunscreens may absorb wavelengths over a range that is slightly wider or narrower than that of UVB. All PABA derivatives absorb wavelengths of approximately 290-320 nm, benzophenone derivatives absorb wavelengths of approximately 250-360 nm, cinnamic acid derivatives absorb wavelengths of 280-320 nm, and salicylate derivatives and other miscellaneous chemical sunscreens absorb wavelengths of about 270-320 nm.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
The wavelength to which the skin is maximally sensitive had been accepted for many years to be 296.7 nm; however, recent evidence suggests that the most erythemogenic UVB wavelength may be slightly lower (e.g., somewhere in the range of 292-295 nm). In addition, of the stronger burning wavelengths that reach the earth's surface, most are approximately 310 nm. Therefore, sunscreens that maximally absorb UVB radiation near either of these wavelengths are particularly effective at preventing sunburn. Maximum absorbance occurs at about 290 nm for PABA, at about 295 nm for glyceryl-p-aminobenzoate, and at about 310 nm for the remaining PABA derivatives. Maximum absorbance occurs at 280-290 nm for benzophenone derivatives, at 310 nm for cinnamic acid derivatives with the exception of diethanolamine-p-methoxycinnamate which has its maximum absorbance at 290 nm, and at 300-305 nm for salicylate derivatives and other miscellaneous sunscreens. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
... The photomutagenic sunscreen Padimate-O attacks DNA on illumination with simulated sunlight, producing strand breaks and lesions that are labile to N,N'-dimethylethylenediamine but few, if any, cyclobutane dimers or other direct photoproducts. The damage can be completely suppressed by the free radical quenchers Tris, ethanol, mannitol and dimethylsulfoxide, which is commonly used as a solvent in conventional photomutagenicity assays.
McHugh PJ, Knowland J; Photochem Photobiol 66(2): 279-81 (1997)
Diminish the penetration of ultraviolet (UV) light through the epidermis by absorbing UV radiation within a specific wavelength range. The amount and wavelength of UV radiation absorbed are affected by the molecular structure of the sunscreen agent. /Sunscreen agents, topical/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
ABOUT THIS PAGE
84
PharmaCompass offers a list of 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate manufacturer or 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate manufacturer or 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate supplier is an individual or a company that provides 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate finished formulations upon request. The 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate suppliers may include 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate GMP manufacturer or 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate's compliance with 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate EP), 2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (2-Ethylhexyl 4-(Dimethylamino)Benzoate USP).
